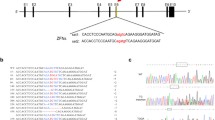
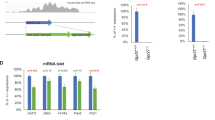
Abstract
Growth hormone (GH) is an anabolic mitogen with widespread influence on cellular growth and differentiation as well as on glucose and lipid metabolism. GH binding to the growth hormone receptor (GHR) on hepatocytes prompts expression of insulin growth factor I (IGF-1) involved in nutritionally induced compensatory hyperplasia of pancreatic β-cell islets and insulin release. A prolonged hyperactivity of the IGF-1/insulin axis in the face of insulinotropic nutrition, on the other hand, can lead to collapse of the pancreatic islets and glucose intolerance. Individuals with Laron syndrome carry mutations in the GHR gene resulting in severe congenital IGF-1 deficiency and elevated GH serum levels leading to short stature as well as perturbed lipid and glucose metabolism. However, these individuals enjoy a reduced prevalence of acne, cancer and possibly diabetes. Minipigs have become important biomedical models for human conditions due to similarities in organ anatomy, physiology, and metabolism relative to humans. The purpose of this study was to generate transgenic Wuzhishan minipigs by handmade cloning with impaired systemic GHR activity and assess their growth profile and glucose metabolism. Transgenic minipigs featuring overexpression of a dominant-negative porcine GHR (GHRdm) presented postnatal growth retardation and proportionate dwarfism. Molecular changes included elevated GH serum levels and mild hyperglycemia. We believe that this model may prove valuable in the study of GH functions in relation to cancer, diabetes and longevity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allevato G, Billestrup N, Goujon L, Galsgaard ED, Norstedt G, Postel-Vinay MC, Kelly PA, Nielsen JH (1995) Identification of phenylalanine 346 in the rat growth hormone receptor as being critical for ligand-mediated internalization and down-regulation. J Biol Chem 270(29):17210–17214
Amit T, Youdim MB, Hochberg Z (2000) Clinical review 112: Does serum growth hormone (GH) binding protein reflect human GH receptor function? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(3):927–932
Amselem S, Duquesnoy P, Duriez B, Dastot F, Sobrier ML, Valleix S, Goossens M (1993) Spectrum of growth hormone receptor mutations and associated haplotypes in Laron syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 2(4):355–359
Ayling RM, Ross R, Towner P, Von Laue S, Finidori J, Moutoussamy S, Buchanan CR, Clayton PE, Norman MR (1997) A dominant-negative mutation of the growth hormone receptor causes familial short stature. Nat Genet 16(1):13–14
Ayling RM, Ross RJ, Towner P, Von Laue S, Finidori J, Moutoussamy S, Buchanan CR, Clayton PE, Norman MR (1999) New growth hormone receptor exon 9 mutation causes genetic short stature. Acta Paediatr 88(428):168–172, discussion 173
Berryman DE, List EO, Coschigano KT, Behar K, Kim JK, Kopchick JJ (2004) Comparing adiposity profiles in three mouse models with altered GH signaling. Growth Horm IGF Res 14(4):309–318
Carter-Su C, King AP, Argetsinger LS, Smit LS, Vanderkuur J, Campbell GS (1996) Signalling pathway of GH. Endocr J 43(Suppl):S65–S70
Cioffi JA, Wang X, Kopchick JJ (1990) Porcine growth hormone receptor cDNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 18(21):6451
Colosi P, Wong K, Leong SR, Wood WI (1993) Mutational analysis of the intracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor. J Biol Chem 268(17):12617–12623
Cunningham BC, Ultsch M, De Vos AM, Mulkerrin MG, Clauser KR, Wells JA (1991) Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science 254(5033):821–825
Dominici FP, Diaz GA, Bartke A, Kopchick JJ, Turyn D (2000) Compensatory alterations of insulin signal transduction in liver of growth hormone receptor knockout mice. J Endocrinol 166(3):579–590
