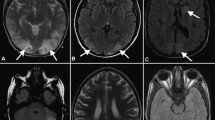
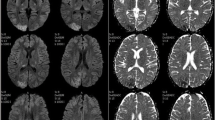
Abstract
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) has been described as a neurological condition observed in a variety of clinical settings and is characterized by focal neurological deficits, seizures, headaches, altered mental status, and visual impairment, associated with transient typical lesions on neuroimaging, predominantly in the posterior part of the brain. The most common risk factors for PRES are hypertension, renal diseases, and the use of calcineurin inhibitors. The incidence of PRES in children with renal disorders varies between 4 and 9%, according to different reports. Vasogenic cerebral edema is considered the major pathophysiological mechanism of PRES. There are two main theories regarding the genesis of this edema: (1) hyperperfusion, due to autoregulatory failure of the cerebral vasculature, and (2) hypoperfusion, due to vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries. In addition, PRES might also be the result of a systemic inflammatory state causing endothelial dysfunction. The management of PRES includes BP control, treatment of seizures, and removal of or reduction in calcineurin inhibitors. Intravenous administration of antihypertensive therapy is preferred, and various drugs have been used in this regard, including nicardipine, labetalol, sodium nitroprusside, and hydralazine. The prognosis of PRES is usually benign, except for rare cases with intracranial hemorrhage.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, Pessin MS, Lamy C, Mas JL, Caplan LR (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334:494–500
Yamada A, Ueda N (2012) Age and gender may affect posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 27(2):277–283
Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hamasaki Y, Hataya H, Shishido S, Asanuma H, Nishimura G, Hiramoto R, Honda M (2006) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children: its high prevalence and more extensive imaging findings. Am J Kidney Dis 48:231–238
Ishikura K, Hamasaki Y, Sakai T, Hataya H, Mak RH, Honda M (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with kidney diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 27(3):375–384
Onder AM, Lopez R, Teomete U, Francoeur D, Bhatia R, Knowbi O, Hizaji R, Chandar J, Abitbol C, Zilleruelo G (2007) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in the pediatric renal population. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1921–1929
Ikeda M, Ito S, Hataya H, Honda M, Anbo K (2001) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a patient with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 37:E30
Stott VL, Hurrell MA, Anderson TJ (2005) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a misnomer reviewed. Intern Med J 35:83–90
Prasad N, Gulati S, Gupta RK, Kumar R, Sharma K, Sharma RK (2003) Is reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy with severe hypertension completely reversible in all patients? Pediatr Nephrol 18:1161–1166
Casey SO, Sampaio RC, Michel E, Truwit CL (2000) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: utility of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MR imaging in the detection of cortical and subcortical lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1199–1206
Singh N, Bonham A, Fukui M (2000) Immuno suppressive associated leukoencephalopathy in organ transplant recipients. Transplantation 69:467–472
Schwartz RB (2002) Hyperperfusion encephalopathies: hypertensive encephalopathy and related conditions. Neurologist 8:22–34
Dillon WP, Rowley H (1998) The reversible posterior cerebral edema syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:591
Pavlakis SG, Frank Y, Chusid R (1999) Hypertensive encephalopathy, reversible occipitoparietal encephalopathy, or reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy: three names for an old syndrome. J Child Neurol 14:277–281
Chandramohan V, Nagarajan VP, Sathyamoorthi MS et al (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a child with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome: case report and review of literature. J Pediatr Neurosci 7(3):221–224
Arzanian MT, Shamsian BS, Karimzadeh P, Kajiyazdi M, Malek F, Hammoud M (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in pediatric hematologic-oncologic disease: literature review and case presentation. Iran J Child Neurol 8(2):1–10
Gafton B, Porumb V, Ungurianu S, Marinca MV, Cocea C, Croitoru A, Balan G, Miron N, Eliade Ciuleanu T, Miron L (2014) Hepatocellular carcinoma: insights in the biological treatment beyond sorafenib. J BUON 19(4):858–866
Endo A, Fuchigami T, Hasegawa M, Hashimoto K, Fujita Y, Inamo Y, Mugishima H (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in childhood: report of four cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Emerg Care 28(2):153–157
El-Naggari MA, Al-Nabhani D, El-Nour I, El-Manzalawy A, Abdelmogheth A-AA (2015) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in two Omani children with underlying renal diseases. Sult Qaboos Univ Med J 15(3):424–428
Saeed B, Abou-Zor N, Amer Z, Kanani I, Hilal M (2008) Cyclosporin-A induced posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 19(3):439–442
Gera DN, Patil SB, Iyer A, Kute VB, Gandhi S, Kumar D, Trivedi HL (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with kidney disease. Indian J Nephrol 24(1):28–34
