Abstract
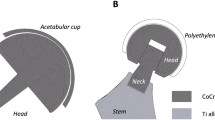
The accurate and detailed characterization of wear particles and ions released from total hip joint prostheses is essential to understand the cause and development of osteolysis, aseptic loosening and hypersensitivity. In this in vitro research, the wear particles and ion release of 22 different test liquids from hip simulator studies were investigated. Wear particles generated from acetabular components made of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) or cross-linked polyethylene containing vitamin E (XLPE) were compared using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and laser diffraction. Additionally, the effect of running-in versus steady-state, accelerated ageing, head materials and calcium sulphate third-body particles on the morphology and size of the created debris was investigated. The Fe, Ni, Mn, Nb, Co, Mo and Al ions released from femoral heads made of stainless steel, CoCrMo and alumina ceramic were analysed using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The combination of SEM and laser diffraction to analyse both the morphology and the particle-size distributions of the polyethylene wear particles was very powerful. The wear particles were predominantly in the submicron range and globular, with occasional fibrils. The size distributions of the UHMWPE and XLPE particles were similar; however, more fibrils were observed among the UHMWPE particles. The average particle size decreased for most samples in the steady-state phase compared to the running-in. The accelerated ageing and the presence of third-body particles generally caused larger UHMWPE wear particles only. Increasing the size of the stainless steel femoral heads led to an increase in the ion level too.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtz, S.M.: UHMWPE biomaterials handbook. Elsevier, Amesterdam (2009)
Lapcikova, M., Slouf, M., Dybal, J., Zolotarevova, E., Entlicher, G., Pokorny, D., Gallo, J., Sosna, A.: Nanometer size wear debris generated from ultra high molecular weight polyethylene in vivo. Wear 266, 349–355 (2009)
Garellick, G., Kärrholm, J., Lindahl, H., Malchau, H., Rogmark, C., Rolfson, O.: The Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Annual Report 2014, Gothenburg (2015)
Endo, M.M., Barbour, P.S.M., Barton, D.C., Fisher, J., Tipper, J.L., Ingham, E., Stone, M.: Comparative wear and wear debris under three different counterface conditions of crosslinked and non-crosslinked ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 11, 23–35 (2001)
Galvin, A., Kang, L., Tipper, J., Stone, M., Ingham, E., Jin, Z., Fisher, J.: Wear of crosslinked polyethylene under different tribological conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 17, 235–243 (2006)
Al-Ma’adeed, M.A., Al-Qaradawi, I.Y., Madi, N., Al-Thani, N.J.: The effect of gamma irradiation and shelf aging in air on the oxidation of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 252, 3316–3322 (2006)
Oral, E., Greenbaum, E.S., Malhi, A.S., Harris, W.H., Muratoglu, O.K.: Characterization of irradiated blends of a-tocopherol and UHMWPE. Biomaterials 26, 6657–6663 (2005)
Lerf, R., Zurbrügg, D., Delfosse, D.: Use of vitamin E to protect cross-linked UHMWPE from oxidation. Biomaterials 31, 3643–3648 (2010)
Slouf, M., Sloufová, I., Horák, Z., Stépánek, P., Entlicher, G., Krejcík, M., Radonský, T., Pokorný, D., Sosna, A.: New fast method for determination of number of UHMWPE wear particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15, 1267–1278 (2004)
Ingram, J.H., Stone, M., Fisher, J., Ingham, E.: The influence of molecular weight, crosslinking and counterface roughness on TNF-alpha production by macrophages in response to ultra high molecular weight polyethylene particles. Biomaterials 25, 3511–3522 (2004)
Green, T.R., Fisher, J., Stone, M., Wroblewski, B.M., Ingham, E.: Polyethylene particles of a “critical size” are necessary for the induction of cytokines by macrophages in vitro. Biomaterials 19, 2297–2302 (1998)
Richards, L., Brown, C., Stone, M.H., Fisher, J., Ingham, E., Tipper, J.L.: Identification of nanometre-sized ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear particles in samples retrieved in vivo. J Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 90, 1106–1113 (2008)
Elfick, A.P.D., Smith, S.L., Green, S.M., Unsworth, A.: The quantitative assessment of UHMWPE wear debris produced in hip simulator testing: the influence of head material and roughness, motion and loading. Wear 249, 517–527 (2001)