Dorer DR, Henikoff S (1994) Expansions of transgene repeats cause heterochromatin formation and gene silencing in Drosophila. Cell 77(7):993–1002
Estrada J, Sommer J, Collins B, Mir B, Martin A, York A, Petters RM, Piedrahita JA (2007) Swine generated by somatic cell nuclear transfer have increased incidence of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Cloning Stem Cells 9(2):229–236
Fain JN, Ihle JH, Bahouth SW (1999) Stimulation of lipolysis but not of leptin release by growth hormone is abolished in adipose tissue from Stat5a and b knockout mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263(1):201–205
Fan Y, Menon RK, Cohen P, Hwang D, Clemens T, DiGirolamo DJ, Kopchick JJ, Le Roith D, Trucco M, Sperling MA (2009) Liver-specific deletion of the growth hormone receptor reveals essential role of growth hormone signaling in hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem 284(30):19937–19944
Fang P, Riedl S, Amselem S, Pratt KL, Little BM, Haeusler G, Hwa V, Frisch H, Rosenfeld RG (2007) Primary growth hormone (GH) insensitivity and insulin-like growth factor deficiency caused by novel compound heterozygous mutations of the GH receptor gene: genetic and functional studies of simple and compound heterozygous states. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(6):2223–2231
Foxcroft GR, Dixon WT, Novak S, Putman CT, Town SC, Vinsky MD (2006) The biological basis for prenatal programming of postnatal performance in pigs. J Anim Sci 84(Suppl):E105–E112
Freemark M, Avril I, Fleenor D, Driscoll P, Petro A, Opara E, Kendall W, Oden J, Bridges S, Binart N et al (2002) Targeted deletion of the PRL receptor: effects on islet development, insulin production, and glucose tolerance. Endocrinology 143(4):1378–1385
Fukunaga R, Ishizaka-Ikeda E, Pan CX, Seto Y, Nagata S (1991) Functional domains of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. EMBO J 10(10):2855–2865
Godowski PJ, Leung DW, Meacham LR, Galgani JP, Hellmiss R, Keret R, Rotwein PS, Parks JS, Laron Z, Wood WI (1989) Characterization of the human growth hormone receptor gene and demonstration of a partial gene deletion in two patients with Laron-type dwarfism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(20):8083–8087
Goujon L, Allevato G, Simonin G, Paquereau L, Le Cam A, Clark J, Nielsen JH, Djiane J, Postel-Vinay MC, Edery M et al (1994) Cytoplasmic sequences of the growth hormone receptor necessary for signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(3):957–961
Guevara-Aguirre J, Balasubramanian P, Guevara-Aguirre M, Wei M, Madia F, Cheng CW, Hwang D, Martin-Montalvo A, Saavedra J, Ingles S et al (2011) Growth hormone receptor deficiency is associated with a major reduction in pro-aging signaling, cancer, and diabetes in humans. Sci Transl Med 3(70):70ra13
Handwerger S, Freemark M (2000) The roles of placental growth hormone and placental lactogen in the regulation of human fetal growth and development. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab JPEM 13(4):343–356
Hansen LH, Wang X, Kopchick JJ, Bouchelouche P, Nielsen JH, Galsgaard ED, Billestrup N (1996) Identification of tyrosine residues in the intracellular domain of the growth hormone receptor required for transcriptional signaling and Stat5 activation. J Biol Chem 271(21):12669–12673
Hiragami-Hamada K, Xie SQ, Saveliev A, Uribe-Lewis S, Pombo A, Festenstein R (2009) The molecular basis for stability of heterochromatin-mediated silencing in mammals. Epigenet Chromatin 2(1):14
Iida K, Takahashi Y, Kaji H, Takahashi MO, Okimura Y, Nose O, Abe H, Chihara K (1999) Functional characterization of truncated growth hormone (GH) receptor-(1-277) causing partial GH insensitivity syndrome with high GH-binding protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(3):1011–1016
Kenth G, Mergelas JA, Goodyer CG (2008) Developmental changes in the human GH receptor and its signal transduction pathways. J Endocrinol 198(1):71–82