Tenta M, Uchida HA, Nunoue T, Umebayashi R, Okuyama Y, Kitagawa M, Maeshima Y, Sugiyama H, Wada J (2015) Successful treatment by mycophenolate mofetil in a patient with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis associated with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. CEN Case Rep 4(2):190–195
Sakai N, Kawasaki Y, Imaizumi T, Kanno S, Go H, Mitomo M, Ushijima Y, Suyama K, Ito M, Hashimoto K, Hosoya M (2010) Two patients with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis complicated by cyclosporine-induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Clin Nephrol 73:482–486
Nakahara C, Hasegawa N, Izumi I, Kanemoto K, Iwasaki N (2005) The use of cyclosporine in a boy with a prior episode of posterior encephalopathy. Pediatr Nephrol 20:657–661
Soylu A, Kavukcu S, Turkmen M, Akbas Y (2001) Posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in poststreptococcal acute glomerulonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 16:601–603
Ohta T, Sakano T, Shiotsu M, Furue T, Ohtani H, Kinoshita Y, Mizoue T, Kiya K, Tanaka I (2004) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy in a patient with Wegener granulomatosis. Pediatr Nephrol 19:442–444
Bartynski WS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. I. Fundamental imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1036–1042
Roth C, Ferbert A (2011) The posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: What’s certain, what’s new? Pract Neurol 11:136–144
Fugate JE, Claassen DO, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF, Kozak OS, Rabinstein AA (2010) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: associated clinical and radiologic findings. Mayo Clin Proc 85:427–432
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, McKinney ZJ, Kozak OS, SantaCruz KS et al (2007) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:904–912
Hobson EV, Craven I, Blank SC (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a truly treatable neurologic illness. Peritoneal Dial Int J Int Soc Peritoneal Dial 32(6):590–594
Bechstein WO (2000) Neurotoxicity of calcineurin inhibitors: impact and clinical management. Transpl Int 13:313–326
Bartynski WS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. II. Controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1043–1049
De Laat P, te Winkel ML, Devos AS, Catsman-Berrevoets CE, Pieters R, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM (2011) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in childhood cancer. Ann Oncol 22:472–478
Magnasco A, Rossi A, Catarsi P, Gusmano R, Ginevri F, Perfumo F, Ghiggeri GM (2008) Cyclosporin and organ specific toxicity: clinical aspects, pharmacogenetics and perspectives. Curr Clin Pharmacol 3:166–173
Mueller-Mang C, Mang T, Pirker A, Klein K, Prchla C, Prayer D (2009) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Do predisposing factors make a difference in MRI appearance? Neuroradiology 51:373–383
Jones BV, Egelhoff JC, Patterson RJ (1997) Hypertensive encephalopathy in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:101–106
de Oliveira RA, Fechine LM, Neto FC, Nicodemus JM, Silva GB Jr, Silva LS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) induced by cyclosporine use in a patient with collapsing focal glomeruloesclerosis. Int Urol Nephrol 40(4):1095–1098
Akutsu N, Iwashita C, Maruyama M, Ootsuki K, Ito T, Saigo K, Kenmochi T (2008) Two cases of calcineurin inhibitor-associated reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in renal transplant recipients. Transpl Proc 40:2416–2418
Ishikura K, Ikeda M, Hamasaki Y, Hataya H, Nishimura G, Hiramoto R, Honda M (2008) Nephrotic state as a risk factor for developing posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in paediatric patients with nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transpl 23(8):2531–2536
Mueller AR, Platz KP, Bechstein WO et al (1994) Neurotoxicity after orthotopic liver transplantation. A comparison between cyclosporine and FK506. Transplantation 58:155–170
Incecik F, Herguner MO, Altunbasak S, Erbey F, Leblebisatan G (2009) Evaluation of nine children with reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome. Neurol India 57:475–477
Bai JPF, Lesko LJ, Burckart GJ (2010) Understanding the genetic basis for adverse effects: the calcineurin inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy 30:195–209
Qin W, Tan CY, Huang X, Huang Z, Tao Y, Fu P (2011) Rapamycin-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy in a kidney transplantation patient. Int Urol Nephrol 43(3):913–916
Becquet O, Pasche J, Gatti H, Chenel C, Abely M, Morville P, Pietrement C (2010) Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis in children of French Polynesia: a 3-year retrospective study. Pediatr Nephrol 25:275–280
Gomez-Lado C, Martinon-Torres F, Alvarez-Moreno A, Eiris- Punal J, Carreira-Sande N, Rodriguez-Nunez A, Castro-Gago M (2007) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: an infrequent complication in the course of haemolytic-uremic syndrome. Rev Neurol 44:475–478
Punaro M, Abou-Jaoude P, Cimaz R, Ranchin B (2007) Unusual neurologic manifestations (II): posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) in the context of juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 16:576–579
