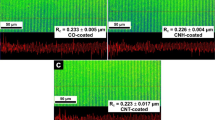
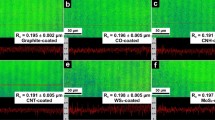
Abstract
When metal surfaces come into contact, lubricants are used to overcome friction. Various forms of hydrocarbons play a central role in lubrication, through both liquid lubricants and surface coatings. Solid lubricants like graphite and complex surface coatings such as diamond-like carbon have led to great advancements in friction mitigation. In addition to these designed carbon films, unintentional carbon films can also spontaneously form during metal–metal sliding. Here, we analyze various systems that produce carbon films, focusing on systems with cyclical metal sliding, hydrocarbon lubricants, and catalytic activity. The systems we analyze include friction polymers, diamond-like carbon coatings, varnish from industrial machines, metal-on-metal hip implants, microelectromechanical systems, and catalysis coke. These films, analyzed at the nanoscale, are primarily graphitic carbon with local regions of sp2 bonding. The graphitic carbon can act as a lubricant in some systems and not in others. Through comparing these various fields, we seek to better understand the formation, evolution, and friction properties of carbon films. Through design and control of carbon films formation, we can control triboactivity to improve system performance.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gangopadhyay, A., McWatt, D., Zdrodowski, R., Liu, Z., Elie, L., Simko, S., Erdemir, A., Ramirez, G., Cuthbert, J., Hock, E.: Development of modified PAG (polyalkylene glycol) high VI high fuel efficient lubricant for LDV applications (2014)
Tanner, D.M., Smith, N.F., Irwin, L.W., Eaton, W.P., Helgesen, K.S., Clement, J.J., Miller, W.M., Miller, S.L., Dugger, M.T., Walraven, J.A.: MEMS reliability: infrastructure, test structures, experiments, and failure modes. In: Sandia National Labs., Albuquerque, NM (US); Sandia National Labs., Livermore, CA (US) (2000)
Hsu, S.M., Gates, R.S.: Effect of materials on tribochemical reactions between hydrocarbons and surfaces. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39(15), 3128–3137 (2006). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/39/15/S02
Hermance, H.W., Egan, T.F.: Organic deposits on precious metal contacts. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 37(3), 739–776 (1958). doi:10.1002/j.1538-7305.1958.tb03885.x
Antler, M.: Tribology of metal coatings for electrical contacts. Thin Solid Films 84(3), 245–256 (1981). doi:10.1016/0040-6090(81)90022-5
Furey, M.J.: The formation of polymeric films directly on rubbing surfaces to reduce wear. Wear 26(3), 369–392 (1973). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(73)90188-9
Gates, R.S., Jewett, K.L., Hsu, S.M.: A study on the nature of boundary lubricating film: analytical method development. Tribol. Trans. 32(4), 423–430 (1989). doi:10.1080/10402008908981909
Hsu, S.M.: Fundamental mechanisms of friction and lubrication of materials. Langmuir 12(19), 4482–4485 (1996). doi:10.1021/la9508856
Morecroft, D.W.: Reactions of octadecane and decoic acid with clean iron surfaces. Wear 18(4), 333–339 (1971). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(71)90076-7
Chaikin, S.W.: On frictional polymer. Wear 10(1), 49 (1967). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(67)90106-8
Mori, S., Imaizumi, Y.: Adsorption of model compounds of lubricant on nascent surfaces of mild and stainless steels under dynamic conditions. Tribol. Trans. 31(4), 449–453 (1988). doi:10.1080/10402008808981847
Herrera-Fierro, P., Shogrin, B.A., Jones, W.R.: Spectroscopic analysis of perfluoropolyether lubricant degradation during boundary lubrication. Lubr. Eng. 56(2), 23–29 (2000)
Zhang, J., Demas, N.G., Polycarpou, A.A., Economy, J.: A new family of low wear, low coefficient of friction polymer blend based on polytetrafluoroethylene and an aromatic thermosetting polyester. Polym. Adv. Technol. 19(8), 1105–1112 (2008). doi:10.1002/pat.1086
Hsu, S.M., Klaus, E.E., Cheng, H.S.: A mechano-chemical descriptive model for wear under mixed lubrication conditions. Wear 128(3), 307–323 (1988). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(88)90066-X
