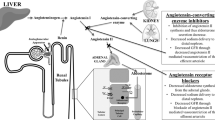
Abstract
For a long time, the inhibition of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone (RAA) axis has been considered a must in almost all patients with progressive chronic kidney disease (CKD), with the aim of reducing the rate of progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). However, recent data from a meta-analysis, including the ALLHAT study, and a study in Canadian diabetic patients questioned the usefulness of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition in delaying the onset of dialysis. Publication of these data led to an intensive recent debate among reputed nephrologists, with numerous pros and cons regarding the pharmacological influence of CKD progression. The authors of the present review critically discuss the arguments and counterarguments of this challenging debate. Finally, a cautious view for the practicing nephrologist is expressed, highlighting the difference between study patients and real-life patients, and the possible overlooked aspects of recent renal protection studies (the importance of central blood pressure, of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and possible, the impact of angiotensin converting inhibitors on stroke), are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casas JP, Chua W, Loukogeorgakis S et al (2005) Effect of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system and other antihypertensive drugs on renal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 366:2026–2033
Suissa S, Hutchinson T, Brophy JM, Kezouh A (2006) ACE-inhibitor use and the long-term risk of renal failure in diabetes. Kidney Int 69:913–919
Mann JF, McClellan WM, Kunz R et al (2006) Progression of renal disease—can we forget about inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system? Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2348–2351
Ritz E, Dikow R (2006) Hypertension and antihypertensive treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2:562–567
Leenen FH, Nwachuku CE, Black HR et al (2006) Clinical events in high-risk hypertensive patients randomly assigned to calcium channel blocker versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in the antihypertensive and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial. Hypertension 48:374–384
Rossing P, Parving H-H, de Zeeuw D (2006) Renoprotection by blocking the RAS in diabetic nephropathy—fact or fiction? Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2354–2357
Jafar TH, Stark PC, Schmid CH et al (2003) Progression of chronic kidney disease: the role of blood pressure control, proteinuria, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition: a patient-level meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 139:244–252
Dahlöf B, Sever PS, Poulter NR et al (2005) Prevention of cardiovascular events with an antihypertensive regimen of amlodipine adding perindopril as required versus atenolol adding bendroflumethiazide as required, in the Anglo-Scandinavian cardiac outcomes trial-blood pressure lowering arm (ASCOT-BPLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:895–906
Remuzzi G, Perico N, Macia M et al (2005) The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 99:S57–S65
Bianchi S, Bigazzi R, Campese VM (2006) Long-term effects of spironolactone on proteinuria and kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 70:2116–2123
Lit YZ, Meyer TW (2006) Work to do on renin-angiotensin system blockade. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:611–612
Cryosostomou A, Pedagogos E, MacGregor L, Becker GJ (2006) Double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effect of the aldosterone receptor antagonist spironolactone in patients who have persistent proteinuria and are on long-term angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy, with or without an angiotensin II receptor blocker. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:256–262
Casas JP, Hingorani AD, MacAllister RJ, Smeeth L (2006) Progression of renal disease—can we forget about inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system? Author’s reply. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2352–2353
Rahman M, Pressel S, Davis BR et al (2005) Renal outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients treated with an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or a calcium channel blocker vs a diuretic: a report from the antihypertensive and lipid-lowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial (ALLHAT). Arch Intern Med 165:936–946
Suissa S (2006) Renoprotection by blocking the RAS in diabetic nephropathy—fact or fiction? Author’s reply. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2357–2358
Gilbertson DT, Liu J, Xue JL et al (2005) Projecting the number of patients with end-stage renal disease in the United States to the year 2015. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:3736–3741
Foley RN, Murray AM, Li S et al (2005) Chronic kidney disease and the risk for cardiovascular disease, renal replacement, and death in the United States Medicare population, 1998 to 1999. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:489–495
Covic A, Haydar AA, Goldsmith DJ (2003) Recent insights from studies using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in patients with renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:645–648
Williams B, Lacy PS, Thom SM et al (2006) Differential impact of blood pressure-lowering drugs on central aortic pressure and clinical outcomes: principal results of the conduit artery function evaluation (CAFE) study. Circulation 113:1213–1225
London GM, Marchais SJ, Guérin AP et al (2002) Impairment of arterial function in chronic renal disease: prognostic impact and therapeutic approach. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17:13–15
Covic A, Mardare N, Gusbeth-Tatomir P et al (2006) Arterial wave reflections and mortality in haemodialysis patients—only relevant in elderly, cardiovascularly compromised? Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2859–2866
Fournier A, Messerli FH, Achard JM et al (2004) Cerebroprotection mediated by angiotensin II: a hypothesis supported by recent randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:1343–1347
Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ et al (1999) The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized aldactone evaluation study investigators. N Engl J Med 341:709–717
Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Lee DS et al (2004) Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the randomized aldactone evaluation study. N Engl J Med 351:543–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Covic, A., Gusbeth-Tatomir, P. & Goldsmith, D.J.A. Current dilemmas in inhibiting the renin–angiotensin system: do not forget real life. Int Urol Nephrol 39, 571–576 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-007-9211-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-007-9211-0