Abstract
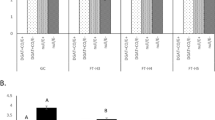
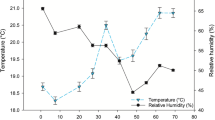
Alkaloid concentration of perennial ryegrass herbage is affected by endophyte strain and host plant genotype. However, previous studies suggest that associations between host and endophyte also depends on environmental conditions, especially those affecting nutrient reserves and that water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) concentration of perennial ryegrass plants may influence grass-endophyte associations. In this study a single transgenic event, with altered expression of fructosyltransferase genes to produce high WSC and biomass, has been crossed into a range of cultivar backgrounds with varying Epichloë endophyte strains. The effect of the association between the transgenic trait and alkaloid production was assessed and compared with transgene free control populations. In the vast-majority of comparisons there was no significant difference between alkaloid concentrations of transgenic and non-transgenic plants within the same cultivar and endophyte backgrounds. There was no significant difference between GOI+ (gene of interest positive) and GOI− (gene of interest negative) populations in Janthritrem response. Peramine concentration was not different between GOI+ and GOI− for 10 of the 12 endophytes-cultivar combinations. Cultivar Trojan infected with NEA6 and Alto with SE (standard endophyte) exhibited higher peramine and lolitrem B (only for Alto SE) concentration, in the control GOI− compared with GOI+. Similarly, cultivar Trojan infected with NEA6 and Alto with NEA3 presented higher ergovaline concentration in GOI−. Differences in alkaloid concentration may be attributable to an indirect effect in the modulation of fungal biomass. These results conclude that the presence of this transgenic insertion, does not alter the risk (toxicity) of the endophyte–grass associations. Endophyte–host interactions are complex and further research into associations with high WSC plant should be performed in a case by case basis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacon CW (1993) Abiotic stress tolerances (moisture, nutrients) and photosynthesis in endophyte-infected tall fescue. Agr Ecosyst Environ 44(1–4):123–141
Badenhorst PE (2014) Phenomic Evaluation and molecular breeding of field-grown transgenic perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) with altered fructan biosynthesis. PhD thesis, La Trobe University, Australia
Badenhorst PE, Smith KF, Spangenberg G (2016) Development of a molecular breeding strategy for the integration of transgenic traits in outcrossing perennial grasses. Agronomy 6(4):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy6040056
Badenhorst PE, Panter S, Palanisamy R, Georges S, Smith KF, Mouradov A, Mason J, Spangenberg GC (2018) Molecular breeding of transgenic perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) with altered fructan biosynthesis through the expression of fructosyltransferases. Mol Breed 38:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0776-3
Blankenship JD, Spiering MJ, Wilkinson HH, Fannin FF, Bush LP, Schardl CL (2001) Production of loline alkaloids by the grass endophyte, Neotyphodium uncinatum, in defined media. Phytochemistry 58:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(01)00272-2
Bultman TL, Bell GD (2003) Interaction between fungal endophytes and environmental stressors influences plant resistance to insects. Oikos 103(1):182–190
Chen A, Bryant RH, Edwards GR (2017) Milk production and composition of dairy cows grazing two perennial ryegrass cultivars allocated in the morning and afternoon. Anim Prod Sci 57:1507–1511
Ekanayake PN, Kaur J, Tian P, Rochfort SJ, Guthridge KM, Sawbridge TI, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2017) Genomic and metabolic characterisation of alkaloid biosynthesis by asexual Epichloë fungal endophytes of tall fescue pasture grasses. Genome 60(6):496–509
Faville MJ, Richardson K, Gagic M, Mace W, Sun XZ, Harrison S, Knapp K, Jahufer MZZ, Palanisamy R, Pirlo S, Johnson R (2010) Genetic improvement of fibre traits in perennial ryegrass. Proc N Z Grassl Assoc 72:71–78