Saikko, V., Vuorinen, V., Revitzer, H.: Analysis of UHMWPE wear particles produced in the simulation of hip and knee wear mechanisms with the RandomPOD system. Biotribology 1–2, 30–34 (2015)
Shanbhag, A.S., Bailey, H.O., Hwang, D., Cha, C.W., Eror, N.G., Rubash, H.E.: Quantitative analysis of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) wear debris associated with total knee replacements. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 53, 100–110 (2000)
Calonius, O., Saikko, V.: Analysis of polyethylene particles produced in different wear conditions in vitro. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 399, 219–230 (2002)
McKellop, H.A., Campbell, P., Park, S.H., Schmalzried, T.P., Grigoris, P., Amstutz, H.C.: Sarmiento, a: The origin of submicron polyethylene wear debris in total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 311, 3–20 (1995)
Schmalzried, T.P., Jasty, M., Rosenberg, A., Harris, W.H.: Histologic identification of polyethylene wear debris using Oil Red O stain. J. Appl. Biomater. 4, 119–125 (1993)
Guttmann, D., Schmalzried, T.P., Jasty, M., Harris, W.H.: Light microscopic identification of submicron polyethylene wear debris. J. Appl. Biomater. 4, 303–307 (1993)
Maloney, W.J., Smith, R.L., Schmalzried, T.P., Chiba, J., Huene, D., Rubash, H.: Isolation and characterization of wear particles generated in patients who have had failure of a hip-arthroplasty without cement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 77, 1301–1310 (1995)
Margevicius, K.J., Bauer, T.W., McMahon, J.T., Brown, S.A., Merritt, K.: Isolation and characterization of debris in membranes around total joint prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 76, 1664–1675 (1994)
Elfick, A.P.D., Green, S.M., Krikler, S., Unsworth, A.: The nature and dissemination of UHMWPE wear debris retrieved from periprosthetic tissue of THR. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 65, 95–108 (2003)
Hongtao, L., Shirong, G., Shoufan, C., Shibo, W.: Comparison of wear debris generated from ultra high molecular weight polyethylene in vivo and in artificial joint simulator. Wear 271, 647–652 (2011)
Affatato, S., Fernandes, B., Tucci, A., Esposito, L., Toni, A.: Isolation and morphological characterisation of UHMWPE wear debris generated in vitro. Biomaterials 22, 2325–2331 (2001)
Wang, A., Essner, A., Stark, C., Dumbleton, J.H.: Comparison of the size and morphology of UHMWPE wear debris produced by a hip joint simulator under serum and water lubricated conditions. Biomaterials 17, 865–871 (1996)
Tipper, J.L., Galvin, A.L., Williams, S., McEwen, H.M.J., Stone, M.H., Ingham, E., Fisher, J.: Isolation and characterization of UHMWPE wear particles down to ten nanometers in size from in vitro hip and knee joint simulators. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 78, 473–480 (2006)
Tipper, J.L., Ingham, E., Hailey, J.L., Besong, A.A., Fisher, J., Wroblewski, B.M., Stone, M.H.: Quantitative analysis of polyethylene wear debris, wear rate and head damage in retrieved Charnley hip prostheses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 117–124 (2000)
Schröder, C., Reinders, J., Zietz, C., Utzschneider, S., Bader, R., Kretzer, J.P.: Characterization of polyethylene wear particle: the impact of methodology. Acta Biomater. 9, 9485–9491 (2013)
Billi, F., Benya, P., Kavanaugh, A., Adams, J., Ebramzadeh, E., McKellop, H.: The John Charnley award: an accurate and sensitive method to separate, display, and characterize wear debris: part 1: polyethylene particles. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 470, 329–338 (2012)
Elfick, A.P., Green, S.M., Pinder, I.M., Unsworth, A.: A novel technique for the detailed size characterization of wear debris. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 267–271 (2000)
Hanawa, T.: Metal ion release from metal implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 24, 745–752 (2004)
Gill, H.S., Grammatopoulos, G., Adshead, S., Tsialogiannis, E., Tsiridis, E.: Molecular and immune toxicity of CoCr nanoparticles in MoM hip arthroplasty. Trends Mol. Med. 18, 145–155 (2012)
Mabilleau, G., Kwon, Y.-M., Pandit, H., Murray, D.W., Sabokbar, A.: Metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty: a review of periprosthetic biological reactions. Acta Orthop. 79, 734–747 (2008)
