Abstract
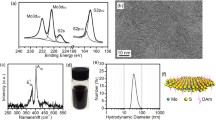
Using a new quartz-made reactor, large amounts of fullerene-like (IF) MoS2 nanoparticles were synthesized by reacting MoO3 vapor with H2S in a reducing atmosphere. The nanoparticles were found to be of high crystalline order; with an average size of 70 nm and consist of more than 30 closed shells. Extensive tribological testing of the nanoparticles in two types of synthetic oils- poly-alpha olefins (PAO)- was carried out and compared to that of bulk (2H platelets) MoS2 and IF-WS2. These tests indicated that under high pressure and relatively low humidity, the IF-MoS2 exhibited a friction coefficient as low as 0.03 and the smallest wear rate of the measured systems. However, its performance was found to be lower in comparison to IF-WS2 after 2500 cycles, due probably to its inferior chemical stability. This study indicates that the tribological performance of the IF nanoparticles depends strongly on their crystalline order and size.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldman, Y., Wasserman, E., Srolovitz, D.J., Tenne, R.: High rate, gas phase growth of MoS2 nested inorganic fullerenes and nanotubes. Science 267, 222–225 (1995)
Zak, A., Feldman, Y., Alperovich, V., Rosentsveig, R., Tenne, R.: Growth mechanism of MoS2 fullerene-like nanoparticles by the gas phase synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 11108–11116 (2000)
Jose-Yacaman, M., Lopez, H., Santiago, P., Galvan, D.H., Garzon, I.L., Reyes, A.: Studies of MoS2 structures produced by electron irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 1065–1067 (1996)
Remskar, M., Mrzel, A., Skraba, Z., Jesih, A., Ceh, M., Demsar, J., Stadelmann, P., Levy, F., Mihailovic, D.: Self-assembly of subnanometer-diameter single-wall MoS2 nanotubes. Science 292, 479–481 (2001)
Hsu, W.K., Chang, B.H., Zhu, Y.Q., Han, W.Q., Terrones, T., Terrones, M., Grobert, N., Cheetham, A.K., Kroto, H.W., Walton, D.R.M.: An alternative route to molybdenum disulfide nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 10155–10158 (2000)
Etzkorn, J., Therese, H.A., Rocker, F.N., Zink U., Kolb, U., Tremel, W.: MOCVD: synthesis of hollow inorganic fullerene-type MoS2 and MoSe2. Adv. Mater. 17, 2372–2375 (2005)
Tian, Y., He, Y., Zhu, Y.: Low temperature synthesis and characterization of molybdenum disulfide nanotubes and nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 87, 87–90 (2004)
Chhowalla, M., Amaratunga, G.A.J.: Thin films of fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles with ultra-low friction and wear. Nature 407, 164–167 (2000)
Parilla, P.A., Dillon, A.C., Jones, K.M., Riker, G., Schulz, D.L., Ginley, D.S., Heben, M.J.: The first true inorganic fullerenes? Nature 397, 114 (1999)
Enyashin, A.N., Gemming, S., Bar-Sadan, M., Popovitz-Biro, R., Hong, S.Y., Prior, Y., Tenne, R., Seifert, G.: Structure and stability of molybdenum sulfide fullerenes. Angew. Chem. Intl. Ed. 46, 623–627 (2007)
Feldman, Y., Frey, G.L., Homyonfer, M., Lyakhovitskaya, V., Margulis, L., Cohen, H., Hodes, G., Hutchison, J.L., Tenne, R.: Bulk synthesis of inorganic fullerene-like MS2 (M = Mo, W) from the respective trioxides and the reaction mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 5362–5367 (1996)
Rosentsveig, R., Margolin, A., Gorodnev, A., Popovitz-Biro, R., Feldman, Y., Rapoport, L., Naveh, G., Tenne, R.: Synthesis of fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles and their tribological behavior. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 4368–4374 (2009)
Naffakh, M., Martin, Z., Fanegas, N., Marco, C., Gomez, M.A., Jimenez, I.: Influence of inorganic fullerene-like WS2 nanoparticles on the thermal behavior of isotactic polypropylene. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 45, 2309–2321 (2007)
Naffakh, M., Marco, C., Gomez, M.A., Jimenez, I.: Unique isothermal crystallization behavior of novel polyphenylene sulfide/inorganic fullerene-like WS2 nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 14819–14828 (2008)
Buchman, A., Dodiuk-Kenig, H., Dotan, A., Tenne, R., Kenig, S.: Toughening of epoxy adhesives by nanoparticles. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 23, 753–768 (2009)
Feldman, Y., Zak, A., Popovitz-Biro, R., Tenne, R.: New reactor for production of tungsten disulfide onion-like (inorganic fullerene-like) nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 2, 663–672 (2000)
Joly-Pottuz, L., Dassenoy, F., Belin, M., Vacher, B., Martin, J.M., Fleischer, N.: Ultralow-friction and wear properties of IF-WS2 under boundary lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 18, 477–485 (2005)
Rapoport, L., Bilik, Yu., Feldman, Y., Homyonfer, M., Cohen, S.R., Tenne, R.: Hollow nanoparticles of WS2 as potential solid-state lubricants. Nature 387, 791–793 (1997)
Rapoport, L., Feldman, Y., Homyonfer, M., Cohen, H., Sloan, J., Hutchison, J.L., Tenne, R.: Inorganic fullerene-like material as additives to lubricants: structure-function relationship. Wear 225–229, 975–982 (1999)
Cizaire, L., Vacher, B., Le-Mogne, T., Martin, J.M., Rapoport, L., Margolin, L., Tenne, R.: Mechanisms of ultra-low friction by hollow inorganic fullerene-like MoS2 nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 160, 282–287 (2002)
Mahalu, D., Peisach, M., Wold, A., Tenne, R.: Controlled photocorrosion of WSe2: influence of molecular oxygen. J. Phys. Chem. 94, 8012–8013 (1990)
Schuffenhauer, C., Wildermuth, G., Felsche, J., Tenne, R.: How stable are inorganic fullerene-like particles?–thermal analysis (STA) of inorganic fullerene-like NbS2, MoS2, and WS2 in oxidizing and inert atmosphere in comparison with the bulk material. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 6, 3991–4002 (2004)
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to Mr. Y. Novema for the difficult glass blowing work in producing these quartz reactors and to Dr. R. Popovitz-Biro for the HRTEM work. We are grateful to the support of the Harold L. Perlman Foundation; the Gurwin Fund, the Horowitz Foundation; the Irving and Cherna Moskowitz Center for Nano and Bio-Nano Imaging and “NanoMaterials Ltd”. RT is the director of the Helen and Martin Kimmel Center for Nanoscale Science and holds the Drake family Chair for Nanotechnology. He acknowledges the support of the ERC grant INTIF 226639 and the Israel Science Foundation. FD and JT thank the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosentsveig, R., Gorodnev, A., Feuerstein, N. et al. Fullerene-like MoS2 Nanoparticles and Their Tribological Behavior. Tribol Lett 36, 175–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9472-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9472-0