Zhang YX, Liu JR, Ding MP, Huang J, Zhang M, Jansen O, Deuschl G, Eschenfelder CC (2008) Reversible posterior encephalopathy syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Intern Med 47:867–875
Ozcakar ZB, Ekim M, Fitoz S, Teber S, Hizel S, Acar B, Yuksel S, Yalcinkaya F (2004) Hypertension induced reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a report of two cases. Eur J Pediatr 163:728–730
Benoist G, Dossier C, Elmaleh M, Dauger S (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome revealing renal artery stenosis in a child. BMJ Case Rep 23:2013
Sharma S, Gupta R, Sehgal R, Aggarwal KC (2014) Atypical presentation of posterior reversible encephalopathy: in a child with bilateral grade IV vesicoureteric reflux. J Trop Pediatr 60:331–333
Girişgen İ, Tosun A, Sönmez F, Özsunar Y (2010) Recurrent and atypical posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a child with peritoneal dialysis. Turk J Pediatr 52:416–419
Awan AQ, Lewis MA, Postlethwaite RJ, Webb NJA (1999) Seizures following renal transplantation in childhood. Pediatr Nephrol 13:275–277
Zheng W (2001) Neurotoxicology of the brain barrier system: new implications. Clin Toxicol 39:711–719
Tuor UI, Grewal D (1994) Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow: influence of local brain development and postnatal age. Am J Physiol 267:H2220–H2228
Kwon S, Koo J, Lee S (2001) Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Neurol 24:361–364
Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA (2008) Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol 65:205–210
Schmithorst VJ, Holland SK, Dardzinski BJ (2008) Developmental differences in white matter architecture between boys and girls. Hum Brain Mapp 29:696–710
Hughes RL (1990) Cyclosporine-related central nervous system toxicity in cardiac transplantation. N Engl J Med 323:420–421
Schwartz RB, Bravo SM, Klufas RA, Hsu L, Barnes PD, Robson CD, Antin JH (1995) Cyclosporine neurotoxicity and its relationship to hypertensive encephalopathy: CT and MR findings in 16 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:627–631
Ong B, Bergin P, Heffernan T, Stuckey S (2009) Transient seizure-related MRI abnormalities. J Neuroimaging 19:301–310
Peter P, George A (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and the pediatric population. J Pediatr Neurosci 7(2):136–138
Covarrubias DJ, Luetmer PH, Campeau NG (2002) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: prognostic utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1038–1048
Pande AR, Ando K, Ishikura R, Nagami Y, Takada Y, Wada A, Watanabe Y, Miki Y, Uchino A, Nakao N (2006) Clinicoradiological factors influencing the reversibility of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a multicenter study. Radiat Med 24:659–668
Ahn KJ, You WJ, Jeong SL, Lee JW, Kim BS, Lee JH et al (2004) Atypical manifestations of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: findings on diffusion imaging and ADC mapping. Neuroradiology 46:978–983
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2007) Distinct imaging patterns and lesion distribution in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1320–1327
Servillo G, Bifulco F, De Robertis E, Piazza O, Striano P, Tortora F, Striano S, Tufano R (2007) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med 33:230–236
Eichler FS, Wang P, Wityk RJ (2002) Diffuse metabolic abnormalities in reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:833–837
Bartynski WS, Boardman JF (2008) Catheter angiography, MR angiography, and MR perfusion in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:447–455
Wright RR, Mathews KD (1996) Hypertensive encephalopathy in childhood. J Child Neurol 11:193–196
Paues J, Vrethem M (2010) Fatal progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma treated with rituximab. J Clin Virol 48:291–293
Kumar D (2010) Emerging viruses in transplantation. Curr Opin Infect Dis 23:374–378
Ko MW, Liu GT (2010) Pediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Horm Res Paediatr 74:381–389
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Meder JF, Mas JL (2004) Neuroimaging in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Neuroimaging 14:89–96
llner A (2003) In: Blaser SI (ed) Pocket radiologist PedsNeuro. Salt Lake City, UT, medical reference. PRES, New York, pp 220–222
Parvex P, Pinsk M, Bell LE, O’Gorman AM, Patenaude YG, Gupta IR (2001) Reversible encephalopathy associated with tacrolimus in pediatric renal transplants. Pediatr Nephrol 16:537–542
Gavrilovici C, Oprea L (2013) Clinical ethics, research ethics and community ethics-the moral triad of nowadays society. Revista Romana De Bioetica 11(3):3–5
Gavrilovici C, Goldsmith DJ, Reid C, Gubeth-Tatomir P, Covic A (2004) What is the role of ambulatory BP monitoring in pediatric nephrology? J Nephrol 17(5):642–652
Abe K (2004) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Intern Med 43:900–901
Nishida M, Sato H, Kobayashi N, Morimoto M, Hamaoka K (2009) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a patient with nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 168:731–734
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavrilovici, C., Miron, I., Voroneanu, L. et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1793–1800 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1684-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1684-x