Abstract
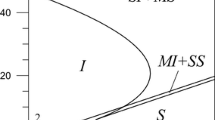
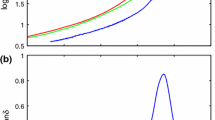
The ice surface softening by friction is investigated considering the additive non-correlated fluctuations of the shear strain and stress, and the temperature. The premelting is construed by the Kelvin–Voigt equation for shear strain and by the relaxation equations of Landau–Khalatnikov type for shear stress and temperature. Taking into account the noises in these equations, the Langevin and Fokker–Planck equations are derived. Their analysis is based on the investigation of extrema of the distribution function, i.e., steady-state values of the shear strain using the Stratonovich interpretation. The phase diagrams are constructed, where the noises intensities and thermostat temperature determine the regions of ice, softened ice and their mixture (stick–slip rubbing). We present that domain of ice friction is bounded by relatively small background sliding block temperatures and fluctuation intensities of the stress and temperature. The ice film softens with growth of the stress noise intensity even at small thermostat temperatures. The friction force time series for all rubbing modes are calculated and compared with experimentally observed ones.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here multiplier 2 is chosen for simplification of the corresponding Fokker–Planck equation (FPE).
Abbreviations
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Shear strain (dimensionless variable)
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Shear stress (Pa)
- \(\tau _\varepsilon\) :
-
Relaxation time of strain (s)
- \(\eta _\varepsilon\) :
-
Effective shear viscosity (Pa s)
- \(\tau _\sigma\) :
-
Relaxation time of stress (s)
- G :
-
Non-relaxed shear modulus (Pa)
- \(\eta\) :
-
Shear viscosity (Pa s)
- \(G_\varepsilon\) :
-
Relaxed shear modulus (Pa)
- \(G_0\) :
-
Typical shear modulus (Pa)
- v :
-
Sliding velocity (m/s)
- \(\omega\) :
-
Circular frequency (Hz)
- T :
-
Temperature of ice surface (K)
- \(T_\mathrm{c}\) :
-
Characteristic ice surface temperature (K)
- Q :
-
Heat flow from the sliding block to the ice surface (K/m\(^3\))
- \(\kappa\) :
-
Heat conductivity [1/(m s)]
- l :
-
Distance into which heat penetrates ice (scale of heat conductivity) (m)
- \(T_\mathrm{e}\) :
-
Thermostat temperature (temperature far away from rubbing surfaces) (K)
- \(c_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Heat capacity (1/m\(^3\))
- g :
-
Coefficient (dimensionless variable)
- \(\tau _T\) :
-
Time of heat conductivity (s)
- a :
-
Lattice constant or intermolecular distance (m)
- c :
-
Sound velocity (m/s)
- \(\rho\) :
-
Ice density (kg/m\(^3\))
- V :
-
Synergetic potential (dimensionless variable)
- \(T_\mathrm{c0}\) :
-
Critical thermostat temperature (K)
- \(I_{\varepsilon ,\sigma ,T}\) :
-
Intensities of strain, stress and temperature noises (s\(^{-2}\), Pa\(^2\), K\(^2\))
- \(\xi _i\) :
-
\(\delta\)-correlated Gaussian source (white noise) (dimensionless variable)
- D :
-
Integral of the correlation function (dimensionless variable)
- I :
-
Effective noise intensity (dimensionless variable)
- P :
-
Probability distribution (dimensionless variable)
- U :
-
Effective potential (dimensionless variable)
- dW :
-
Wiener process (s)
- \(T_\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Maximal time (s)
- N :
-
Number of time series members (dimensionless variable)
- \(\mu ^2\) :
-
Dispersion (dimensionless variable)
- \(r_{1,2}\) :
-
Pseudorandom numbers (dimensionless variable)
- A :
-
Contact area (m\(^2\))
- F :
-
Friction force (N)
- \(S_\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Spectral power density (conventional units)
- \(\nu\) :
-
Frequency (Hz)
References
Akkok, M., Ettles, C.M.M., Calabrese, S.J.: Parameters affecting the kinetic friction of ice. ASME J. Tribol. 109, 552–559 (1987)
Baurle, L., Kaempfer, T.U., Szabo, D., Spencer, N.D.: Sliding friction of polyethylene on snow and ice: contact area and modeling. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 47(3), 276–289 (2007)
Beeman, M., Durham, W.B., Kirby, S.H.: Friction of ice. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 93(B7), 7625–7633 (1988). doi:10.1029/JB093iB07p07625