Hsu, S.M., Klaus, E.E.: Estimation of the molecular junction temperatures in four-ball contacts by chemical reaction rate studies. ASLE Trans. 21(3), 201–210 (1978). doi:10.1080/05698197808982875
Hsu, S.M., Klaus, E.E.: Some chemical effects in boundary lubrication part I: base oil-metal interaction. ASLE Trans. 22(2), 135–145 (1979). doi:10.1080/05698197908982909
Lenahan, P.M., Curry, S.E.: First observation of the 29Si hyperfine spectra of silicon dangling bond centers in silicon nitride. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56(2), 157 (1990). doi:10.1063/1.103278
Schmellenmeier, H.: Die Beeinflussung von festen Oberflachen durch eine ionisierte. Exp. Tech. Phys. 1, 49–68 (1953)
Aisenberg, S.: Ion-Beam Deposition of Thin Films of Diamondlike Carbon. J. Appl. Phys. 42(7), 2953 (1971). doi:10.1063/1.1660654
Eryilmaz, O.L., Erdemir, A.: TOF-SIMS and XPS characterization of diamond-like carbon films after tests in inert and oxidizing environments. Wear 265(1–2), 244–254 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2007.10.012
Erdemir, A., Donnet, C.: Tribology of diamond-like carbon films: recent progress and future prospects. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39(18), R311–R327 (2006). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/39/18/R01
Singh, H., Ramirez, G., Eryilmaz, O., Greco, A., Doll, G., Erdemir, A.: Fatigue resistant carbon coatings for rolling/sliding contacts. Tribol. Int. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2016.02.008
Lawes, S.D.A., Fitzpatrick, M.E., Hainsworth, S.V.: Evaluation of the tribological properties of DLC for engine applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40(18), 5427–5437 (2007). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/40/18/S03
Grill, A.: Tribology of diamondlike carbon and related materials: an updated review. Surf Coat Tech 94–5(1–3), 507–513 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(97)00458-1
Lettington, A.H.: Applications of diamond-like carbon thin films. Carbon 36(5–6), 555–560 (1998). doi:10.1016/s0008-6223(98)00062-1
Hauert, R.: A review of modified DLC coatings for biological applications. Diam. Relat. Mater. 12(3–7), 583–589 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0925-9635(03)00081-5
Erdemir, A., Bindal, C., Pagan, J., Wilbur, P.: Characterization of transfer layers on steel surfaces sliding against diamond-like hydrocarbon films in dry nitrogen. Surf. Coat. Tech. 76–77(1–3), 559–563 (1995). doi:10.1016/0257-8972(95)02518-9
Ponsonnet, L., Donnet, C., Varlot, K., Martin, J.M., Grill, A., Patel, V.: EELS analysis of hydrogenated diamond-like carbon films. Thin Solid Films 319(1–2), 97–100 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(97)01094-8
Pastewka, L., Moser, S., Gumbsch, P., Moseler, M.: Anisotropic mechanical amorphization drives wear in diamond. Nat. Mater. 10(1), 34–38 (2011). doi:10.1038/Nmat2902
Moon, M.W., Jensen, H.M., Hutchinson, J.W., Oh, K.H., Evans, A.G.: The characterization of telephone cord buckling of compressed thin films on substrates. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50(11), 2355–2377 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0022-5096(02)00034-0
Wu, W.J., Hon, M.H.: Thermal stability of diamond-like carbon films with added silicon. Surf. Coat. Tech. 111(2–3), 134–140 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(98)00719-1
Scharf, T.W., Singer, I.L.: Role of third bodies in friction behavior of diamond-like nanocomposite coatings studied by in situ tribometry. Tribol. Trans. 45(3), 363–371 (2002). doi:10.1080/10402000208982561
Savage, R.H.: Graphite lubrication. J. Appl. Phys. 19(1), 1–10 (1948). doi:10.1063/1.1697867
Rabinowicz, E., Imai, M.: Frictional properties of pyrolitic boron nitride and graphite. Wear 7(3), 298–300 (1964). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(64)90092-4
Fusaro, R.L., Sliney, H.E.: Graphite fluoride (CFx)n—a new solid lubricant. ASLE Trans. 13(1), 56–65 (1970). doi:10.1080/05698197008972282