Guerre P (2015) Ergot alkaloids produced by endophytic fungi of the genus Epichloë. Toxins 7(3):773–790
Guerre P (2016) Lolitrem B and indole diterpene alkaloids produced by endophytic fungi of the genus Epichloë and their toxic effects in livestock. Toxins 8(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8020047
Hennessy LM, Popay AJ, Finch SC, Clearwater MJ, Cave VM (2016) Temperature and plant genotype alter alkaloid concentrations in ryegrass infected with an Epichloë endophyte and this affects an insect herbivore. Front Plant Sci 7:1097. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01097
Humphreys MO (1989a) Water-soluble carbohydrates in perennial ryegrass breeding. I. Genetic differences among cultivars and hybrid progeny grown as spaced plants. Grass Forage Sci 44:231–236
Humphreys MO (1989b) Water-soluble carbohydrates in perennial ryegrass breeding. II. Cultivar and hybrid progeny performance in cut plots. Grass Forage Sci 44:237–244
Humphreys MO (1989c) Water-soluble carbohydrates in perennial ryegrass breeding. III. Relationships with herbage production, digestibility and crude protein content. Grass Forage Sci 44:423–430
Kaur T, Singh B, Kaur A, Kaur S (2015) Endophyte-mediated interactions between cauliflower, the herbivore Spodoptera litura, and the ectoparasitoid Bracon hebetor. Oecologia 179(2):487–494
Lane GA, Tapper BA, Davies E, Hume DE, Latch GCM, Barker DJ, Easton HS, Rolston MP (1997) Effect of growth conditions on alkaloid concentrations in perennial ryegrass naturally infected with endophyte. In: Bacon CW, Hill AC (eds) Neotyphodium/grass interactions. Plenum Press, New York, pp 179–182
Leuchtmann A, Bacon CW, Schardl CL, White JF Jr, Tadych M (2014) Nomenclatural realignment of Neotyphodium species with genus Epichloë. Mycologia 106:202–215. https://doi.org/10.3852/13-251
Liu Q, Parsons AJ, Xue H, Fraser K, Ryan GD, Newman JA, Rasmussen S (2011) Competition between foliar Neotyphodium lolii endophytes and mycorrhizal Glomus spp. fungi in Lolium perenne depends on resource supply and host carbohydrate content. Funct Ecol 25:910–920
Ludemann CL, Cullen BR, Malcolm B, Smith KF (2013) Economic values of changes in energy concentration of pasture in contrasting temperate dairy regions in Australia. Aust Farm Bus Manag J 10:1–15
Ludemann CI, Eckard RJ, Cullen BR, Jacobs JL, Malcolm B, Smith KF (2015) Higher energy concentration traits in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) may increase profitability and improve energy conversion on dairy farms. Agric Syst 137:89–100
Miller LA, Moorby JM, Davies DR, Humphreys MO, Scollan ND, MacRae JC, Theodorou MK (2001) Increased concentration of water-soluble carbohydrate in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.): milk production from late-lactation dairy cows. Grass Forage Sci 56(4):383–394
Nicol AM, Klotz JL (2016) Ergovaline, an endophytic alkaloid. 2. Intake and impact on animal production, with reference to New Zealand. Anim Prod Sci 56(11):1775–1786
Panter S, Mouradov A, Badenhorst P, Martelotto L, Griffith M, Smith KF, Spangenberg G (2017) Re-programming photosynthetic cells of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L) for fructan biosynthesis through transgenic expression of fructan biosynthetic genes under the control of photosynthetic promoters. Agronomy 7(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy7020036
Popay AJ, Hume DE, Davis KL, Tapper BA (2003) Interactions between endophyte (Neotyphodium spp.) and ploidy in hybrid and perennial ryegrass cultivars and their effects on Argentine stem weevil (Listronotus bonariensis). N Z J Agric Res 46:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2003.9513559
Rasmussen S, Parsons AJ, Bassett S, Christensen MJ, Hume DE, Johnson LJ, Johnson RD, Simpson WR, Stacke C, Voisey CR, Xue H (2007) High nitrogen supply and carbohydrate content reduce fungal endophyte and alkaloid concentration in Lolium perenne. N Phytol 173(4):787–797
Rasmussen S, Parsons AJ, Fraser K, Xue H, Newman JA (2008) Metabolic profiles of Lolium perenne are differentially affected by nitrogen supply, carbohydrate content, and fungal endophyte infection. Plant Physiol 146(3):1440–1453
