Abstract
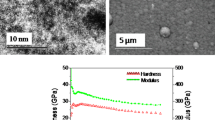
Nanoindentation and nanoscratch tests were performed for titanium nitride (TiN) coatings on different tool steel substrates to investigate the indentation/scratch induced deformation behavior of the coatings and the adhesion of the coating–substrate interfaces and their tribological property. In this work, TiN coatings with a thickness of about 500 nm were grown on GT35, 9Cr18 and 40CrNiMo steels using vacuum magnetic-filtering arc plasma deposition. In the nanoindentation tests, the hardness and modulus curves for TiN/GT35 reduced the slowest around the film thickness 500 nm with the increase of indentation depth, followed by TiN/9Cr18 and TiN/40CrNiMo. Improving adhesion properties of coating and substrate can decrease the differences of internal stress field. The scratch tests showed that the scratch response was controlled by plastic deformation in the substrate. The substrate plays an important role in determining the mechanical properties and wear resistance of such coatings. TiN/GT35 exhibited the best load-carrying capacity and scratch/wear resistance. As a consequence, GT35 is the best substrate for TiN coatings of the substrate materials tested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Quaeyhaegens, J. D'Haen, L. M. Stals, et al., Surf. Coat. and Technol. 61 (1993) 227.
K. Xu, J. Chen, R. Gao and J. He, Surf. Coat. and Technol. 58 (1993) 37.
M. G. Hocking, V. Vasantasree, P. S. Sidky, Metallic and Ceramic Coatings: Production, High Temperature Properties and Applications (Wiley, New York, 1989) 86.
J. H. Huang, Y. P. Tsai and G. P. Yu, Thin Solid Films 355/356 (1999) 440.
J. C. Knight, T. F. Page and I. M. Hutchings, Thin Solid Films 177 (1989) 117.
S. V. Hainsworth and W. C. Soh, Surf. Coat. Technol. 163/163 (2003) 515.
W. C. Oliver and G. M. Pharr, J. Mat. Res. 7 (1992) 1564.
C. Charitidis, Y. Panayiotatos and S. Logothetidis, Diam. Rel. Mat. 12 (2003) 1088.
K. W. Lee, Y.-W. Chung, C. Y. Chan, I. Bello, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 168 (2003) 57.
N. R. Moody, A. Strojny, D. L. Medlin, et al., J. Mat. Res. 14 (1999) 2306.
B. Bhushan, Handbook of Micro/Nanotribology, 2nd ed. (Boca Raton, CRC Press, 1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Huan, Y. Substrate Effects on the Micro/Nanomechanical Properties of TiN Coatings. Tribology Letters 17, 911–916 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8099-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8099-4