Abstract
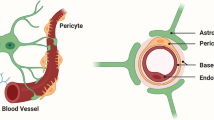
For many CNS acting drugs, penetration into the central nervous system (CNS) is limited by the blood-CNS-barriers. In an effort to quantitate the role of the protein components that make up the blood-CNS-barriers, we created transgenic mice that allow conditional gene knockout using Cre/loxP technology. We targeted the expression of Cre-recombinase to the choroid plexus (the blood-cerebral spinal fluid barrier) using the lymphotropic papovavirus control region (LPVcr) and to brain endothelium (the blood–brain-barrier) using the proximal promoter region of the human von Willebrand Factor gene (hVWF-f). We verified that LPVcr restricts expression to the choroid plexus in adult mice by using the LPVcr to drive n-LacZ expression in transgenic mice. The LPV-Cre and hVWF-Cre plasmids were then constructed and tested for Cre-recombinase function in vitro, and subsequently used to create transgenic mice. The resulting transgenic mice were characterized for cell-type specific Cre-mediated endonuclease activity by crossing them with transgenic mice containing a loxP-flanked-LacZ/EGFP dual reporter gene Z/EG. The dual Cre-Z/EG transgenic offspring were evaluated for the location of EGFP mRNA expression by reverse transcriptase PCR and for protein expression by immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemistry for EGFP verified expression in the target cells, and no ectopic expression outside of the expected cell types. The LPV-Cre.0607 transgenic line expressed functional Cre only in the choroid plexus and hVWF-Cre.1304 line in brain endothelium.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aird WC, Jahroudi N, Weiler-Guettler H, Rayburn HB, Rosenberg RD (1995) Human von Willebrand factor gene sequences target expression to a subpopulation of endothelial cells in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(10):4567–4571
Alva JA, Zovein AC, Monvoisin A, Murphy T, Salazar A, Harvey NL, Carmeliet P, Iruela-Arispe ML (2006) Ve-cadherin-cre-recombinase transgenic mouse: a tool for lineage analysis and gene deletion in endothelial cells. Dev Dyn 235(3):759–767
Auerbach AB (2004) Production of functional transgenic mice by DNA pronuclear microinjection. Acta Biochim Pol 51(1):9–31
Brinster RL, Chen HY, Messing A, van Dyke T, Levine AJ, Palmiter RD (1984) Transgenic mice harboring sv40 t-antigen genes develop characteristic brain tumors. Cell 37(2):367–379
Brinster RL, Chen HY, Trumbauer ME, Yagle MK, Palmiter RD (1985) Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82(13):4438–4442
Chen JD, Van Dyke T (1991) Uniform cell-autonomous tumorigenesis of the choroid plexus by papovavirus large t antigens. Mol Cell Biol 11(12):5968–5976
Chen JD, Neilson K, Van Dyke T (1989) Lymphotropic papovavirus early region is specifically regulated transgenic mice and efficiently induces neoplasia. J Virol 63(5):2204–2214
de Lange EC (2004) Potential role of abc transporters as a detoxification system at the blood-csf barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56(12):1793–1809
Feigenbaum L, Hinrichs SH, Jay G (1992) Jc virus and simian virus 40 enhancers and transforming proteins: role in determining tissue specificity and pathogenicity in transgenic mice. J Virol 66(2):1176–1182
Geyer J, Gavrilova O, Petzinger E (2009) Brain penetration of ivermectin and selamectin in mdr1a, b p-glycoprotein- and bcrp- deficient knockout mice. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 32(1):87–96
Gu L, Tsark WM, Brown DA, Blanchard S, Synold TW, Kane SE (2009) A new model for studying tissue-specific mdr1a gene expression in vivo by live imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(13):5394–5399
Jahroudi N, Lynch DC (1994) Endothelial-cell-specific regulation of von Willebrand factor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 14(2):999–1008
Jahroudi N, Schmaier A, Srikanth S, Mahdi F, Lutka FA, Bowser R (2003) VonWillebrand factor promoter targets the expression of amyloid beta protein precursor to brain vascular endothelial cells of transgenic mice. J Alzheimers Dis 5(2):149–158
Jonker JW, Buitelaar M, Wagenaar E, Van Der Valk MA, Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, Plosch T, Kuipers F, Elferink RP, Rosing H, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH (2002) The breast cancer resistance protein protects against a major chlorophyll-derived dietary phototoxin and protoporphyria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(24):15649–15654
Kaddoumi A, Choi SU, Kinman L, Whittington D, Tsai CC, Ho RJ, Anderson BD, Unadkat JD (2007) Inhibition of p-glycoprotein activity at the primate blood-brain barrier increases the distribution of nelfinavir into the brain but not into the cerebrospinal fluid. Drug Metab Dispos 35(9):1459–1462
Katsuno T, Umeda K, Matsui T, Hata M, Tamura A, Itoh M, Takeuchi K, Fujimori T, Nabeshima Y, Noda T, Tsukita S (2008) Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells. Mol Biol Cell 19(6):2465–2475
Koni PA, Joshi SK, Temann UA, Olson D, Burkly L, Flavell RA (2001) Conditional vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 deletion in mice: impaired lymphocyte migration to bone marrow. J Exp Med 193(6):741–754
Kos CH (2004) Cre/loxP system for generating tissue-specific knockout mouse models. Nutr Rev 62(6 Pt 1):243–246
Kwon GS, Hadjantonakis AK (2009) Transthyretin mouse transgenes direct rfp expression or cre-mediated recombination throughout the visceral endoderm. Genesis 47(7):447–455
