Abstract
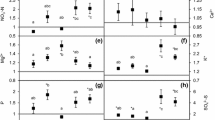
Acidification and N-deposition are continuous processes that alter the composition of plant communities. We investigated vegetation transitions in sandy grasslands and tested two hypotheses: (1) a shift from vegetation dominated by Koeleria glauca to one dominated by Corynephorus canescens is due to acidification and (2) a shift from vegetation dominated by K. glauca to one dominated by Arrhenatherum elatius is due to increased mineral-N. The occurrence of K. glauca and C. canescens followed pH shifts strikingly well. However, the pH varied considerably between sites, and we found that differences in preference for bare sand may be important for the coexistence of these two species at both high and low pH. In 75% of the gradients, the dominance of A. elatius was related to high content of mineral-N. Most species preferred lime-rich soils and we concluded that both N-enrichment and acidification may lead to loss of species in calcareous sandy grasslands.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berendse F, Elberse WT, Geerts RHME (1992) Competition and nitrogen loss from plants in grassland ecosystems. Ecology 73:46–53
Bobbink R, Hornung M, Roelofs JGM (1998) The effects of air-borne nitrogen pollutants on species diversity in natural and semi-natural European vegetation. J Ecol 86:717–738
Braak CJF (1988–2005) CANOCO, version 4.54
Brady NC, Weil RR (2002) The nature and properties of soils. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Carroll JA, Caporn SJM, Johnson D, Morecroft MD, Lee JA (2003) The interactions between plant growth, vegetation structure and soil processes in semi-natural acidic and calcareous grasslands receiving long-term inputs of simulated pollutant nitrogen deposition. Environ Pollut 121:363–376
Connell JH, Slatyer RO (1977) Mechanisms of succession in natural communities and their role in community stability and organization. Am Nat 111:1119–1144
Critchley CNR, Chambers BJ, Fowbert JA, Sanderson RA, Bhogal A, Rose SC (2002) Association between lowland grassland plant communities and soil properties. Biol Conserv 105:199–215
Eichberg C, Storm C, Schwabe A (2007) Endozoochorous dispersal, seedling emergence and fruiting success in disturbed and undisturbed successional stages of sheep-grazed inland sand ecosystems. Flora 202:3–26
Ellenberg H (1974) Indicator values of vascular plants in central Europe. Scripta Geobot 9:1–97
Ellenberg H (1991) Indicator values of vascular plants in central Europe 1. Indicator values of vascular plants not including Rubus. Scripta Geobot 18:9–166
Forey E, Chapelet B, Vitasse Y, Tilquin M, Touzard B, Michalet R (2008) The relative importance of disturbance and environmental stress at local and regional scales in French coastal sand dunes. J Veg Sci 19:493
Gärdenfors U (ed) (2005) Rödlistade arter i Sverige [Official Swedish red list]. ArtDatbanken, USL, Uppsala
Grime JP (ed) (2001) Plant strategies, vegetation processes and ecosystem properties. Wiley, Chichester
Hasse T, Daniels FJA (2006) Species responses to experimentally induced habitat changes in a Corynephorus grassland. J Veg Sci 17:122–135
Hultén E (ed) (1971) Atlas över växternas utbredning i Norden. Generalstabens litografiska anstalts förlag, Stockholm
Hunt R, Hodgson JG, Thompson K, Bungener P, Dunnett NP, Askew AP (2004) A new practical tool for deriving a functional signature for herbaceous vegetation. Appl Veg Sci 7:163–170
Janssens F, Peeters A, Tallowin JRB, Bakker JP, Bekker RM, Fillat F, Oomes MJM (1998) Relationship between soil chemical factors and grassland diversity. Plant Soil 202:69–78
Jentsch A, Beyschlag W (2003) Vegetation ecology of dry acidic grasslands in the lowland area of central Europe. Flora 198:3–25
Jentsch A, Friedrich S, Beyschlag W, Nezadal W (2002) Significance of ant and rabbit disturbances for seedling establishment in dry acidic grasslands dominated by Corynephorus canescens. Phytocoenologia 32:553–580
John M (1970) Colorimetric determination of phosphorus in soil and plant materials with ascorbic acid. Soil Sci 109:214–220
Klimešová J, Klimeš L (2006) Clo-Pla3. http://clopla.butbn.cas.cz/
Mattiasson G (1974) Sandstäpp: vegetation, dynamik och skötsel [Sand steppe: vegetation, dynamics, and management]. Meddelanden för Avdelningen för Ekologisk Botanik [Ecological Botany]. Lund University, Lund
