Abstract
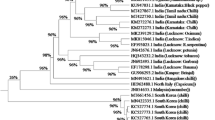
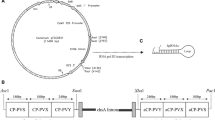
RNA interference (RNAi) is commonly used to produce virus tolerant transgenic plants. The objective of the current study was to generate transgenic sugarcane plants expressing a short hairpin RNAs (shRNA) targeting the coat protein (CP) gene of sugarcane mosaic virus (SCMV). Based on multiple sequence alignment, including genomic sequences of four SCMV strains, a conserved region of ~ 456 bp coat protein (CP) gene was selected as target gene and amplified through polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Subsequently, siRNAs2 and siRNA4 were engineered as stable short hairpin (shRNA) transgenes of 110 bp with stem and loop sequences derived from microRNA (sof-MIR168a; an active regulatory miRNA in sugarcane). These transgenes were cloned in independent RNAi constructs under the control of the polyubiquitin promoter. The RNAi constructs were delivered into two sugarcane cultivars ‘SPF-234 and NSG-311 in independent experiments using particle bombardment. Molecular identification through PCR and Southern blot revealed anti-SCMV positive transgenic lines. Upon mechanical inoculation of transgenic and non-transgenic sugarcane lines with SCMV, the degree of resistance was found variable among the two sugarcane cultivars. For sugarcane cultivar NSG-311, the mRNA expression of the CP–SCMV was reduced to 10% in shRNA2-transgenic lines and 80% in shRNA4-transgenic lines. In sugarcane cultivar SPF-234, the mRNA expression of the CP–SCMV was reduced to 20% in shRNA2-transgenic lines and 90% in shRNA4 transgenic lines, revealing that transgenic plants expressing shRNA4 were almost immune to SCMV infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar S (2005) Impact of sugarcane disease on cane and sugar yield. In: Proceedings of the 3rd agricultural biotechnology workshop
Atreya PL, Atreya CD, Pirone TP (1991) Amino acid substitutions in the coat protein result in loss of insect transmissibility of a plant virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88(17):7887–7891
Basnayake SW, Moyle R, Birch RG (2011) Embryogenic callus proliferation and regeneration conditions for genetic transformation of diverse sugarcane cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 30(3):439–448
Bukovinszky T, Gols R, Hemerik L, Van Lenteren JC, Vet LE (2007) Time allocation of a parasitoid foraging in heterogeneous vegetation: implications for host–parasitoid interactions. J Anim Ecol 76(5):845–853
Bull T, Glasziou K (1963) The evolutionary significance of sugar accumulation in Saccharum. Aust J Biol Sci 16(4):737–742
Chung BY, Miller WA, Atkins JF, Firth AE (2008) An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(15):5897–5902
Dolja V, Haldeman R, Robertson N, Dougherty W, Carrington J (1994) Distinct functions of capsid protein in assembly and movement of tobacco etch potyvirus in plants. EMBO J 13(6):1482
Duan C-G, Wang C-H, Guo H-S (2012) Application of RNA silencing to plant disease resistance. Silence 3(1):5
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T (2001) Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411(6836):494–498
Frizzi A, Huang S (2010) Tapping RNA silencing pathways for plant biotechnology. Plant Biotechnol J 8(6):655–677
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998) Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 19:806–811
Gargouri-Bouzid R, Jaoua L, Mansour RB, Yemna H, Malika A, Radhouane E (2005) PVY resistant transgenic potato plants (cv Claustar) expressing the viral coat protein. J Plant Biotechnol 7(3):1–6
Guo J, Gao S, Lin Q, Wang H, Que Y, Xu L (2015) Transgenic sugarcane resistant to Sorghum mosaic virus based on coat protein gene silencing by RNA interference. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/861907
Hammond SM, Bernstein E, Beach D, Hannon GJ (2000) An RNA-directed nuclease mediates post-transcriptional gene silencing in Drosophila cells. Nature 404(6775):293–296