Kitamura T, Ido Kitamura Y: (2007) Role of FoxO proteins in pancreatic beta cells. Endocr J 54(4):507–515
Laron Z (2004) Laron syndrome (primary growth hormone resistance or insensitivity): the personal experience 1958–2003. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(3):1031–1044
Laron Z, Pertzelan A, Mannheimer S (1966) Genetic pituitary dwarfism with high serum concentation of growth hormone—a new inborn error of metabolism? Isr J Med Sci 2(2):152–155
Leung DW, Spencer SA, Cachianes G, Hammonds RG, Collins C, Henzel WJ, Barnard R, Waters MJ, Wood WI (1987) Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature 330(6148):537–543
List EO, Sackmann-Sala L, Berryman DE, Funk K, Kelder B, Gosney ES, Okada S, Ding J, Cruz-Topete D, Kopchick JJ (2011) Endocrine parameters and phenotypes of the growth hormone receptor gene disrupted (GHR−/−) mouse. Endocr Rev 32(3):356–386
Liu JL, Coschigano KT, Robertson K, Lipsett M, Guo Y, Kopchick JJ, Kumar U, Liu YL (2004) Disruption of growth hormone receptor gene causes diminished pancreatic islet size and increased insulin sensitivity in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(3):E405–E413
Liu H, Li Y, Wei Q, Liu C, Bolund L, Vajta G, Dou H, Yang W, Xu Y, Luan J et al (2013) Development of transgenic minipigs with expression of antimorphic human cryptochrome 1. PLoS One 8(10):e76098
Melnik BC, John SM, Schmitz G (2011) Over-stimulation of insulin/IGF-1 signaling by western diet may promote diseases of civilization: lessons learnt from laron syndrome. Nutr Metab 8:41
Mercado M, DaVila N, McLeod JF, Baumann G (1994) Distribution of growth hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid containing and lacking exon 3 in human tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 78(3):731–735
Milman S, Atzmon G, Huffman DM, Wan J, Crandall JP, Cohen P, Barzilai N (2014) Low insulin-like growth factor-1 level predicts survival in humans with exceptional longevity. Aging Cell 13(4):769–771
Murakami M, Narazaki M, Hibi M, Yawata H, Yasukawa K, Hamaguchi M, Taga T, Kishimoto T (1991) Critical cytoplasmic region of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130 is conserved in the cytokine receptor family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88(24):11349–11353
Piwien-Pilipuk G, Huo JS, Schwartz J (2002) Growth hormone signal transduction. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab JPEM 15(6):771–786
Rhodes CJ (2005) Type 2 diabetes-a matter of beta-cell life and death? Science 307(5708):380–384
Rosenfeld RG, Rosenbloom AL, Guevara-Aguirre J (1994) Growth hormone (GH) insensitivity due to primary GH receptor deficiency. Endocr Rev 15(3):369–390
Ross RJ, Esposito N, Shen XY, Von Laue S, Chew SL, Dobson PR, Postel-Vinay MC, Finidori J (1997) A short isoform of the human growth hormone receptor functions as a dominant negative inhibitor of the full-length receptor and generates large amounts of binding protein. Mol Endocrinol 11(3):265–273
Rowland JE, Lichanska AM, Kerr LM, White M, d’Aniello EM, Maher SL, Brown R, Teasdale RD, Noakes PG, Waters MJ (2005) In vivo analysis of growth hormone receptor signaling domains and their associated transcripts. Mol Cell Biol 25(1):66–77
Saveliev A, Everett C, Sharpe T, Webster Z, Festenstein R (2003) DNA triplet repeats mediate heterochromatin-protein-1-sensitive variegated gene silencing. Nature 422(6934):909–913
Silbergeld A, Dastot F, Klinger B, Kanety H, Eshet R, Amselem S, Laron Z (1997) Intronic mutation in the growth hormone (GH) receptor gene from a girl with Laron syndrome and extremely high serum GH binding protein: extended phenotypic study in a very large pedigree. J Clin Endocrinol Metab JPEM 10(3):265–274
Stenson PD, Ball EV, Mort M, Phillips AD, Shiel JA, Thomas NS, Abeysinghe S, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (2003) Human gene mutation database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum Mutat 21(6):577–581