Mossberg B, Stenberg L (2003) Den Nya Nordiska Floran. Wahlström & Widstrand, Stockholm
Olsson K-A (1994) Sandstäpp i Skåne - ett upprop. Lunds botaniska förening. Medlemsblad 1994:4–7
Olsson PA, Tyler G (2004) Occurrence of non-mycorrhizal plant species in south Swedish rocky habitats is related to exchangeable soil phosphate. J Ecol 92:808–815
Olsson PA, Mårtensson L-M, Bruun HH (in press) Acidification of sandy grasslands—consequences for nutrient availability and plant diversity. Appl Veg Sci
Pärtel M (2002) Local plant diversity patterns and evolutionary history at the regional scale. Ecology 83:2361–2366
Rehounkova K, Prach K (2006) Spontaneous vegetation succession in disused gravel-sand pits: role of local site and landscape factors. J Veg Sci 17:583–590
Rodwell JS, Schaminée JHJ, Mucina L, Pignatti S, Dring J, Moss D (2002) The diversity of European vegetation. An overview of phytosociological alliances and their relationships to EUNIS habitats. Wageningen University and Research Center Publications, Wageningen
Roem WJ, Berendse F (2000) Soil acidity and nutrient supply ratio as possible factors determining changes in plant species diversity in grassland and heathland communities. Biol Conserv 92:151–161
Roem WJ, Klees H, Berendse F (2002) Effects of nutrient addition and acidification on plant species diversity and seed germination in heathland. J Appl Ecol 39:937–948
Rozema J, Laan P, Broekman R, Ernst WHO, Appelo CAJ (1985) On the lime transition and decalcification in the coastal dunes of the province of north Holland and the island of Schiermonnikoog. Acta Bot Neerland 34:393–412
Ruzicka J, Hansen EH (1981) Flow injection analysis. Wiley, New York
Storm C, Süss K (2008) Are low-productive plant communities responsive to nutrient addition? Evidence from sand pioneer grassland. J Veg Sci 19:343–354
Strom L, Olsson T, Tyler G (1994) Differences between calcifuge and acidifuge plants in root exudation of low-molecular organic acids. Plant Soil 167:239–245
Süss K, Storm C, Zehm A, Schwabe A (2004) Succession in inland sand ecosystems: Which factors determine the occurrence of the tall grass species Calamagrostis epigejos (L.) Roth and Stipa capillata L.? Plant Biol 6:465–476
Symonides E (1979) The structure and population dynamics of psammophytes on inland dunes. I. Populations of initial stages. Ekol Pol 27:3–37
Theodose TA, Roths JB (1999) Variation in nutrient availability and plant species diversity across forb and graminoid zones of a northern New England high salt marsh. Plant Ecol 143:219–228
Tyler G (1992) Inability to solubilize phosphate in limestone soils key factor controlling calcifuge habit of plants. Plant Soil 145:65–70
Tyler G (1996) Soil chemistry and plant distributions in rock habitats of southern Sweden. Nord J Bot 16:609–635
Tyler T (2003) The state of the sand-steppe vegetation of eastern Scania (Skane) in early spring 2003. Bot Notiser 136:1–22
Veer MAC, Kooijman AM (1997) Effects of grass-encroachment on vegetation and soil in Dutch dry dune grasslands. Plant Soil 192:119–128
Waldhardt R, Otte A (2003) Indicators of plant species and community diversity in grasslands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 98:339–351
Wassen MJ, Venterink HO, Lapshina ED, Tanneberger F (2005) Endangered plants persist under phosphorus limitation. Nature (London) 437:547–550
Zohlen A, Tyler G (2004) Soluble inorganic tissue phosphorus and calcicole-calcifuge behaviour of plants. Ann Bot (London) 94:427–432
Internet references
Geological Survey of Sweden (2007). http://maps.sgu.se. Accessed 8 June 2007
Swedish Environmental Research Institute (2007). http://www.ivl.se/miljo/projekt/kron/depn0506.asp. Accessed 27 Dec 2007
Acknowledgements
Financial support from Region Skåne, The Swedish Research Council, The Swedish Research Council for the Environment, Agricultural Sciences and Spatial Planning (FORMAS) and the Oskar and Lilli Lamm Memorial Foundation is gratefully acknowledged. We also wish to thank Hans Henrik Bruun for statistical advice and for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mårtensson, LM., Olsson, P.A. Soil chemistry of local vegetation gradients in sandy calcareous grasslands. Plant Ecol 206, 127–138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9629-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-009-9629-9