Rasmussen S, Parsons AJ, Xue H, Liu Q, Jones CS, Ryan GD, Newman JA (2014) Transcript profiling of fructan biosynthetic pathway genes reveals association of a specific fructosyltransferase isoform with the high sugar trait in Lolium perenne. J Plant Physiol 171:475–485
Robins JG, Lovatt AJ (2016) Cultivar by environment effects of perennial ryegrass cultivars selected for high water soluble carbohydrates managed under differing precipitation regimes. Euphytica 208:571–581
Ryan GD, Rasmussen S, Parsons AJ, Newman JA (2015) The effects of carbohydrate supply and host genetic background on Epichloë endophyte and alkaloid concentrations in perennial ryegrass. Fungal Ecology 18:115–125
Smith KF, Reed KFM, Foot JZ (1997) An assessment of the relative importance of specific traits for the genetic improvement of nutritive value in dairy pasture. Grass Forage Sci 52:167–175
Smith KF, Kearney GA, Culvenor RA (1998a) The use of repeated measurements analysis for the evaluation of seasonal variation in the dry matter yield and nutritive value of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) cultivars. Aust J Exp Agric 38:145–154
Smith KF, Simpson RJ, Oram RN, Lowe KF, Kelly KB, Evans PM, Humphreys MO (1998b) Seasonal variation in the herbage yield and nutritive value of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) cultivars with high or normal herbage water-soluble carbohydrate concentrations grown in three contrasting Australian dairy environments. Aust J Exp Agric 38:821–830
Smith KF, Stewart A, Spangenberg G (2007) Breeding high energy grasses for Australia and New Zealand. N Z Grassl Assoc 69:173–177
Tanaka A, Christensen MJ, Takemoto D, Park P, Scott B (2006) Reactive oxygen species play a role in regulating a fungus–perennial ryegrass mutualistic interaction. Plant Cell 18(4):1052–1066
Turner LR, Donaghy DJ, Pembleton KG, Rawnsley RP (2015) Longer defoliation interval ensures expression of the ‘high sugar’ trait in perennial ryegrass cultivars in cool temperate Tasmania, Australia. J Agric Sci 153:995–1005
van Zijll de Jong E, Dobrowolski MP, Bannan NR, Stewart AV, Smith KF, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2008a) Global genetic diversity of the perennial ryegrass fungal endophyte Neotyphodium lolii. Crop Sci 48(4):1487–1501
van Zijll de Jong E, Dobrowolski MP, Sandford A, Smith KF, Willocks MJ, Spangenberg GC, Forster JW (2008b) Detection and characterisation of novel fungal endophyte genotypic variation in cultivars of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Aust J Agric Res 59(3):214–221
Wiewióra B, Żurek G, Pańka D (2015) Is the vertical transmission of Neotyphodium lolii in perennial ryegrass the only possible way to the spread of endophytes? PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117231
Winichayakul S, Cookson R, Scott R, Zhou J, Zou X, Roldan M, Richardson K, Roberts N (2008) Delivery of grasses with high levels of unsaturated, protected fatty acids. Proc N Z Grassl Assoc 70:211–216
Winichayakul S, Scott RW, Roldan M, Hatier JHB, Livingston S, Cookson R, Curran AC, Roberts NJ (2013) In vivo packaging of triacylglycerols enhances Arabidopsis leaf biomass and energy density. Plant Physiol 162(2):626–639
Yamada T, Forster JW, Humphreys MW, Takamizo T (2005) Genetics and molecular breeding in Lolium/Festuca grass species complex. Grassl Sci 51(2):89–106
Acknowledgements
The research described here was funded by the Victorian Department of Economic Development, Jobs, Transport and Resources (DEDJTR). The authors would like to thank the Molecular Genomics, Molecular Phenomics and Molecular Plant Breeding teams for their support collecting and processing samples. Specially, Mr. Aaron Elkins and Mrs Michelle Drayton for their assistance analysing alkaloid concentrations and endophyte infection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraldo, P.A., Elliott, C., Badenhorst, P. et al. Evaluation of endophyte toxin production and its interaction with transgenic perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) with altered expression of fructosyltransferases. Transgenic Res 27, 397–407 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-018-0087-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-018-0087-9