Hirai MY, Sugiyama K, Sawada Y, Tohge T, Obayashi T, Suzuki A, Araki R, Sakurai N, Suzuki H, Aoki K (2007) Omics-based identification of Arabidopsis Myb transcription factors regulating aliphatic glucosinolate biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(15):6478–6483
Joung YH, Kamo K (2006) Expression of a polyubiquitin promoter isolated from Gladiolus. Plant Cell Rep 25(10):1081–1088
Kalantidis K, Psaradakis S, Tabler M, Tsagris M (2002) The occurrence of CMV-specific short RNAs in transgenic tobacco expressing virus-derived double-stranded RNA is indicative of resistance to the virus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15(8):826–833
Li Y, Liu R, Zhou T, Fan Z (2013) Genetic diversity and population structure of sugarcane mosaic virus. Virus Res 171(1):242–246
Lu PY, Xie F, Woodle MC (2005) In vivo application of RNA interference: from functional genomics to therapeutics. Adv Genet 54:115–142
Nasir IA, Tabassum B, Qamar Z, Javed MA, Tariq M, Farooq AM, Butt SJ, Qayyum A, Husnain T (2014) Herbicide-tolerant sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) plants: an unconventional method of weed removal. Turk J Biol 38(4):439–449
Peláez P, Sanchez F (2013) Small RNAs in plant defense responses during viral and bacterial interactions: similarities and differences. Front Plant Sci 4:343
Pérez-Quintero ÁL, Neme R, Zapata A, López C (2010) Plant microRNAs and their role in defense against viruses: a bioinformatics approach. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):138
Rao AQ, Irfan M, Saleem Z, Nasir IA, Riazuddin S, Husnain T (2011) Overexpression of the phytochrome B gene from Arabidopsis thaliana increases plant growth and yield of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 12(4):326–334
Revers F, Le Gall O, Candresse T, Maule AJ (1999) New advances in understanding the molecular biology of plant/potyvirus interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12(5):367–376
Sharp PA (2001) RNA interference—2001. Genes Dev 15(5):485–490
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98(3):503IN3509–508IN5517
Tabassum B, Nasir IA, Husnain T (2011) Potato virus Y mRNA expression knockdown mediated by siRNAs in cultured mammalian cell line. Virol Sin 26(2):105–113
Tabassum B, Nasir IA, Khan A, Aslam U, Tariq M, Shahid N, Husnain T (2016) Short hairpin RNA engineering: in planta gene silencing of potato virus Y. Crop Prot 86:1–8
Urcuqui-Inchima S, Haenni A-L, Bernardi F (2001) Potyvirus proteins: a wealth of functions. Virus Res 74(1):157–175
Vijayapalani P, Maeshima M, Nagasaki-Takekuchi N, Miller WA (2012) Interaction of the trans-frame potyvirus protein P3N-PIPO with host protein PCaP1 facilitates potyvirus movement. PLoS Pathog 8(4):e1002639
Voinnet O (2002) RNA silencing: small RNAs as ubiquitous regulators of gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5(5):444–451
Wei T, Zhang C, Hong J, Xiong R, Kasschau KD, Zhou X, Carrington JC, Wang A (2010) Formation of complexes at plasmodesmata for potyvirus intercellular movement is mediated by the viral protein P3N-PIPO. PLoS Pathog 6(6):e1000962
Wolfe M, Baresel J, Desclaux D, Goldringer I, Hoad S, Kovacs G, Löschenberger F, Miedaner T, Østergård H, Van Bueren EL (2008) Developments in breeding cereals for organic agriculture. Euphytica 163(3):323
Xu H, Yao Y, Zhao Y, Smith LP, Baigent SJ, Nair V (2008) Analysis of the expression profiles of Marek’s disease virus-encoded microRNAs by real-time quantitative PCR. J Virol Methods 149(2):201–208
Yao W, Ruan M, Qin L, Yang C, Chen R, Chen B, Zhang M (2017) Field performance of transgenic sugarcane lines resistant to sugarcane mosaic virus. Front Plant Sci 8:104
Yu H, Kumar P (2003) Post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants by RNA. Plant Cell Rep 22(3):167–174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, U., Tabassum, B., Nasir, I.A. et al. A virus-derived short hairpin RNA confers resistance against sugarcane mosaic virus in transgenic sugarcane. Transgenic Res 27, 203–210 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-018-0066-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-018-0066-1