Kato, K., Umehara, N., Adachi, K.: Friction, wear and N2-lubrication of carbon nitride coatings: a review. Wear 254(11), 1062–1069 (2003). doi:10.1016/s0043-1648(03)00334-x
Shen, Y., Xu, J.J., Jin, M., Wang, J.J., Wang, L., Han, X.G., Zhang, H.P., Zhang, Y.D.: Tribological behavior among piston ring-hydrorefined mineral oil-cylinder liner for diesel engine. Appl. Mech. Mater. 148, 1307–1311 (2012)
Johnson, M., Spurlock, M.: Strategic oil analysis: estimating remaining lubricant life. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. (2010)
Livingstone, G., Oakton, D.: The emerging problem of lubricant varnish. Maint. Asset Manage. 25, 38–42 (2010)
Lucas, L.: Problems and sources of varnish in hydraulic fluid. Hydraul Pneum. (2007)
Sasaki, A., Uchiyama, S., Kawasaki, M.: Varnish formation in the gas turbine oil systems. J. ASTM Int. 5(2), 1–12 (2008)
Phillips, W.D., Staniewski, J.W.G.: The origin, measurement and control of fine particles in non-aqueous hydraulic fluids and their effect on fluid and system performance. Lubr. Sci. 28(1), 43–64 (2016). doi:10.1002/ls.1300
Atherton, B.: How to stop varnish before it costs you. Plast. Today (2008)
Atherton, B.: Discovering the root cause of varnish formation. Pract. Oil Anal. (2007)
Phillips, W.D.: The high-temperature degradation of hydraulic oils and fluids©. J. Synth. Lubr. 23(1), 39–70 (2006). doi:10.1002/jsl.11
Sasaki, A., Uchiyama, S., Yamamoto, T.: Generation of static electricity during oil filtration. Lubr. Eng. 55(9), 14–21 (1999)
Barber, A., Filippini, B., Profilet, R., Tam, N.: A Fluid solution to preventing varnish formation in hydraulic systems. In: Lubricants Symposium 2008, pp. 175–175 (2008)
Ribeiro, N.M., Pinto, A.C., Quintella, C.M., da Rocha, G.O., Teixeira, L.S.G., Guarieiro, L.L.N., Rangel, M.D., Veloso, M.C.C., Rezende, M.J.C., da Cruz, R.S., de Oliveira, A.M., Torres, E.A., de Andrade, J.B.: The role of additives for diesel and diesel blended (ethanol or biodiesel) fuels: a review. Energy Fuels 21(4), 2433–2445 (2007). doi:10.1021/ef070060r
Heo, G., Lee, S., Kim, H., Park, U., Lee, G., Han, D., Chu, M., Choi, U., Hur, K., Lee, S.G., Kim, H.S., Park, W.K., Lee, K.C., Han, D.H., Chu, M.K., Choi, W.J.: Varnishing processing unit for processing surface of workpiece, has circulating pump provided with nozzle in which hydro static ball pressurizes exterior of workpiece, where circulating pump supplies hydraulic fluid to varnishing tool. KR2010095230-A; KR1077093-B1
Hum, W., Holt, D.G.L., Blumenfeld, M.L., Galiano-Roth, A.S.: Improving varnish control in a mechanical device requiring hydraulic fluids, turbine oils, industrial fluids, circulating oils, or combinations by supplying the mechanical device with a lubricating composition. US2015099675-A1; WO2015050690-A1
ASTM: Standard test method for measurement of lubricant generated insoluble color bodies in in-service turbine oils using membrane patch colorimetry. In: ASTM International, West Conshohocken. vol. ASTM D7843-12. ASTM International (2012)
Robertson, J.: Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 37(4–6), 129–281 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0927-796x(02)00005-0
Ferrari, A.C., Robertson, J.: Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 61(20), 14095–14107 (2000). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.61.14095
Chu, P.K., Li, L.H.: Characterization of amorphous and nanocrystalline carbon films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 96(2–3), 253–277 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.07.048
Pappas, D.L., Saenger, K.L., Cuomo, J.J., Dreyfus, R.W.: Characterization of laser vaporization plasmas generated for the deposition of diamond-like carbon. J. Appl. Phys. 72(9), 3966–3970 (1992). doi:10.1063/1.352249
Cuomo, J.J., Pappas, D.L., Bruley, J., Doyle, J.P., Saenger, K.L.: Vapor deposition processes for amorphous carbon films with sp3 fractions approaching diamond. J. Appl. Phys. 70(3), 1706–1711 (1991)
Liao, Y., Pourzal, R., Wimmer, M.A., Jacobs, J.J., Fischer, A., Marks, L.D.: Graphitic tribological layers in metal-on-metal hip replacements. Science 334(6063), 1687–1690 (2011). doi:10.1126/science.1213902