Willert, H.G., Buchhorn, G.H., Fayyazi, A., Flury, R., Windler, M., Koster, G., Lohmann, C.H.: Metal-on-metal bearings and hypersensitivity in patients with artificial hip joints. A clinical and histomorphological study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 87, 28–36 (2005)
Delaunay, C., Petit, I., Learmonth, I.D., Oger, P., Vendittoli, P.A.: Metal-on-metal bearings total hip arthroplasty: the cobalt and chromium ions release concern. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 96, 894–904 (2010)
Visuri, T., Pukkala, E., Paavolainen, P., Pulkkinen, P., Riska, E.B.: Cancer risk after metal on metal and polyethylene on metal total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 4000, S280–S289 (1996)
Billi, F., Benya, P., Kavanaugh, A., Adams, J., Ebramzadeh, E., McKellop, H.: The John Charnley award: an accurate and extremely sensitive method to separate, display, and characterize wear debris: part 2: metal and ceramic particles. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 470, 339–350 (2012)
Lass, R., Grübl, A., Kolb, A., Stelzeneder, D., Pilger, A., Kubista, B., Giurea, A., Windhager, R.: Comparison of synovial fluid, urine, and serum ion levels in metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty at a minimum follow-up of 18 years. J. Orthop. Res. 32, 1234–1240 (2014)
Matusiewicz, H.: Potential release of in vivo trace metals from metallic medical implants in the human body: from ions to nanoparticles—a systematic analytical review. Acta Biomater. 10, 2379–2403 (2014)
Vendittoli, P.-A., Mottard, S., Roy, A.G., Dupont, C., Lavigne, M.: Chromium and cobalt ion release following the Durom high carbon content, forged metal-on-metal surface replacement of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 89, 441–448 (2007)
Savarino, L., Granchi, D., Ciapetti, G., Cenni, E., Nardi Pantoli, A., Rotini, R., Veronesi, C.A., Baldini, N., Giunti, A.: Ion release in patients with metal-on-metal hip bearings in total joint replacement: a comparison with metal-on-polyethylene bearings. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 63, 467–474 (2002)
Howlin, R.P., Brayford, M.J., Webb, J.S., Cooper, J.J., Aiken, S.S., Stoodley, P.: Antibiotic-loaded synthetic calcium sulfate beads for prevention of bacterial colonization and biofilm formation in periprosthetic infections. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 111–120 (2015)
Heuberger, R., Wahl, P., Krieg, J., Gautier, E.: Low in vitro third-body wear on total hip prostheses induced by calcium sulphate used for local antibiotic therapy. Eur. Cells Mater. 28, 246–257 (2014)
Sieving, A., Wu, B., Mayton, L., Nasser, S., Wooley, P.H.: Morphological characteristics of total joint arthroplasty-derived ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) wear debris that provoke inflammation in a murine model of inflammation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 64A, 457–464 (2003)
Eckold, D.G., Dearn, K.D., Shepherd, D.E.T.: The evolution of polymer wear debris from total disc arthroplasty. Biotribology 1–2, 42–50 (2015)
Scott, M., Widding, K., Jani, S.: Do current wear particle isolation procedures underestimate the number of particles generated by prosthetic bearing components? Wear 251, 1213–1217 (2001)
Mabrey, J.D., Afsar-Keshmiri, A., Engh, G.A., Sychterz, C.J., Wirth, M.A., Rockwood, C.A., Mauli Agrawal, C.: Standardized analysis of UHMWPE wear particles from failed total joint arthroplasties. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 63, 475–483 (2002)
Gladkis, L.G., Timmers, H., Scarvell, J.M., Smith, P.N.: Detailed three-dimensional size and shape characterisation of UHMWPE wear debris. Wear 270, 455–463 (2011)
Nine, M.J., Choudhury, D., Hee, A.C., Mootanah, R., Osman, N.A.A.: Wear debris characterization and corresponding biological response: artificial hip and knee joints. Materials (Basel) 7, 980–1016 (2014)
Topolovec, M., Milošev, I., Cör, A., Bloebaum, R.: Wear debris from hip prostheses characterized by electron imaging. Open Med. 8, 476–484 (2013)
Ingham, E., Fisher, J.: The role of macrophages in osteolysis of total joint replacement. Biomaterials 26, 1271–1286 (2005)
Day, J.S., Baxter, R.M., Ramsey, M.L., Morrey, B.F., Connor, P.M., Kurtz, S.M., Steinbeck, M.J.: Characterization of wear debris in total elbow arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 22, 924–931 (2013)
Baxter, R.M., MacDonald, D.W., Kurtz, S.M., Steinbeck, M.J.: Characteristics of highly cross-linked polyethylene wear debris in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 101B, 467–475 (2013)
