Abstract
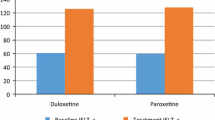
Aim: Though premature ejaculation (PE) has been overshadowed by current attention given to erectile dysfunction, it is the most widespread form of male sexual dysfunction. Delayed or inhibited ejaculation, a known side effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), has made SSRIs potentially useful in the treatment of this disorder. In the present study, we examined the efficacy of duloxetine, an SSRI, in the treatment of PE. Method: The study included 20 married patients diagnosed with PE. The patients were randomly assigned to two groups, duloxetine (group I) and placebo (group II), each consisting of 10 patients. The effects on the ejaculatory function were estimated by the intravaginal ejaculation latency time. All patients were evaluated by using clinical global impression-improvement Scale (CGI-I). Results: The increase in the intravaginal ejaculation latency time in the duloxetine group was statistically significant than that of placebo group. Of group I patients, four (40%) were considered as “very much improved” and four (40%) “much improved” by CGI-I and only one of group II patients (10%) showed “much improved”. Conclusion: Duloxetine appears to be superior to placebo in the pharmacological treatment of PE when administered on a chronic basis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laumann EO, Paik A and Rosen RC (1999). Sexual dysfunction in the United States: prevalence and predictors. JAMA 281: 537–541
El-Sakka AI (2003). Premature ejaculation in non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Int J Androl 26(6): 329–334
Masters WH and Johnson VE (1970). Human Sexual Inadequacy. Little, Brown and Co, Boston
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Diosrders DSM-IV TR, 4th edn. text revision. Washington DC, 2000.
Colpi G, Weidner W and Jungwirth A (2004). EUA guidelines on ejaculatory dysfunction. Eur Urol 46: 555–558
Rudkin L, Taylor MG and Hawton K (2004). Strategies for managing sexual dysfunction induced by antidepressant medication. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4: CD003382
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Gibbon M and First M (1987). Structured Interview for DSM-III-R (SCID). New York State Psychiatric Institute, Biometrics Research, New York, NY
DeCastros R (1985). Reversal of MAOI-induced anorgasmia with cyproheptadine. Am J Psychiat 142: 783–787
Guy W. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. National Institute of Mental Health, Rockville, 2001: 218–222.
Waldinger MD, Hengeveld MW and Zwinderman AH (2001). Effect of SSRI antidepressants on ejaculation: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study with fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, and sertraline. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21(2): 241–246
Atmaca M, Kuloglu M and Tezcan E (2002). The efficacy of citalopram in the treatment of premature ejaculation: a placebo controlled study. Int J Imp Res 14: 502–505
Hull EM, Lorrain DS and Du J (1999). Hormone–neurotransmitter interactions in the control of sexual behavior. Behav Brain Res 105(1): 105–116
Lauerma H (1996). Successful treatment of citalopram-induced anorgasmia by cyproheptadine. Acta Psychiatr Scand 93(1): 69–70
McMahon CG and Touma K (1999). Treatment of premature ejaculation with paroxetine hydrochloride as needed: 2 single-blind placebo controlled crossover studies. J Urol 161(6): 1826–1830
Kim SW and Paick JS (1999). Short-term analysis of the effects of as needed use of sertraline at 5 PM for the treatment of premature ejaculation. Urology 54(3): 544–547
Wong DT, Bymaster FP and Mayle DA (1993). LY248686, a new inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine uptake. Neuropsychopharmacol 8(1): 23–33
Hudson JI, Wohlreich MM and Kajdasz DK (2005). The dual transporter inhibitor duloxetine: a review of its preclinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetic profile, and clinical results in depression. Curr Pharm Des 11(12): 1475–1493
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athanasios, Z., Polyanthi, P. & George, K. The efficacy of duloxetine in the treatment of premature ejaculation. Int Urol Nephrol 39, 115–118 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-006-6659-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-006-6659-2