Buscher, R., Tager, G., Dudzinski, W., Gleising, B., Wimmer, M.A., Fischer, A.: Subsurface microstructure of metal-on-metal hip joints and its relationship to wear particle generation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 72(1), 206–214 (2005). doi:10.1002/jbm.b.30132
Wimmer, M.A., Sprecher, C., Hauert, R., Tager, G., Fischer, A.: Tribochemical reaction on metal-on-metal hip joint bearings—a comparison between in vitro and in vivo results. Wear 255(7–12), 1007–1014 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00127-3
Zahiri, C.A., Schmalzried, T.P., Ebramzadeh, E., Szuszczewicz, E.S., Salib, D., Kim, C., Amstutz, H.C.: Lessons learned from loosening of the McKee-Farrar metal-on-metal total hip replacement. J. Arthroplasty 14(3), 326–332 (1999). doi:10.1016/s0883-5403(99)90059-1
Tager, K.H.: Studies on surface and new joint capsule of Mckee-Farrar prosthesis implanted for several years. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 86(1), 101–113 (1976). doi:10.1007/Bf00415308
Walker, P.S., Salvati, E., Hotzler, R.K.: The wear on removed McKee-Farrar total hip prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 56(1), 92–100 (1974)
Mavraki, A., Cann, P.M.: Lubricating film thickness measurements with bovine serum. Tribol. Int. 44(5), 550–556 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2010.07.008
Mishina, H., Kojima, M.: Changes in human serum albumin on arthroplasty frictional surfaces. Wear 265(5–6), 655–663 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2007.12.006
Wang, A., Yue, S., Bobyn, J.D., Chan, F.W., Medley, J.B.: Surface characterization of metal-on-metal hip implants tested in a hip simulator. Wear 225, 708–715 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00384-6
Hesketh, J., Ward, M., Dowson, D., Neville, A.: The composition of tribofilms produced on metal-on-metal hip bearings. Biomaterials 35(7), 2113–2119 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.11.065
Myant, C., Cann, P.: In contact observation of model synovial fluid lubricating mechanisms. Tribol. Int. 63, 97–104 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2012.64.029
Wimmer, M., Mathew, M., Laurent, M., Nagelli, C., Liao, Y., Marks, L., Pourzal, R., Fischer, A., Jacobs, J.: Tribochemical reactions in metal-on-metal hip joints influence wear and corrosion. In: Metal-On-Metal Total Hip Replacement Devices. ASTM International (2013)
Dugger, M.T.: Tribological Challenges in MEMS and Their Mitigation Via Vapor Phase Lubrication. In: George, T., Islam, M.S., Dutta, A.K. (eds.) Proceedings of SPIE Micro- and Nanotechnology Sensors, Systems, and Applications Iii, vol. 8031 (2011)
Strawhecker, K., Asay, D., McKinney, J., Kim, S.: Reduction of adhesion and friction of silicon oxide surface in the presence of n-propanol vapor in the gas phase. Tribol. Lett. 19(1), 17–21 (2005)
Asay, D.B., Dugger, M.T., Kim, S.H.: In-situ vapor-phase lubrication of MEMS. Tribol. Lett. 29(1), 67–74 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11249-007-9283-0
Asay, D.B., Kim, S.H.: Molar volume and adsorption isotherm dependence of capillary forces in nanoasperity contacts. Langmuir 23(24), 12174–12178 (2007). doi:10.1021/la701954k
Carroll, B., Gogotsi, Y., Kovalchenko, A., Erdemir, A., McNallan, M.J.: Effect of humidity on the tribological properties of carbide-derived carbon (CDC) films on silicon carbide. Tribol. Lett. 15(1), 51–55 (2003). doi:10.1023/A:1023508006745
Ersoy, D.A., McNallan, M.J., Gogotsi, Y., Erdemir, A.: Tribological properties of carbon coatings produced by high temperature chlorination of silicon carbide. Tribol. Trans. 43(4), 809–815 (2000). doi:10.1080/10402000008982412
Graham, E., Klaus, E.: Lubrication from the vapor phase at high temperatures. ASLE Trans. 29(2), 229–234 (1986)
Hook, D.A., Timpe, S.J., Dugger, M.T., Krim, J.: Tribological degradation of fluorocarbon coated silicon microdevice surfaces in normal and sliding contact. J. Appl. Phys. 104(3), 034303 (2008)
Tanner, D.M., Miller, W.M., Eaton, W.P., Irwin, L.W., Peterson, K.A., Dugger, M.T., Senft, D.C., Smith, N.F., Tangyunyong, P., Miller, S.L.: The effect of frequency on the lifetime of a surface micromachined microengine driving a load. In: Reliability Physics Symposium Proceedings. 36th Annual. 1998 IEEE International, pp. 26–35 (1998)