Affatato, S., Bersaglia, G., Rocchi, M., Taddei, P., Fagnano, C., Toni, A.: Wear behaviour of cross-linked polyethylene assessed in vitro under severe conditions. Biomaterials 26, 3259–3267 (2005)
Zietz, C., Fabry, C., Middelborg, L., Fulda, G., Mittelmeier, W., Bader, R.: Wear testing and particle characterisation of sequentially crosslinked polyethylene acetabular liners using different femoral head sizes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 24, 2057–2065 (2013)
Yamamoto, K., Clarke, I.C., Masaoka, T., Oonishi, H., Williams, P.A., Good, V.D., Imakiire, A.: Microwear phenomena of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene cups and debris morphology related to gamma radiation dose in simulator study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 56, 65–73 (2001)
Weimin, F., Huanghe, S., Xiang, L., Feng, L., Qing, W.: The impact of storage time on the wear rates of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene acetabular liners in hip simulators. J. Arthroplasty 24, 543–548 (2009)
Affatato, S., Freccero, N., Taddei, P.: The biomaterials challenge: a comparison of polyethylene wear using a hip joint simulator. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 53, 40–48 (2016)
Grupp, T.M., Holderied, M., Mulliez, M.A., Streller, R., Jäger, M., Blömer, W., Utzschneider, S.: Biotribology of a vitamin E-stabilized polyethylene for hip arthroplasty—influence of artificial ageing and third-body particles on wear. Acta Biomater. 10, 3068–3078 (2014)
Oral, E., Christensen, S.D., Malhi, A.S., Wannomae, K.K., Muratoglu, O.K.: Wear resistance and mechanical properties of highly crosslinked UHMWPE doped with vitamin-E. J. Arthroplasty 21, 580–591 (2006)
De Villiers, D., Traynor, A., Collins, S.N., Shelton, J.C.: The increase in cobalt release in metal-on-polyethylene hip bearings in tests with third body abrasives. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 229, 611–618 (2015)
Okazaki, Y., Gotoh, E.: Comparison of metal release from various metallic biomaterials in vitro. Biomaterials 26, 11–21 (2005)
Simoes, T.A., Bryant, M.G., Brown, A.P., Milne, S.J., Ryan, M., Neville, A., Brydson, R.: Evidence for the dissolution of molybdenum during tribocorrosion of CoCrMo hip implants in the presence of serum protein. Acta Biomater. 45, 410–418 (2016)
Wapner, K.L.: Implications of metallic corrosion in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 271, 12–20 (1991)
Gurappa, I.: Characterization of different materials for corrosion resistance under simulated body fluid conditions. Mater. Charact. 49, 73–79 (2002)
Germain, M.A., Hatton, A., Williams, S., Matthews, J.B., Stone, M.H., Fisher, J., Ingham, E.: Comparison of the cytotoxicity of clinically relevant cobalt-chromium and alumina ceramic wear particles in vitro. Biomaterials 24, 469–479 (2003)
Coleman, R.F., Herrington, J., Scales, J.T.: Concentration of wear products in hair, blood, and urine after total hip replacement. Br. Med. J. 1, 527–529 (1973)
Heisel, C., Streich, N., Krachler, M., Jakubowitz, E., Kretzer, J.P.: Characterization of the running-in period in total hip resurfacing arthroplasty: an in vivo and in vitro metal ion analysis. J Bone Jt. Surg Am. 90, 125–133 (2008)
Leslie, I., Williams, S., Brown, C., Isaac, G., Jin, Z., Ingham, E., Fisher, J.: Effect of bearing size on the long-term wear, wear debris, and ion levels of large diameter metal-on-metal hip replacements—an in vitro study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 87, 163–172 (2008)
Bortel, E., Charbonnier, B., Heuberger, R.: Development of a synthetic synovial fluid for tribological testing. Lubricants 3, 664–686 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Olivier Loeffel for his kind introduction and help in SEM analysis, Thomas Imwinkelried for his valuable insight and support during the laser diffraction analysis and proof reading of the article (both RMS Foundation), and Mathys Ltd. Bettlach for providing the total hip prosthesis components. Last but not least, the financial support of the RMS Foundation is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zohdi, H., Andreatta, B. & Heuberger, R. Particles and Ions Generated in Total Hip Joint Prostheses: In Vitro Wear Test Results of UHMWPE and XLPE Acetabular Components. Tribol Lett 65, 92 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0872-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0872-2