Lakso M, Sauer B, Mosinger B Jr, Lee EJ, Manning RW, Yu SH, Mulder KL, Westphal H (1992) Targeted oncogene activation by site-specific recombination in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(14):6232–6236
Lakso M, Pichel JG, Gorman JR, Sauer B, Okamoto Y, Lee E, Alt FW, Westphal H (1996) Efficient in vivo manipulation of mouse genomic sequences at the zygote stage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(12):5860–5865
Lorico A, Rappa G, Finch RA, Yang D, Flavell RA, Sartorelli AC (1997) Disruption of the murine mrp (multidrug resistance protein) gene leads to increased sensitivity to etoposide (vp-16) and increased levels of glutathione. Cancer Res 57(23):5238–5242
Messing A, Pinkert CA, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL (1988) Developmental study of sv40 large t antigen expression in transgenic mice with choroid plexus neoplasia. Oncogene Res 3(1):87–97
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: Claudin-5/tmvcf constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147(1):185–194
Nagy A (2000) Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis 26(2):99–109
Nagy A, Mar L (2001) Creation and use of a cre recombinase transgenic database. Methods Mol Biol 158:95–106
Nagy A, Mar L, Watts G (2009) Creation and use of a cre recombinase transgenic database. Methods Mol Biol 530:365–378
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161(3):653–660
Novak A, Guo C, Yang W, Nagy A, Lobe CG (2000) Z/e.g, a double reporter mouse line that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein upon Cre-mediated excision. Genesis 28(3–4):147–155
Perraud F, Yoshimura K, Louis B, Dalemans W, Ali-Hadji D, Schultz H, Claudepierre MC, Chartier C, Danel C, Bellocq JP et al (1992) The promoter of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene directing sv40 t antigen expression induces malignant proliferation of ependymal cells in transgenic mice. Oncogene 7(5):993–997
Rao VV, Dahlheimer JL, Bardgett ME, Snyder AZ, Finch RA, Sartorelli AC, Piwnica-Worms D (1999) Choroid plexus epithelial expression of mdr1 p glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associated protein contribute to the blood-cerebrospinal-fluid drug-permeability barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(7):3900–3905
Salama NN, Kelly EJ, Bui T, Ho RJ (2005) The impact of pharmacologic and genetic knockout of p-glycoprotein on nelfinavir levels in the brain and other tissues in mice. J Pharm Sci 94(6):1216–1225
Schinkel AH, Smit JJ, van Tellingen O, Beijnen JH, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CA, van der Valk MA, Robanus-Maandag EC, te Riele HP et al (1994) Disruption of the mouse mdr1a p-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77(4):491–502
Schinkel AH, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CA, Borst P (1995) Absence of the mdr1a p-glycoprotein in mice affects tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics of dexamethasone, digoxin, and cyclosporin a. J Clin Invest 96(4):1698–1705
Semprini S, Troup TJ, Kotelevtseva N, King K, Davis JR, Mullins LJ, Chapman KE, Dunbar DR, Mullins JJ (2007) Cryptic loxP sites in mammalian genomes: genome-wide distribution and relevance for the efficiency of bac/pac recombineering techniques. Nucleic Acids Res 35(5):1402–1410
Sternberg N, Hamilton D (1981) Bacteriophage p1 site-specific recombination. I. Recombination between loxP sites. J Mol Biol 150(4):467–486
Stratman JL, Barnes WM, Simon TC (2003) Universal pcr genotyping assay that achieves single copy sensitivity with any primer pair. Transgenic Res 12(4):521–522
Thyagarajan B, Guimaraes MJ, Groth AC, Calos MP (2000) Mammalian genomes contain active recombinase recognition sites. Gene 244(1–2):47–54
Wijnholds J, deLange EC, Scheffer GL, van den Berg DJ, Mol CA, van der Valk M, Schinkel AH, Scheper RJ, Breimer DD, Borst P (2000) Multidrug resistance protein 1 protects the choroid plexus epithelium and contributes to the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. J Clin Invest 105(3):279–285
Xu J, Kausalya PJ, Phua DC, Ali SM, Hossain Z, Hunziker W (2008) Early embryonic lethality of mice lacking zo-2, but not zo-3, reveals critical and nonredundant roles for individual zonula occludens proteins in mammalian development. Mol Cell Biol 28(5):1669–1678
Zhang Y, Huang G, Shornick LP, Roswit WT, Shipley JM, Brody SL, Holtzman MJ (2007) A transgenic FOXJ1-cre system for gene inactivation in ciliated epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36(5):515–519
Acknowledgments
We thank Terry Kavanagh for the use of the Cryocut cryomicrotome, Richard Palmiter for the pLacF plasmid, Nancy Jahroudi for the pHGH-K plasmid, Terry Van Dyke for the pLST plasmid, Corrinne Lobe for the Z/EG plasmid, Washington University ES Cell Core for the pTurboCre plasmid, and Kerstin Verdina for assistance in editing. This work was supported by the National Institute of Health grants NS39178, AI077390, and AI52663. Rodney J. Y. Ho is also supported by the Milo Gibaldi Endowment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crouthamel, M.H., Kelly, E.J. & Ho, R.J.Y. Development and characterization of transgenic mouse models for conditional gene knockout in the blood–brain and blood-CSF barriers. Transgenic Res 21, 113–130 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-011-9512-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-011-9512-z