Blackford, J.R., Skouvaklis, G., Purser, M., Koutsos, V.: Friction on ice: stick and slip. Faraday Discuss. 156, 243–254 (2012)
Ducret, S., Zahouani, H., Midol, A., Lanteri, P., Mathia, T.: Friction and abrasive wear of UHWMPE sliding on ice. Wear 258(14), 26–31 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2004.09.026. (Second International Conference on Erosive and Abrasive Wear)
Eirich, F. (ed.): Rheology. Academic Press, New York (1960)
Eisenberg, D.S., Kauzmann, W.: The Structure and Properties of Water, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2011)
Fortt, A., Schulson, E.: The resistance to sliding along Coulombic shear faults in ice. Acta Mater. 55(7), 2253–2264 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2006.11.022
Fortt, A.L., Schulson, E.M.: Frictional sliding across coulombic faults in first-year sea ice: a comparison with freshwater ice. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans (2011). doi:10.1029/2011JC006969
Gardiner, C.W.: Handbook of Stochastic Methods, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Ghrib, T. (ed.): New Tribological Ways, Adhesion Theory for Low Friction on Ice by Katsutoshi Tusima, 1st edn. InTech, University of Toyama, Toyama (2011)
ter Haar, D. (ed.): Collected Papers of L.D. Landau. Pergamon Press, London (1965)
Haken, H.: Synergetics. An Introduction. Nonequilibrium Phase Transitions and Self-Organization in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (1983)
Horstemke, V., Lefever, R.: Noise-Induced Transitions. Springer, Berlin (1984)
Kennedy, F.E., Schulson, E.M., Jones, D.E.: The friction of ice on ice at low sliding velocities. Philos. Mag. A 80(5), 1093–1110 (2000)
Khomenko, A., Lyashenko, I.: Stochastic theory of ultrathin lubricant film melting in the stick–slip regime. Tech. Phys. 50(11), 1408–1416 (2005). doi:10.1134/1.2131946
Khomenko, A., Lyashenko, I.: Melting of ultrathin lubricant film due to dissipative heating of friction surfaces. Tech. Phys. 52(9), 1239–1243 (2007). doi:10.1134/S1063784207090241
Khomenko, A.V.: Noise influence on solid–liquid transition of ultrathin lubricant film. Phys. Lett. A 329(1–2), 140–147 (2004)
Khomenko, A.V.: Self-organization of adatom adsorption structure at interaction with tip of dynamic force microscope. Condens. Matter Phys. 17(3), 33401 (2014)
Khomenko, A.V., Khomenko, K.P., Falko, V.V.: Nonlinear model of ice surface softening during friction. Condens. Matter Phys. 19(3), 33002 (2016)
Khomenko, A.V., Lyashenko, I.A.: Statistical theory of the boundary friction of atomically flat solid surfaces in the presence of a lubricant layer. Phys. Uspekhi 55(10), 1008–1034 (2012). doi:10.3367/UFNe.0182.201210f.1081
Khomenko, A.V., Lyashenko, I.A., Borisyuk, V.N.: Multifractal analysis of stress time series during ultrathin lubricant film melting. Fluct. Noise Lett. 09(01), 19–35 (2010). doi:10.1142/S0219477510000046
Khomenko, A.V., Lyashenko, Y.A.: Periodic intermittent regime of a boundary flow. Tech. Phys. 55(1), 26–32 (2010). doi:10.1134/S1063784210010056
Khomenko, A.V., Yushchenko, O.V.: Solid–liquid transition of ultrathin lubricant film. Phys. Rev. E 68, 036110 (2003)
Kietzig, A.M., Hatzikiriakos, S.G., Englezos, P.: Ice friction: the effects of surface roughness, structure, and hydrophobicity. J. Appl. Phys. 106(2), 024303 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3173346
Kietzig, A.M., Hatzikiriakos, S.G., Englezos, P.: Physics of ice friction. J. Appl. Phys. 107(8), 081101 (2010)
Klapproth, C., Kessel, T., Wiese, K., Wies, B.: An advanced viscous model for rubber-ice-friction. Tribol. Int. 99, 169–181 (2016). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2015.09.012
Kozin, V., Zhestkaja, V., Pogorelova, A., Chizhiumov, S., Dzhabrailov, M., Morozov, V., Kustov, A.: Applied problems of ice cover dynamics. Natural Sciences Academy Publishing, Moscow (2008). (in Russian)
Lahayne, O., Pichler, B., Reihsner, R., Eberhardsteiner, J., Suh, J., Kim, D., Nam, S., Paek, H., Lorenz, B., Persson, B.N.J.: Rubber friction on ice: experiments and modeling. Tribol. Lett. 62(2), 1–19 (2016). doi:10.1007/s11249-016-0665-z
