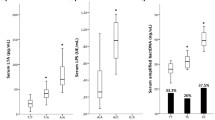
Abstract
Background
Toll-like receptors (TLRs), expressed on cells of the innate immune system, are the first line of host defense. Recognition of bacterial pathogens by the peritoneum is mediated in part by TLR. In this study, we investigated the role of TLR4 (Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile) and TLR2 (Arg677Trp and Arg753Gln) gene polymorphisms in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD).
Method
A total of 100 ESRD patients on PD and 150 healthy controls were enrolled in the study. The patients were divided into two groups: ESRD patients on PD with peritonitis (n = 38) and without peritonitis (n = 62). Genotyping of TLR4 (Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile) and TLR2 (Arg677Trp and Arg753Gln) genes were performed by polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment-length polymorphism (PCR–RFLP).
Results
Heterozygous variant of TLR4 (Thr399Ile) Thr/Ile genotype showed significant association with both groups of patients (patients with and without peritonitis) with no difference between the groups. Overall, TLR4 (Thr399Ile) Thr/Ile genotype demonstrated an association with ESRD on PD (OR 3.9). Further, TLR4 (Thr399Ile) polymorphism showed significant association with PD patients having two or more episodes of peritonitis compared to patients with no peritonitis. No such association of increased risk of ESRD was observed with TLR4 (Asp299Gly) Asp/Gly genotype and TLR2 polymorphisms. Haplotype frequencies, Gly/Ile and Asp/Ile, conferred 2.46- and 4.62-fold increased risk of ESRD, respectively.
Conclusions
TLR4 Thr399Ile genotype was associated with ESRD patients on PD; however, the genotype frequency was similar in PD patients with and without peritonitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S, Brown G (2005) ESRD patients in 2004: global overview of patient numbers, treatment modalities and associated trends. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(12):2587–2593. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi159
Topley N (1998) Membrane longevity in peritoneal dialysis: impact of infection and bio-incompatible solutions. Adv Ren Replace Ther 5(3):179–184
Park JH, Kim YG, Shaw M, Kanneganti TD, Fujimoto Y, Fukase K, Inohara N, Nunez G (2007) Nod1/RICK and TLR signaling regulate chemokine and antimicrobial innate immune responses in mesothelial cells. J Immunol 179(1):514–521
Kato S, Yuzawa Y, Tsuboi N, Maruyama S, Morita Y, Matsuguchi T, Matsuo S (2004) Endotoxin-induced chemokine expression in murine peritoneal mesothelial cells: the role of toll-like receptor 4. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(5):1289–1299
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 11(4):443–451
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282(5396):2085–2088
Misch EA, Hawn TR (2008) Toll-like receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility to human disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 114(5):347–360. doi:10.1042/CS20070214
Kiechl S, Lorenz E, Reindl M, Wiedermann CJ, Oberhollenzer F, Bonora E, Willeit J, Schwartz DA (2002) Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N Engl J Med 347(3):185–192. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012673
Ferwerda B, McCall MB, Alonso S, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Mouktaroudi M, Izagirre N, Syafruddin D, Kibiki G, Cristea T, Hijmans A, Hamann L, Israel S, ElGhazali G, Troye-Blomberg M, Kumpf O, Maiga B, Dolo A, Doumbo O, Hermsen CC, Stalenhoef AF, van Crevel R, Brunner HG, Oh DY, Schumann RR, de la Rua C, Sauerwein R, Kullberg BJ, van der Ven AJ, van der Meer JW, Netea MG (2007) TLR4 polymorphisms, infectious diseases, and evolutionary pressure during migration of modern humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(42):16645–16650. doi:10.1073/pnas.0704828104
Kang TJ, Chae GT (2001) Detection of toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) mutation in the lepromatous leprosy patients. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 31(1):53–58
Nyati KK, Prasad KN, Verma A, Singh AK, Rizwan A, Sinha S, Paliwal VK, Pradhan S (2010) Association of TLR4 Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile polymorphisms with Guillain–Barre syndrome in Northern Indian population. J Neuroimmunol 218(1–2):116–119. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.10.018
Sanchez E, Orozco G, Lopez-Nevot MA, Jimenez-Alonso J, Martin J (2004) Polymorphisms of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 genes in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens 63(1):54–57
Shinzato T, Nakai S, Akiba T, Yamagami S, Yamazaki C, Kitaoka T, Kubo K, Maeda K, Morii H (1999) Report of the annual statistical survey of the Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy in 1996. Kidney Int 55(2):700–712. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00297.x
Kurz P, Kohler H, Meuer S, Hutteroth T, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH (1986) Impaired cellular immune responses in chronic renal failure: evidence for a T cell defect. Kidney Int 29(6):1209–1214
