Abstract
Background and objectives
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in process of cancer cell growth and apoptosis and have received increasing attention. SChLAP1 is a novel lncRNA that is required for development and progression of prostate cancer. We hypothesized that SChLAP1 also has important biological functions in human bladder cancer which is another type of urological cancer.
Methods
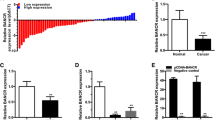
The expression of SChLAP1 in bladder cancer was determined using real-time qPCR. Bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells were transfected with SChLAP1 siRNA or negative control siRNA. Cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration were determined using CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry analysis and wound healing assay, respectively.
Results
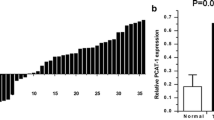
SChLAP1 was overexpressed in bladder cancer tissues compared to paired normal bladder tissues. Cell growth arrest, apoptosis induction and migration inhibition were also observed in bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells after transfection with SChLAP1 siRNA.
Conclusions
Our data suggest that SChLAP1 plays oncogenic roles and can be used as a therapeutic target for treating human bladder cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Egerod FL, Bartels A, Fristrup N, Borre M, Ørntoft TF, Oleksiewicz MB et al (2009) High frequency of tumor cells with nuclear Egr-1 protein expression in human bladder cancer is associated with disease progression. BMC Cancer 9:385
Rosser CJ, Urquidi V, Goodison S (2013) Urinary biomarkers of bladder cancer: an update and future perspectives. Biomark Med 7:779–790
Xue Y, Ma G, Zhang Z, Hua Q, Chu H, Tong N, Yuan L, Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z, Wang M (2015) A novel antisense long noncoding RNA regulates the expression of MDC1 in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 6:484–493
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y, Zhang F, Liu Y (2014) TGF-β-induced upregulation of malat1 promotes bladder cancer metastasis by associating with suz12. Clin Cancer Res 20(6):1531–1541
Tan J, Qiu K, Li M, Liang Y (2015) Double-negative feedback loop between long non-coding RNA TUG1 and miR-145 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in human bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett 589(20 Pt B):3175–3181
Li HJ, Li X, Pang H, Pan JJ, Xie XJ, Chen W (2015) Long non-coding RNA UCA1 promotes glutamine metabolism by targeting miR-16 in human bladder cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45(11):1055–1063
Yan TH, Lu SW, Huang YQ, Que GB, Chen JH, Chen YP, Zhang HB, Liang XL, Jiang JH (2014) Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR predicts recurrence in stage Ta/T1 bladder cancer. Tumour Biol 35(10):10249–10257
Batista PJ, Chang HY (2013) Long non-coding RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 152:1298–1307
Sahu A, Iyer MK, Prensner JR et al (2014) The role of long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 74(19 Supplement):541
Prensner JR, Zhao S, Erho N et al (2014) RNA biomarkers associated with metastatic progression in prostate cancer: a multi-institutional high-throughput analysis of SChLAP1. Lancet Oncol 15(13):1469–1480
Mehra R, Udager AM, Ahearn TU, Cao X, Feng FY, Loda M, Petimar JS, Kantoff P, Mucci LA, Chinnaiyan AM (2015) Overexpression of the long non-coding RNA SChLAP1 independently predicts lethal prostate cancer. Eur Urol. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.12.003
Mehra R, Shi Y, Udager AM, Prensner JR, Sahu A, Iyer MK, Siddiqui J, Cao X, Wei J, Jiang H, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM (2014) A novel RNA in situ hybridization assay for the long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 predicts poor clinical outcome after radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer. Neoplasia 16(12):1121–1127
Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Sahu A et al (2013) The long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 promotes aggressive prostate cancer and antagonizes the SWI/SNF complex. Nat Genet 45(11):1392–1398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Jianjun Zhang and Zhenfeng Shi have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Shi, Z., Nan, Y. et al. Inhibiting malignant phenotypes of the bladder cancer cells by silencing long noncoding RNA SChLAP1. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 711–716 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1230-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1230-2