Sung, D., Gellman, A.: The surface chemistry of alkyl and arylphosphate vapor phase lubricants on Fe foil. Tribol. Int. 35(9), 579–590 (2002)
Singer, I., Mogne, T.L., Donnet, C., Martin, J.: Friction behavior and wear analysis of SiC sliding against Mo in SO2, O2 and H2S at gas pressures between 4 and 40 Pa. Tribol. Trans. 39(4), 950–956 (1996)
Hibi, Y., Enomoto, Y., Tanaka, A.: Lubricity of metal ethoxide formed on sliding surfaces of Si3N4-TiN-Ti composites in ethanol. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19(20), 1809–1812 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1006742323483
Barnick, N.J., Blanchet, T.A., Sawyer, W.G., Gardner, J.E.: High temperature lubrication of various ceramics and metal alloys via directed hydrocarbon feed gases. Wear 214(1), 131–138 (1998)
Dugger, M.: Nano/Micro-Tribology of MEMS. In: vol. SAND2014-4771C. U.S. Department of Engery (2014)
Asay, D.B., Dugger, M.T., Ohlhausen, J.A., Kim, S.H.: Macro- to nanoscale wear prevention via molecular adsorption. Langmuir 24(1), 155–159 (2008). doi:10.1021/la702598g
Barbier, J.: Deactivation of reforming catalysts by coking—a Review. Appl. Catal. 23(2), 225–243 (1986). doi:10.1016/S0166-9834(00)81294-4
Forzatti, P., Lietti, L.: Catalyst deactivation. Catal. Today 52(2–3), 165–181 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00074-7
Trimm, D.L.: Control of coking. Chem. Eng. Process. 18(3), 137–148 (1984). doi:10.1016/0255-2701(84)80003-3
Trimm, D.L.: Coke formation and minimisation during steam reforming reactions. Catal. Today 37(3), 233–238 (1997). doi:10.1016/s0920-5861(97)00014-x
Li, C., Stair, P.C.: Ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy characterization of coke formation in zeolites. Catal. Today 33(1–3), 353–360 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(96)00120-4
Rostrup-Nielsen, J., Tottrup, P.: Symp. Science of Catal. Appl. Industry, FPDIL Sindri (39), 379 (1979)
Guisnet, M., Magnoux, P.: Coking and deactivation of zeolites—influence of the pore structure. Appl. Catal. 54(1), 1–27 (1989). doi:10.1016/S0166-9834(00)82350-7
Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.: Industrial relevance of coking. Catal. Today 37(3), 225–232 (1997). doi:10.1016/s0920-5861(97)00016-3
Gallezot, P., Leclercq, C., Guisnet, M., Magnoux, P.: Coking, aging, and regeneration of zeolites: VII. Electron microscopy and EELS studies of external coke deposits on USHY, H-OFF, and H-ZSM-5 zeolites. J. Catal. 114(1), 100–111 (1988)
Corthals, S., Van Nederkassel, J., Geboers, J., De Winne, H., Van Noyen, J., Moens, B., Sels, B., Jacobs, P.: Influence of composition of MgAl2O4 supported NiCeO2ZrO2 catalysts on coke formation and catalyst stability for dry reforming of methane. Catal. Today 138(1–2), 28–32 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2008.04.038
Behera, B., Ray, S.S., Singh, I.D.: NMR Studies of FCC Feeds, Catalysts and Coke. In: Ocelli, M.L. (ed.) Fluid Catalytic Cracking Vii Materials: Methods and Process Innovations, vol. 166. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, pp. 163–200 (2007)
Liu, B.S., Jiang, L., Sun, H., Au, C.T.: XPS, XAES, and TG/DTA characterization of deposited carbon in methane dehydroaromatization over Ga-Mo/ZSM-5 catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(11), 5092–5100 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.11.031
Hardiman, K.M., Cooper, C.G., Adesina, A.A., Lange, R.: Post-mortem characterization of coke-induced deactivated alumina-supported Co–Ni catalysts. Chem. Eng. Sci. 61(8), 2565–2573 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.ces.2005.11.021
Tiratsoo, E.N.: Natural Gas, vol. 1979. Gulf Pub Co, Houston (1979)
Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.: Aspects of CO2-reforming of methane. In: Curry-Hyde, H.E., Howe, R.F. (eds.) Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, vol. 81, pp. 25–41. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1994)