Smogorzewski M, Massry SG (2001) Defects in B-cell function and metabolism in uremia: role of parathyroid hormone. Kidney Int Suppl 78:S186–S189. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.59780186.x
Chansrichavala P, Chantharaksri U, Sritara P, Chaiyaroj SC (2009) Atorvastatin attenuates TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB activation in a MyD88-dependent pathway. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 27(1):49–57
Arbour NC, Lorenz E, Schutte BC, Zabner J, Kline JN, Jones M, Frees K, Watt JL, Schwartz DA (2000) TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet 25(2):187–191. doi:10.1038/76048
Mockenhaupt FP, Cramer JP, Hamann L, Stegemann MS, Eckert J, Oh NR, Otchwemah RN, Dietz E, Ehrhardt S, Schroder NW, Bienzle U, Schumann RR (2006) Toll-like receptor (TLR) polymorphisms in African children: common TLR-4 variants predispose to severe malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(1):177–182. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506803102
Garza-Gonzalez E, Bosques-Padilla FJ, Mendoza-Ibarra SI, Flores-Gutierrez JP, Maldonado-Garza HJ, Perez-Perez GI (2007) Assessment of the toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly, Thr399Ile and interleukin-8 -251 polymorphisms in the risk for the development of distal gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 7:70. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-7-70
Pandey S, Mittal RD, Srivastava M, Srivastava K, Singh S, Srivastava S, Mittal B (2009) Impact of toll-like receptors [TLR] 2 (-196 to -174 del) and TLR 4 (Asp299Gly, Thr399Ile) in cervical cancer susceptibility in North Indian women. Gynecol Oncol 114(3):501–505. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.05.032
Richez C, Blanco P, Rifkin I, Moreau JF, Schaeverbeke T (2011) Role for toll-like receptors in autoimmune disease: the example of systemic lupus erythematosus. Joint Bone Spine 78(2):124–130. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2010.09.005
Allam R, Scherbaum CR, Darisipudi MN, Mulay SR, Hagele H, Lichtnekert J, Hagemann JH, Rupanagudi KV, Ryu M, Schwarzenberger C, Hohenstein B, Hugo C, Uhl B, Reichel CA, Krombach F, Monestier M, Liapis H, Moreth K, Schaefer L, Anders HJ (2012) Histones from dying renal cells aggravate kidney injury via TLR2 and TLR4. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(8):1375–1388. doi:10.1681/ASN.2011111077
Zhang K, Zhou B, Wang Y, Rao L, Zhang L (2013) The TLR4 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 49(4):946–954. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.09.022
Zhang K, Zhang L, Zhou B, Wang Y, Song Y, Rao L (2012) Lack of association between TLR4 Asp299Gly polymorphism and atherosclerosis: evidence from meta-analysis. Thromb Res 130(4):e203–e208. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2012.07.008
Lorenz E, Mira JP, Cornish KL, Arbour NC, Schwartz DA (2000) A novel polymorphism in the toll-like receptor 2 gene and its potential association with staphylococcal infection. Infect Immun 68(11):6398–6401
Schroder NW, Hermann C, Hamann L, Gobel UB, Hartung T, Schumann RR (2003) High frequency of polymorphism Arg753Gln of the toll-like receptor-2 gene detected by a novel allele-specific PCR. J Mol Med 81(6):368–372. doi:10.1007/s00109-003-0443-x
Bochud PY, Hawn TR, Aderem A (2003) Cutting edge: a toll-like receptor 2 polymorphism that is associated with lepromatous leprosy is unable to mediate mycobacterial signaling. J Immunol 170(7):3451–3454
Ben-Ali M, Barbouche MR, Bousnina S, Chabbou A, Dellagi K (2004) Toll-like receptor 2 Arg677Trp polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to tuberculosis in Tunisian patients. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11(3):625–626. doi:10.1128/CDLI.11.3.625-626.2004
Biswas D, Gupta SK, Sindhwani G, Patras A (2009) TLR2 polymorphisms, Arg753Gln and Arg677Trp, are not associated with increased burden of tuberculosis in Indian patients. BMC Res Notes 2:162. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-162
Myles A, Aggarwal A (2013) Lack of association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in toll-like receptors 2 and 4 with enthesitis-related arthritis category of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Indian population. Rheumatol Int 33(2):417–421. doi:10.1007/s00296-012-2396-2
Acknowledgments
Kamini Singh, Priyanka Mishra, and Jahanarah Khatoon duly acknowledges the financial assistance from the Indian Council of Medical research (File Nos. 3/1/2(24)/Nephro/2013-NCD-II, 80/823/2013-ECD-I and 3/1/3/2011 HRD-87 (32606)) (ICMR) New Delhi, India, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee, and written informed consent was obtained from all the study subjects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K., Prasad, K.N., Mishra, P. et al. Toll-like receptors TLR4 (Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile) and TLR2 (Arg677Trp and Arg753Gln) gene polymorphisms in end-stage renal disease patients on peritoneal dialysis. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 2031–2037 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1124-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-1124-8