Abstract
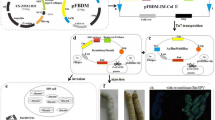
Fibrinogen from human blood is used as a main component of coagulants, including surgical tissue sealants. The development of a recombinant human fibrinogen (rFib) is anticipated to eliminate the risks of blood-borne infections. Here, we report the efficient production of rFib in a transgenic silkworm system. A silkworm line carrying cDNAs of the fibrinogen Aα and γ chains (Aα/γ-silkworm) produced Aα and γ chains in its cocoons, however, the Bβ chains were not detected from cocoons of another silkworm line carrying the cDNA of fibrinogen Bβ chains (Bβ-silkworm). A silkworm line for all three fibrinogen chains was generated by crossing Aα/γ-silkworms with Bβ-silkworms, which secreted Aα2Bβ2γ2 fibrinogen (rFib) into cocoons at high contents. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of the three rFib chains were identical to those of the corresponding chains of native fibrinogen (nFib). The N-glycan profile of the rFib comprised oligomannose-type (53%), complex-type (34%), and paucimannose-type (13%); neither high-mannose-type (six or more mannose residues) nor core-fucosylated glycans were observed. The coagulation activity of the rFib was evaluated for the amount of thrombin-released fibrinopeptide A (FpA) and the kinetics for turbidity increase (non-covalent network formation) in the solution. FpA release rates were equivalent between rFib and nFib; by contrast, the kinetics of the turbidity increase for rFib were accelerated nearly two-fold, for both the rate and maximum value, compared to those of nFib. These results demonstrate that the rFib produced in the transgenic silkworm system is comparable to nFib in both physical and coagulative properties. This rFib is a promising candidate component for safe hemostatic pharmaceuticals.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Wang X, Murata T, Obara M, Akutsu H, Machida M, Umezawa A, Tomita M (2010) Production of a non-triple helical collagen alpha chain in transgenic silkworms and its evaluation as a gelatin substitute for cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 106:860–870
Adamczyk B, Struwe WB, Ercan A, Nigrovic PA, Rudd PM (2013) Characterization of fibrinogen glycosylation and its importance for serum/plasma N-glycome analysis. J Proteome Res 12:444–454
Alving BM, Chung SI, Murano G, Tang DB, Finlayson JS (1982) Rabbit fibrinogen: time course of constituent chain production in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys 217:1–9
Bole DG, Hendershot LM, Kearney JF (1986) Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol 102:1558–1566
Calcaterra J, Van Cott KE, Butler SP, Gil GC, Germano M, van Veen HA, Nelson K, Forsberg EJ, Carlson MA, Velander WH (2013) Recombinant human fibrinogen that produces thick fibrin fibers with increased wound adhesion and clot density. Biomacromolecules 14:169–178
Cederbaum SD, Fareed GC, Lovett MA, Shapiro LJ (1984) Recombinant DNA in medicine. West J Med 141:210–222
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology (N Y) 11:905–910
de Moerloose P, Casini A, Neerman-Arbez M (2013) Congenital fibrinogen disorders: an update. Semin Thromb Hemost 39:585–595
Farrell DH, Huang S, Davie EW (1993) Processing of the carboxyl 15-amino acid extension in the alpha-chain of fibrinogen. J Biol Chem 268:10351–10355
Hartwig R, Danishefsky KJ (1991) Studies on the assembly and secretion of fibrinogen. J Biol Chem 266:6578–6585
Hendershot L, Bole D, Köhler G, Kearney JF (1987) Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate posttranslationally with immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein. J Cell Biol 104:761–767
Hino M, Ishiko O, Honda KI, Yamane T, Ohta K, Takubo T, Tatsumi N (2000) Transmission of symptomatic parvovirus B19 infection by fibrin sealant used during surgery. Br J Haematol 108:194–195
Hirashima M, Imamura T, Yano K, Kawamura R, Meta A, Tokieda Y, Nakashima T (2016) High-level expression and preparation of recombinant human fibrinogen as biopharmaceuticals. J Biochem 159:261–270
Hou Y, Xia Q, Zhao P, Zou Y, Liu H, Guan J, Gong J, Xiang Z (2007) Studies on middle and posterior silk glands of silkworm (Bombyx mori) using two-dimensional electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 37:486–496
Iizuka M, Tomita M, Shimizu K, Kikuchi Y, Yoshizato K (2008) Translational enhancement of recombinant protein synthesis in transgenic silkworms by a 5′-untranslated region of polyhedrin gene of Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus. J Biosci Bioeng 105:595–603
Iizuka M, Ogawa S, Takeuchi A, Nakakita S, Kubo Y, Miyawaki Y, Hirabayashi J, Tomita M (2009) Production of a recombinant mouse monoclonal antibody in transgenic silkworm cocoons. FEBS J 276:5806–5820
Kubelka V, Altmann F, Kornfeld G, März L (1994) Structures of the N-linked oligosaccharides of the membrane glycoproteins from three lepidopteran cell lines (Sf-21, IZD-Mb-0503, Bm-N). Arch Biochem Biophys 308:148–157
Kulakosky PC, Hughes PR, Wood HA (1998) N-linked glycosylation of a baculovirus-expressed recombinant glycoprotein in insect larvae and tissue culture cells. Glycobiology 8:741–745