Strous GJ, van Kerkhof P, Govers R, Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL (1996) The ubiquitin conjugation system is required for ligand-induced endocytosis and degradation of the growth hormone receptor. EMBO J 15(15):3806–3812
Tiulpakov A, Rubtsov P, Dedov I, Peterkova V, Bezlepkina O, Chrousos GP, Hochberg Z (2005) A novel C-terminal growth hormone receptor (GHR) mutation results in impaired GHR-STAT5 but normal STAT-3 signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90(1):542–547
van Bunderen CC, Oosterwerff MM, van Schoor NM, Deeg DJ, Lips P, Drent ML (2013) Serum IGF1, metabolic syndrome, and incident cardiovascular disease in older people: a population-based study. Eur J Endocrinol 168(3):393–401
Vijayakumar A, Wu Y, Sun H, Li X, Jeddy Z, Liu C, Schwartz GJ, Yakar S, LeRoith D (2012) Targeted loss of GHR signaling in mouse skeletal muscle protects against high-fat diet-induced metabolic deterioration. Diabetes 61(1):94–103
Wang X, Souza SC, Kelder B, Cioffi JA, Kopchick JJ (1995) A 40-amino acid segment of the growth hormone receptor cytoplasmic domain is essential for GH-induced tyrosine-phosphorylated cytosolic proteins. J Biol Chem 270(11):6261–6266
Williams A, Harker N, Ktistaki E, Veiga-Fernandes H, Roderick K, Tolaini M, Norton T, Williams K, Kioussis D (2008) Position effect variegation and imprinting of transgenes in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res 36(7):2320–2329
Woods KA, Fraser NC, Postel-Vinay MC, Savage MO, Clark AJ (1996) A homozygous splice site mutation affecting the intracellular domain of the growth hormone (GH) receptor resulting in Laron syndrome with elevated GH-binding protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(5):1686–1690
Zhou Y, Xu BC, Maheshwari HG, He L, Reed M, Lozykowski M, Okada S, Cataldo L, Coschigamo K, Wagner TE et al (1997) A mammalian model for Laron syndrome produced by targeted disruption of the mouse growth hormone receptor/binding protein gene (the Laron mouse). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(24):13215–13220
Acknowledgment
We are grateful to all participants of the transgenic group at BGI and the cloning group at BGI Ark Biotechnology (BAB). This work was supported by research grants from China and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program 2011CB944201), National Transgenic Project of China (2014ZX0801007B), Special Foundation of Shenzhen Municipal Government of China for the development of Bio-industry (ZYC201105170390A), Shenzhen overseas high level talents innovation Program (KQC201109050086A), Shenzhen Municipal Basic Research Program (JCYJ20120830105157538).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest and financial disclosure statements are clearly listed.
Additional information
Feida Li, Yong Li and Huan Liu have contributed equally to this work .
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
List of primers. The color-code refers to PCR (black) and RT-qPCR (red) primers. The underlined sequences mark the recognition sites for the restriction enzyme NheI and XhoI, respectively (PPTX 44 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Summary of cloning efficiencies obtained with the GHRdm transgenic Wuzhishan fetal donor fibroblasts (PPTX 42 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Skeleton size of a GHRdm transgenic versus a non-transgenic Wuzhishan minipig (PPTX 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Li, Y., Liu, H. et al. Transgenic Wuzhishan minipigs designed to express a dominant-negative porcine growth hormone receptor display small stature and a perturbed insulin/IGF-1 pathway. Transgenic Res 24, 1029–1042 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9912-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-015-9912-6