Mizoh, Y.: Wear of tribe-elements of video tape recorders. Wear 200(1–2), 252–264 (1996). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(96)07278-X
Bharat, B., Hahn, F.W.: Stains on magnetic tape heads. Wear 184(2), 193–202 (1995)
Rabinowicz, E.: The tribology of magnetic recording systems—an overview. Tribol. Mech. Magn. Storage Syst. 3, 1–7 (1986)
Mizoh, Y.: Wear of magnetic video head. J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 40(12), 981–986 (1995)
Osaki, H.: Flexible media—recent developments from the tribology point of view. Tribol. Int. 33(5–6), 373–382 (2000). doi:10.1016/S0301-679x(00)00057-8
Kuroe, A., Shinoda, F., Mikoda, M.: An experimental analysis of the recorded signal decrease phenomena in the repeated tape running. Electr. Inf. Soc. 194–200 (1991)
Montgomery, R.S.: Run-in and glaze formation on gray cast iron surfaces. Wear 14(2), 99 (1969). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(69)90340-8
Sugishita, J., Fujiyoshi, S.: The effect of cast iron graphites on friction and wear performance I: graphite film formation on grey cast iron surfaces. Wear 66(2), 209–221 (1981)
Takeuchi, E.: The mechanisms of wear of cast iron in dry sliding. Wear 11(3), 201–212 (1968). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(68)90558-9
Leach, P.W., Borland, D.W.: The unlubricated wear of flake graphite cast-iron. Wear 85(2), 257–266 (1983). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(83)90068-6
Erdemir, A.: Review of engineered tribological interfaces for improved boundary lubrication. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 249–256 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.08.008
Erdemir, A., Eryilmaz, O.L., Urgen, M., Kazmanli, K.: Method to produce catalytically active nanocomposite coatings. In: Google Patents (2013)
Dowson, D., Jin, Z.M.: Metal-on-metal hip joint tribology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 220(2), 107–118 (2006). doi:10.1243/095441105x69114
Rostrup-Nielsen, J.R.: Sulfur-passivated nickel catalysts for carbon-free steam reforming of methane. J. Catal. 85(1), 31–43 (1984). doi:10.1016/0021-9517(84)90107-6
Fang, S., Lin, G.X.: Managing varnish of turbine oil. In: Kim, Y.H., Yarlagadda, P. (eds.) Materials, Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, vol. 842. Advanced Materials Research, pp. 341–344 (2014)
Bell, J., Tipper, J.L., Ingham, E., Stone, M.H., Fisher, J.: The influence of phospholipid concentration in protein-containing lubricants on the wear of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene in artificial hip joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H-J. Eng. Med. 215(H2), 259–263 (2001). doi:10.1243/0954411011533661
Keenan, M.R., Kotula, P.G.: Accounting for poisson noise in the multivariate analysis of ToF-SIMS spectrum images. Surf. Interface Anal. 36(3), 203–212 (2004)
Tang, S., Gao, S., Hu, S., Wang, J., Zhu, Q., Chen, Y., Li, X.: Inhibition Effect of APCVD titanium nitride coating on coke growth during n-hexane thermal cracking under supercritical conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53(13), 5432–5442 (2014). doi:10.1021/ie401889p
Hibi, Y., Enomoto, Y.: Mechanochemical reaction and relationship to tribological response of silicon nitride in n-alcohol. Wear 231(2), 185–194 (1999). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00094-0
Mccarty, J.G., Wise, H.: Hydrogenation of surface carbon on alumina-supported nickel. J. Catal. 57(3), 406–416 (1979). doi:10.1016/0021-9517(79)90007-1
Dowden, D.A.: Crystal and ligand field models of solid catalysts. Catal. Rev. 5(1), 1–32 (1972). doi:10.1080/01614947208076863
Yan, Y., Neville, A., Dowson, D., Hollway, F.: Biotribocorrosion of CoCrMo orthopaedic implant materials—assessing the formation and effect of the biofilm. Tribol. Int. 40(10–12), 1728 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2007.02.019
Yan, Y., Neville, A., Dowson, D., Williams, S., Fisher, J.: Tribofilm formation in biotribocorrosion – does it regulate ion release in metal-on-metal artificial hip joints? Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Eng. Med. 224(9), 997–1006 (2010). doi:10.1243/13506501jet762