Landau, L.D., Khalatnikov, I.M.: On the anomalous absorption of sound near a second-order phase transition point. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 96, 469–472 (1954)
Landau, L.D., Lifshitz, E.M.: Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol.7: Theory of Elasticity, 3rd edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1986)
Landau, L.D.: Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol.5: Statistical Physics. Butterworth, London (1999)
Lifshits, E.M., Pitaevskii, L.P.: Course of Theoretical Physics, Vol.10: Physical Kinetics, 1st edn. Pergamon Press, Oxford (1981)
Limmer, D.T., Chandler, D.: Premelting, fluctuations, and coarse-graining of water–ice interfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 141(18), 18 (2014)
Lishman, B., Sammonds, P., Feltham, D., Wilchinsky, A.: The rate- and state- dependence of sea ice friction. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions, pp. POAC09–66 (2009)
Marmo, B.A., Blackford, J.R., Jeffree, C.E.: Ice friction, wear features and their dependence on sliding velocity and temperature. J. Glaciol. 51(174), 391–398 (2005)
Olemskoi, A.I.: Theory of stochastic systems with singular multiplicative noise. Phys. Uspekhi 41(3), 269–301 (1998). doi:10.1070/PU1998v041n03ABEH000377
Olemskoi, A.I., Khomenko, A.V.: Three-parameter kinetics of a phase transition. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 83(6), 1180–1192 (1996)
Olemskoi, A.I., Khomenko, A.V.: Phenomenological equations of the glass transition in liquids. Tech. Phys. 45, 672–676 (2000)
Olemskoi, A.I., Khomenko, A.V.: The synergetic theory of the glass transition in liquids. Tech. Phys. 45, 677–682 (2000)
Olemskoi, A.I., Khomenko, A.V.: Synergetic theory for a jamming transition in traffic flow. Phys. Rev. E 63, 036116 (2001)
Olemskoi, A.I., Khomenko, A.V., Kharchenko, D.O.: Self-organized criticality within fractional Lorenz scheme. Phys. A 323, 263–293 (2003)
Persson, B.N.J.: Sliding Friction. Physical Principles and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling, W.T., Flannery, B.P.: Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York (2007)
Risken, H.: The Fokker-Planck-Equation. Methods of Solution and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1989)
Samadashvili, N., Reischl, B., Hynninen, T., Ala-Nissilä, T., Foster, A.: Atomistic simulations of friction at an ice–ice interface. Friction 1(3), 242–251 (2013). doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0021-3
Schulson, E.M., Fortt, A.L.: Friction of ice on ice. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 117(B12), B12204 (2012)
Skokov, V.N., Koverda, V.N., Skripov, V.P.: A critical nonequilibrium phase transition and 1/f noise in a current-carrying thin HTSC film-boiling nitrogen system. Cryogenics 37(5), 263–265 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0011-2275(97)00001-5
Sukhorukov, S., Loset, S.: Friction of sea ice on sea ice. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 94, 1–12 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2013.06.005
Toropov, E., Kharchenko, D.: Influence of noise on the nature of synergetic systems. Russ. Phys. J. 39(4), 355–361 (1996). doi:10.1007/BF02068059
Wiese, K., Kessel, T.M., Mundl, R., Wies, B.: An analytical thermodynamic approach to friction of rubber on ice. Tire Sci. Technol. 40(2), 124–150 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine (Project “Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of metals fragmentation and friction of spatially nonhomogeneous boundary lubricants between surfaces with nanodimensional irregularities,” No. 0115U000692) and visitor Grant of Forschungszentrum-Jülich, Germany. A.K. is grateful to Dr. Bo N.J. Persson for hospitality during his stay in Forschungszentrum-Jülich. We thank Daria Troshchenko for attentive reading and correction of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khomenko, A., Khomenko, M., Persson, B.N.J. et al. Noise Effect on Ice Surface Softening During Friction. Tribol Lett 65, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0853-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-017-0853-5