Abstract
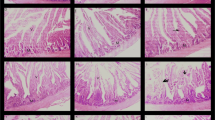
Artemisinin has received much attention in the treatment of malaria in recent years, and it is now considered as a potential candidate to reduce coccidial infection in chickens. It is a sesquiterpene compound which has been isolated from Aretemisia annua for the first time. The present study aimed to investigate the occurrence of artemisinin in A. sieberi (AS) and to test the anticoccidial effects of plant extract in broiler chickens. The aerial parts of the plant were collected during different seasons from Yazd Province, in the centre of Iran. The artemisinin content of the AS was extracted with petrol ether and analysed by high-performance liquid chromatography using UV detection. Anticoccidial effects of the plant extract were tested on chicks challenged with various species of Eimeria. The infected chickens were treated with doses of 1 or 2.5 mg/kg per day artemisinin via oral administration of plant extract. The analytical results showed that the level of artemisinin in AS was 0.2% and 0.14% of dried weight (DW) of plant materials in summer and autumn, respectively. Treatment of experimentally infected chickens with AS extracts showed that artemisinin was able to reduce the severity of coccidial infection induced by Eimeria tenella and E. acervulina, but not E. maxima. The anticoccidial effects of artemisinin were shown by significant decrease in output of number of oocysts per gram of faeces in chickens challenged with different species of Eimeria. This study showed that the levels of artemisinin in AS were comparable with those in other species including A. annua, and that the extract of this plant can reduce coccidial infection in broiler chickens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Artemisia sieberi
- DW:
-
dried weight
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- OPG:
-
oocysts per gram
References
Acton, N., Klayman, D.L. and Rollman, I.J., 1985. Reductive electrochemical HPLC assay for artemisinin (qinghaosu). Planta Medica, 51, 445–446
Allen, P.C., Lydon, J. and Danforth, H.D., 1997. Effects of components of Artemisia annua on coccidia infections in chickens. Poultry Science, 76, 1156–1163
Allen, P.C. and Fetterer, R.H., 2000. Recent advances in biology and immunobiology of Eimeria species and in diagnosis and control of infection with these coccidian parasites of poultry. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 1, 58–65
Cazelles, J., Robert, A. and Meunier, B., 2002. Alkylating capacity and reaction products of antimalarial trioxanes after activation by a heme model. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 67, 609–619
Charles, D.J., Cebert, E. and Simon, J.E., 1991. Characterization of the essential oil of Artemisia annua L. Journal of Essential Oil Research, 3, 33–39
Charles, D.J., Simon, J.E., Wood, K.V. and Heinstein, P., 1990. Germplasm variation in artemisinin content of Artemisia annua L. using an alternative method of artemisinin analysis from crude plant extracts. Journal of Natural Products, 53, 157–160
Fayer, R. and Ellis, W., 1994. Qinghaosu (artemisinin) and derivatives fail to protect neonatal BALB/c mice against Cryptosporidium parvum (Cp) infection. The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 41, 41S
Ferreira, J.F.S., Charles, D.J., Wood, K., Simson J.E. and Janick, J., 1994. A comparison of gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography for artemisinin analysis. Phytochemical Analysis, 5, 116–120
Ferreira, J.F.S., Simson, J.E. and Janick, J., 1995. Developmental studies of Artemisia annua: flowering and artemisinin production under greenhouse and field conditions. Planta Medica, 61, 167–170
Ferreira, J.F.S. and Janick, J., 1996. Immunoquantitative analysis of artemisinin from Artemisia annua using polyclonal antibodies. Phyytochemistry, 41, 97–104
Kamchonwongpaisan, S. and Meshnick, S.R., 1996. The mode of action of antimalarial artemisinin and its derivatives. General Pharmacology, 27(4), 587–592
Klayman, D.L., 1985. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science, 228, 1049–1055
Liersch, R., Soicke, H., Stehr, C. and Tullner, H-U., 1986. Formation of artemisinin in Artemisia annua during one vegetation period. Planta Medica, 52, 387–390
Meshnick, S.R., Tsang, T.W., Lin, F.B., Pan, H.Z., Chang, C.N., Kuypers Chiu, F.D. and Lubin, B., 1989. Activated oxygen mediates the antimalarial activity of qinghaosu. Progress in Clinical and Biological Research, 313, 95–104
Meshnick, S.R., Yang, Y.Z., Lima, V., Kuypers, S., Kamchonwongpaisan, F. and Yuthavong, Y., 1993. Iron-dependent free radical generation from the antimalarial agent artemisinin (qinghaosu). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 37, 1108–1114
Morales, MR., Charles, D.J. and Simon, J.E., 1993. Seasonal accumulation of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. Acta Horticulturae, 344, 416–420
Posner, G.H., Wang, D., Cumming, J.N., Oh, C.H., French, A.N., Bodley, A.L. and Shapiro, T.A., 1995. Further evidence supporting the importance of the restrictions on a carbon-centered radical for high antimalarial activity of 1,2,4-trioxanes like artemisinin. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 38, 2273–2275
White, N.J., 1994a. Artemisinin, current status. Transaction of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 88 (Supplement 11), S3–S4
White, N.J., 1994b. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of artemisinin and derivatives. Transaction of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 88 (Supplement 11), S41–S43
Woerdenbag, H.J., Pras, N., Bos, R., Visser, J.F., Hendriks, H. and Malingre, T.M., 1991. Analysis of artemisinin and related sesquiterenoids from Artemisia annua L. by combined gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry, 2, 215–219
Woerdenbag, H.J., Pras, J., van Uden, W., Wallaart, T.E., Beekman, A.C. and Lugt, C.B., 1994. Progress in the research of artemisinin-related antimalarials: an update. Pharmacy World and Science, 16, 169–180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arab, H.A., Rahbari, S., Rassouli, A. et al. Determination of artemisinin in Artemisia sieberi and anticoccidial effects of the plant extract in broiler chickens. Trop Anim Health Prod 38, 497–503 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-006-4390-8
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-006-4390-8