Nakayama, K.: Triboemission of charged-particles from various solids under boundary lubrication conditions. Wear 178(1–2), 61–67 (1994). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(94)90129-5
Nevshupa, R.A., Nakayama, K.: Triboemission behavior of photons at dielectric/dielectric sliding: time dependence nature at 10[sup −4]–10[sup 4]s. J. Appl. Phys. 93(11), 9321 (2003). doi:10.1063/1.1570934
Nevshupa, R.A., Nakayama, K.: Effect of nanometer thin metal film on triboemission of negatively charged particles from dielectric solids. Vacuum 67(3–4), 485–490 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0042-207x(02)00234-8
Ferrante, J.: Exoelectron emission from a clean, annealed magnesium single crystal during oxygen adsorption. ASLE Trans. 20(4), 328–332 (1977). doi:10.1080/05698197708982851
Warren, W.L., Lenahan, P.M.: Electron-nuclear double-resonance and electron-spin-resonance study of silicon dangling-bond centers in silicon nitride. Phys. Rev. B 42(3), 1773–1780 (1990)
Podgornik, B., Hren, D., Vižintin, J.: Low-friction behaviour of boundary-lubricated diamond-like carbon coatings containing tungsten. Thin Solid Films 476(1), 92–100 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2004.09.028
de Barros’Bouchet, M.I., Martin, J.M., Le-Mogne, T., Vacher, B.: Boundary lubrication mechanisms of carbon coatings by MoDTC and ZDDP additives. Tribol. Int. 38(3), 257–264 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.08.009
Nakayama, K.: Triboemission of electrons, ions, and photons from diamondlike carbon films and generation of tribomicroplasma. Surf. Coat. Tech. 188, 599–604 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.07.103
Sanchez-Lopez, J.C., Erdemir, A., Donnet, C., Rojas, T.C.: Friction-induced structural transformations of diamondlike carbon coatings under various atmospheres. Surf. Coat. Tech. 163, 444–450 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(02)00641-2
Liu, Y., Erdemir, A., Meletis, E.I.: Influence of environmental parameters on the frictional behavior of DLC coatings. Surf. Coat. Tech. 94–5(1–3), 463–468 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(97)00450-7
Erdemir, A., Bindal, C., Fenske, G.R., Zuiker, C., Wilbur, P.: Characterization of transfer layers forming on surfaces sliding against diamond-like carbon. Surf. Coat. Tech. 86–7(1–3), 692–697 (1996). doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(96)03073-3
Kim, D.S., Fischer, T.E., Gallois, B.: The effects of oxygen and humidity on friction and wear of diamond-like carbon-films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 49(1–3), 537–542 (1991). doi:10.1016/0257-8972(91)90113-B
Lhomme, V., Bruneau, C., Soyer, N., Brault, A.: Thermal behavior of some organic phosphates. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 23(1), 98–102 (1984). doi:10.1021/i300013a021
Appleby, W.G., Gibson, J.W., Good, G.M.: Coke formation in catalytic cracking. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1(2), 102–110 (1962). doi:10.1021/i260002a006
Merkle, A., Erdemir, A., Eryilmaz, O., Johnson, J., Marks, L.: In situ TEM studies of tribo-induced bonding modifications in near-frictionless carbon films. Carbon 48(3), 587–591 (2010)
Mangolini, F., Rose, F., Hilbert, J., Carpick, R.W.: Thermally induced evolution of hydrogenated amorphous carbon. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4826100
Nalwa, H.S.: Handbook of Surfaces and Interfaces of Materials, Five-Volume Set. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (2001)
Liao, Y., Marks, L.D.: Modeling of thermal-assisted dislocation friction. Tribol. Lett. 37(2), 283–288 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11249-009-9520-9
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the NSF under the Grant Number CMMI-1030703. EEH is funded through the National Defense Science and Engineering Graduate Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoffman, E.E., Marks, L.D. Graphitic Carbon Films Across Systems. Tribol Lett 63, 32 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0720-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0720-9