Lalonde ME, Durocher Y (2017) Therapeutic glycoprotein production in mammalian cells. J Biotechnol 251:128–140
Langer BG, Weisel JW, Dinauer PA, Nagaswami C, Bell WR (1988) Deglycosylation of fibrinogen accelerates polymerization and increases lateral aggregation of fibrin fibers. J Biol Chem 263:15056–15063
Luan YT (2008) Abstr. In: Cell culture engineering XI, p 61
Minagawa S, Sekiguchi S, Nakaso Y, Tomita M, Takahisa M, Yasuda H (2015) Identification of core alpha 1,3-Fucosyltransferase gene from silkworm: an insect popularly used to express mammalian proteins. J Insect Sci (Online) 15:110
Minagawa S, Nakaso Y, Tomita M, Igarashi T, Miura Y, Yasuda H, Sekiguchi S (2018) Novel recombinant feline interferon carrying N-glycans with reduced allergy risk produced by a transgenic silkworm system. BMC Vet Res 14:260
Mosesson MW, Siebenlist KR, Meh DA (2001) The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann NY Acad Sci 936:11–30
Murthy SN, Wilson J, Guy SL, Lorand L (1991) Intramolecular crosslinking of monomeric fibrinogen by tissue transglutaminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10601–10604
Nakagawa H, Kawamura Y, Kato K, Shimada I, Arata Y, Takahashi N (1995) Identification of neutral and sialyl N-linked oligosaccharide structures from human serum glycoproteins using three kinds of high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 226:130–138
Ogawa S, Tomita M, Shimizu K, Yoshizato K (2007) Generation of a transgenic silkworm that secretes recombinant proteins in the sericin layer of cocoon: production of recombinant human serum albumin. J Biotechnol 128:531–544
Piechocka IK, Kurniawan NA, Grimbergen J, Koopman J, Koenderink GH (2017) Recombinant fibrinogen reveals the differential roles of alpha- and gamma-chain cross-linking and molecular heterogeneity in fibrin clot strain-stiffening. J Thromb Haemost 15:938–949
Prunkard D, Cottingham I, Garner I, Bruce S, Dalrymple M, Lasser G, Bishop P, Foster D (1996) High-level expression of recombinant human fibrinogen in the milk of transgenic mice. Nat Biotechnol 14:867–871
Roy SN, Procyk R, Kudryk BJ, Redman CM (1991) Assembly and secretion of recombinant human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem 266:4758–4763
Spotnitz WD (2014) Fibrin sealant: the only approved hemostat, sealant, and adhesive—a laboratory and clinical perspective. ISRN Surg 2014:203943
Tada M, Tatematsu K, Ishii-Watabe A, Harazono A, Takakura D, Hashii N, Sezutsu H, Kawasaki N (2015) Characterization of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody produced by transgenic silkworms (Bombyx mori). MAbs 7:1138–1150
Tamura T, Thibert C, Royer C, Kanda T, Abraham E, Kamba M, Komoto N, Thomas JL, Mauchamp B, Chavancy G, Shirk P, Fraser M, Prudhomme JC, Couble P (2000) Germline transformation of the silkworm Bombyx mori L. using a piggyBac transposon-derived vector. Nat Biotechnol 18:81–84
Tojo N, Miyagi I, Miura M, Ohi H (2008) Recombinant human fibrinogen expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris was assembled and biologically active. Protein Expr Purif 59:289–296
Tomita M (2011) Transgenic silkworms that weave recombinant proteins into silk cocoons. Biotechnol Lett 33:645–654
Tomita M, Munetsuna H, Sato T, Adachi T, Hino R, Hayashi M, Shimizu K, Nakamura N, Tamura T, Yoshizato K (2003) Transgenic silkworms produce recombinant human type III procollagen in cocoons. Nat Biotechnol 21:52–56
Tomita M, Hino R, Ogawa S, Iizuka M, Adachi T, Shimizu K, Sotoshiro H, Yoshizato K (2007) A germline transgenic silkworm that secretes recombinant proteins in the sericin layer of cocoon. Transgenic Res 16:449–465
Townsend RR, Hilliker E, Li YT, Laine RA, Bell WR, Lee YC (1982) Carbohydrate structure of human fibrinogen. Use of 300-MHz 1H-NMR to characterize glycosidase-treated glycopeptides. J Biol Chem 257:9704–9710
Tretter V, Altmann F, Kubelka V, März L, Becker WM (1993) Fucose alpha 1,3-linked to the core region of glycoprotein N-glycans creates an important epitope for IgE from honeybee venom allergic individuals. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 102:259–266
Usami A, Suzuki T, Nagaya H, Kaki H, Ishiyama S (2010) Silkworm as a host of baculovirus expression. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 11:246–250
Weisel JW (2005) Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv Protein Chem 70:247–299
Yagi H, Yamamoto M, Yu SY, Takahashi N, Khoo KH, Lee YC, Kato K (2010) N-Glycosylation profiling of turtle egg yolk: expression of galabiose structure. Carbohydr Res 345:442–448
Yu S, Sher B, Kudryk B, Redman CM (1984) Fibrinogen precursors. Order of assembly of fibrinogen chains. J Biol Chem 259:10574–10581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minagawa, S., Sekiguchi, S., Nakaso, Y. et al. Production of a correctly assembled fibrinogen using transgenic silkworms. Transgenic Res 29, 339–353 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-020-00202-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-020-00202-1