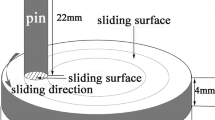
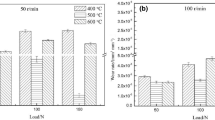
Abstract
Sliding wear tests were performed for H13 steel and a cast steel under atmospheric conditions of 25, 200, and 400°C. XRD results identify that oxidative wear prevailed for the steels during sliding at 200–400°C. However, the oxidative wear at 200°C presented entirely different wear behaviors from the one at 400°C. With an increase of load, the oxidative wear at 200°C exhibited slowly increased and lower wear rates, despite relatively less tribo-oxides. On the contrary, although there were more tribo-oxides, the oxidative wear at 400°C presented rapidly increased and higher wear rates. The former oxidative wear could be classified into mild wear; the latter one fell beyond mild wear. The two types of oxidative wear universally existed; their discrepancies were mainly attributed not to the tribo-oxides, but to the extent of softening and deformation of substrate. Hence, we suggested that the two types of oxidative wear should be distinguished in the coming research, and were termed oxidative mild wear and oxidative wear, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Straffelini, G., Trabucco, D., Molinari, A.: Oxidative wear of heat-treated steels. Wear 250, 485–491 (2001)
Abouei, V., Saghafian, H., Kheirandish, Sh.: Dry sliding oxidative wear in plain carbon dual phase steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 14, 43–48 (2007)
Quinn, T.F.J., Sullivan, J.L., Rowson, D.M.: Developments in the oxidational theory of mild wear. Tribol. Int. 13, 153–158 (1980)
Wilson, J.E., Stott, F.H., Wood, G.C.: The development of wear protective oxides and their influence on sliding friction. Proc. R. Soc. 369A, 557–574 (1980)
Barrau, O., Boher, C.: Analysis of the friction and wear behaviour of hot work tool steel for forging. Wear 255, 1444–1454 (2003)
Garza-Montes-de-Oca, N.F., Rainforth, W.M.: Wear mechanisms experienced by a work roll grade high speed under different environmental condition. Wear 267, 441–448 (2009)
Inman, I.A., Datta, S., Du, H.L., Burnell-Gray, J.S., Luo, Q.: Microscopy of glazed layers formed during high-temperature sliding wear at 750°C. Wear 254, 461–467 (2003)
Sullivan, J.L., Athwal, S.S.: Mild wear of a low alloy steel at temperatures up to 500°C. Tribol. Int. 16, 123–131 (1983)
Childs, T.H.C.: The sliding wear mechanisms of metals, mainly steels. Tribol. Int. 13, 285–293 (1980)
Quinn, T.F.J., Winer, W.O.: The thermal aspects of oxidational wear. Wear 102, 67–80 (1985)
Cui, X.H., Wang, S.Q., Wang, F., Chen, K.M.: Research on oxidative wear mechanism of the cast steels. Wear 265, 468–476 (2008)
Wang, S.Q., Wei, M.X., Wang, F., Cui, X.H., Dong, C.: Transition of mild wear to severe wear in oxidative wear of H21 steel. Tribol. Lett. 32, 67–72 (2008)
Hong, Hyun.-Soo.: The role of atmospheres and lubricant in the oxidational wear of metals. Tribol. Int. 35, 725–729 (2002)
Rainforth, W.M., Leonard, A.J., Perrin, C., Bedolla-Jacuinde, A., Wang, Y., Jones, H., Luo, Q.: High-resolution observations of friction-induced oxide and its interaction with the worn surface. Tribol. Int. 35, 731–748 (2002)
Acknowledgments
Financial support of our work by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51071078) and the Natural Science Fund of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2009221) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, M.X., Chen, K.M., Wang, S.Q. et al. Analysis for Wear Behaviors of Oxidative Wear. Tribol Lett 42, 1–7 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9741-y