Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effect of association of tamsulosin/tadalafil taken daily compared with tamsulosin/placebo in the lower urinary tract with urodynamic study (UDS).
Methods
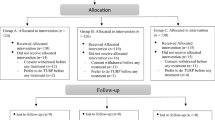
All patients underwent baseline UDS before randomization to tamsulosin 0.4 mg/tadalafil 5 mg (Group 1; n = 20) or tamsulosin 0.4 mg/placebo (Group 2; n = 20) once daily for 30 days. End-of-study UDS were performed on completion of the treatment period. The primary end point was to demonstrate changes in urodynamic variables in the voiding phase, detrusor pressure at maximum flow (PdetQmax), and maximum flow rate (Qmax), from baseline to week four.
Results
The primary outcome measure of this clinical trial, PdetQmax, showed a significant reduction in tamsulosin/tadalafil group (13 ± 17.0) compared to tamsulosin/placebo (−1.2 ± 14.35) group (P = 0.03). Qmax increased in both groups, tamsulosin/tadalafil (1.0 ± 2.4) and tamsulosin/placebo (1.4 ± 2.4), but the difference was not significant between treatment groups (P = 0.65). Total IPSS, storage, and voiding sub-score improved significantly in tamsulosin/tadalafil compared with tamsulosin/placebo group.
Conclusions
The association of tamsulosin/tadalafil reduces detrusor pressure at maximum flow without changing the maximum flow rate during micturition and significantly improves lower urinary tract symptoms compared with the isolated use of tamsulosin.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filippi S, Morelli A, Sandner P et al (2007) Characterization and functional role of androgen-dependent PDE5 activity in the bladder. Endocrinology 148(3):1019–1029
Shapiro E, Lepor H (1995) Pathophysiology of clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urol Clin N Am 22(2):285–290
Andersson KE, de Groat WC, McVary KT et al (2011) Tadalafil for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: pathophysiology and mechanism(s) of action. Neurourol Urodyn 30(3):292–301
Boyle P, Robertson C, Mazzetta C et al (2003) The association between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in four centres: the UrEpik study. BJU Int 92(7):719–725
Sairam K, Kulinskaya E, McNicholas TA et al (2002) Sildenafil influences lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 90(9):836–839
McVary KT, Monnig W, Camps JL Jr et al (2007) Sildenafil citrate improves erectile function and urinary symptoms in men with erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, double-blind trial. J Urol 177(3):1071–1077
Roehrborn CG, McVary KT, Elion-Mboussa A et al (2008) Tadalafil administered once daily for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a dose finding study. J Urol 180(4):1228–1234
Stief CG, Porst H, Neuser D et al (2008) A randomised, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy of twice-daily vardenafil in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 53(6):1236–1244
AUA guideline on management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (2003). Chapter 1: diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol 170(2 Pt 1):530–547
Oger S, Behr-Roussel D, Gorny D et al (2009) Combination of doxazosin and sildenafil exerts an additive relaxing effect compared with each compound alone on human cavernosal and prostatic tissue. J Sex Med 6(3):836–847
Schafer W, Abrams P, Liao L et al (2002) Good urodynamic practices: uroflowmetry, filling cystometry, and pressure-flow studies. Neurourol Urodyn 21(3):261–274
Bechara A, Romano S, Casabe A et al (2008) Comparative efficacy assessment of tamsulosin vs. tamsulosin plus tadalafil in the treatment of LUTS/BPH. Pilot study. J Sex Med 5(9):2170–2178
Oger S, Behr-Roussel D, Gorny D et al (2010) Combination of alfuzosin and tadalafil exerts an additive relaxant effect on human detrusor and prostatic tissues in vitro. Eur Urol 57(4):699–707
Griffiths DJ (1973) The mechanics of the urethra and of micturition. Br J Urol 45(5):497–507
Dmochowski R, Roehrborn C, Klise S et al (2010) Urodynamic effects of once daily tadalafil in men with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, placebo controlled 12-week clinical trial. J Urol 183(3):1092–1097
Kedia GT, Uckert S, Jonas U et al (2008) The nitric oxide pathway in the human prostate: clinical implications in men with lower urinary tract symptoms. World J Urol 26(6):603–609
Monica FZ, Reges R, Cohen D et al (2011) Long-term administration of BAY 41–2272 prevents bladder dysfunction in nitric oxide-deficient rats. Neurourol Urodyn 30(3):456–460
Uckert S, Sormes M, Kedia G et al (2008) Effects of phosphodiesterase inhibitors on tension induced by norepinephrine and accumulation of cyclic nucleotides in isolated human prostatic tissue. Urology 71(3):526–530
Acknowledgments
Fundação Cearense de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—FUNCAP and National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development—CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Regadas, R.P., Reges, R., Cerqueira, J.B.G. et al. Urodynamic effects of the combination of tamsulosin and daily tadalafil in men with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 39–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0317-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0317-7