Abstract
Purpose
Our aim was to evaluate the prognostic implications of a preoperative novel index, systemic immune inflammation index (SII) in patients undergoing surgery due to renal cell carcinoma.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of 176 patients who underwent radical nephrectomy and diagnosed with RCC was carried out. Systemic immune inflammation index, which is calculated by neutrophil x platelet/lymphocyte, and other inflammation indexes such as neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/lymphocyte were included. The Kaplan–Meier analysis was plotted, and the groups were compared using a log-rank test. The ROC curve for the aforementioned inflammation indexes was plotted.
Results
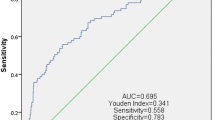
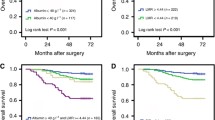
SII (× 109/l) for lower and higher T stage group were 743.70 ± 587.55 and 907.06 ± 631.96, respectively, which is statistically significant (p = 0.01). Patients with higher Fuhrman grade (G3 and G4) were found to have higher SII (p = 0.001). SII 830 was demonstrated as the best cut-off value for overall survival. The optimal cut-off point for SII was defined as 850 for disease-specific survival. High SII scores were associated with poor overall survival in RCC patients (p = 0.034). However, no significant association was found for disease-specific survival (p = 0.29).
Conclusions
Systemic immune inflammation index was found to be associated with increased TNM stage and poor prognosis of RCC patients udergoing radical nephrectomy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
B. Ljungberg (2019) Renal cell carcinoma- epidemıology, aetıology and pathology. EAU-Guidelines-2019. https://uroweb.org/guideline/renal-cell-carcinoma/#3.
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 49:1374–1403
Hu B, Yang XR, Xu Y, Sun YF, Sun C, Guo W, Zhang X, Wang WM, Qiu SJ, Zhou J, Fan J (2014) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 20:6212–6222
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357:539–545
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A et al (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454:436–444
Wang W, Ma X, Shi Z et al (2014) Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway polymorphisms and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res 5:396–410
Li X, Han Z, Cheng Z, Yu J, Liu S, Yu X, Liang P (2014) Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a predictor of recurrence following thermal ablation for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective analysis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110546
Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P (2013) Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 13:159–175
Labelle M, Begum S, Hynes RO (2011) Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell 20:576–590
Schumacher D, Strilic B, Sivaraj KK, Wettschureck N, Offermanns S (2013) Platelet-derived nucleotides promote tumor-cell transendothelial migration and metastasis via P2Y2 receptor. Cancer Cell 24:130–137
Ferrone C, Dranoff G (2010) Dual roles for immunity in gastrointestinal cancers. J Clin Oncol 28:4045–4051
Fukuda H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Shimizu S, Tanabe K (2018) Predictive value of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with cytoreductive nephrectomy. Oncotarget 9:14296–14305
Zhang X, Hu D, Lin X, Zhang H, Xia Y, Lin J, Zheng X, Peng F, Jie J, Niu W (2019) Prognostic value of an inflammation-related index in 6,865 Chinese patients with postoperative digestive tract cancers: the FIESTA study. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00427.eCollection
Tong YS, Tan J, Zhou XL et al (2017) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1326-1
Templeton AJ, Knox JJ, Lin X et al (2016) Change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in response to targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma as a prognosticator and biomarker of efficacy. Eur Urol 70:358–364
Hirahara T, Arigami T, Yanagita S, Matsushita D, Uchikado Y, Kita Y, Mori S, Sasaki K, Omoto I, Kurahara H, Maemura K, Okubo K, Uenosono Y, Ishigami S, Natsugoe S (2019) Combined neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in patients with advanced gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5903-y
Nakamura N, Kinami S, Fujii Y, Miura S, Fujita J, Kaida D, Tomita Y, Miyata T, Fujita H, Ueda N, Iida Y, Kosaka T (2019) The neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of peritoneal metastasis during staging laparoscopy for advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective cohort analysis. World J Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-019-1651-3
Ma M, Yu N, Wu B (2019) High systemic immune-inflammation index represents an unfavorable prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Manag Res 11:3973–3979
Zhao LY, Yang DD, Ma XK, Liu MM, Wu DH, Zhang XP, Ruan DY, Lin JX, Wen JY, Chen J, Lin Q, Dong M, Qi JJ, Hu PS, Zeng ZL, Chen ZH, Wu XY (2019) The Prognostic Value of aspartate aminotransferase to lymphocyte ratio and systemic immune-inflammation index for overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with palliative treatments. J Cancer 10:2299–2311
Jomrich G, Gruber ES, Winkler D, Hollenstein M, Gnant M, Sahora K, Schindl M (2019) Systemic Immune-inflammation index (SII) predicts poor survival in pancreatic cancer patients undergoing resection. J Gastrointest Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04187-z
Chen L, Kong X, Wang Z, Wang X, Fang Y, Wang J (2020) Pre-treatment systemic immune-inflammation index is a useful prognostic indicator in patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Cell Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14934
Li X, Hu P, Liu J, Zhang J, Liu Q (2020) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicted overall survival and radiosensitivity in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol 16:103–115
Wang B, Huang Y, Lin T (2020) Prognostic impact of elevated pre-treatment systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Med (Baltim). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018571
Berardi R, Santoni M, Rinaldi S, Bower M, Tiberi M, Morgese F, Caramanti M, Savini A, Ferrini C, Torniai M, Fiordoliva I, Newsom-Davis T (2019) Pre-treatment systemic immune-inflammation represents a prognostic factor in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Transl Med. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.09.18
Lolli C, Basso U, Derosa L et al (2016) Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the clinical outcome in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib. Oncotarget 7:54564–54571
Chrom P, Zolnierek J, Bodnar L, Stec R, Szczylik C (2019) External validation of the systemic immune-inflammation index as a prognostic factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and its implementation within the international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium model. Int J Clin Oncol 24:526–532
Acknowledgements
No research support or funding was received in connection with this study. The authors have no significant affiliation or involvement, either direct or indirect, with any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EO, HB, and KO were involved in the design of the study. MOH, SNG, and KO performed data acquisition. HB, and EO were involved in the statistical analysis and interpretation of data. HB, KO, and MOH wrote the draft manuscript. EO and SNG helped with the manuscript editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Katip Celebi University, Ataturk Training and Research Hospital Ethics Committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and the study was performed inaccordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozbek, E., Besiroglu, H., Ozer, K. et al. Systemic immune inflammation index is a promising non-invasive marker for the prognosis of the patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 52, 1455–1463 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02440-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-020-02440-y