Abstract
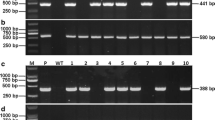
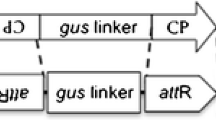
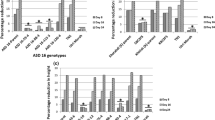
Rice stripe disease, with the pathogen Rice stripe virus (RSV), is one of the most widespread and severe virus diseases. Cultivating a resistant breed is an essential and efficient method in preventing rice stripe disease. Following RNA interference (RNAi) theory, we constructed three RNAi binary vectors based on coat protein (CP), special-disease protein (SP) and chimeric CP/SP gene sequence. Transgenic lines of rice cv. Yujing6 were generated through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. We inoculated T1 generation plants from each line derived from CP/SP, CP, and SP transgenic rice plants with two RSV isolates from Shandong Province and Jiangsu Province using viruliferous vector insects. In these resistance assays, chimeric CP/SP RNAi lines showed stronger resistance against two isolates than CP or SP single RNAi lines. Stable integration and expression of RNAi transgenes were confirmed by Southern and northern blot analysis of independent transgenic lines. In the resistant transgenic lines, lower levels of transgene transcripts and specific short interference RNAs were observed relative to the susceptible transgenic plant, which showed that virus resistance was increased by RNAi. Genetic analysis demonstrated that transgene and virus resistance was stably inherited in the T2 progeny plants.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bar:
-
Bialaphos resistance gene
- CP:
-
Coat protein
- dsRNA:
-
Double-strand RNA
- hpRNA:
-
Hairpin RNA
- nt:
-
Nucleotide
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PPT:
-
Phosphinothricin
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PTGS:
-
Posttranscriptional gene silencing
- RMVR:
-
RNA-mediated virus resistance
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- siRNA:
-
Short interfering RNA
- SP:
-
Special-disease protein
- vRNA:
-
Viral RNA
- vcRNA:
-
Viral complementary RNA
References
Chen Z, Xu ZF, Ye JJ, Yao HP, Zheng S, Ding JY (2005) Combination of small interfering RNAs mediates greater inhibition of human hepatitis B virus replication and antigen expression. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 6:236–241
Chen XM, Liu J, Li X, Jiang F, Xie XY, Zhu CX, Wen FJ (2010) Inhibiting virus infection by RNA interference of the eight functional genes of the potato virus Y genome. J Phytopathol 158:776–784. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0434.2010.01701.x
Cheng ZB, Ren CM, Zhou YJ, Fan YJ, Xie LH (2008) Pathogenicity of Rice stripe tenuivious isolates from different areas. Acta Phytopathol Sinica 38(2):129–131
Cui GR, Wu H, Liu YG (2004) Selecting herbicide-resistant calli of rice and appraising to seedling with PPT and Basta. Seed 23:7–10
Ding SW, Li H, Lu R, Li F, Li WX (2004) RNA silencing: a conserved antiviral immunity of plants and animals. Virus Res 102:109–115. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2004.01.021
Duan FP, Liang CY, Li YQ (2001) Research advances of Bar gene and its transgenic crops. Guihaia 21:166–172
Dykxhoorn DM, Lieberman J (2006) Silencing viral infection. PLoS Med 3:1000–1004. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030242
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994. doi:10.1007/BF00014672
Hannon GJ (2002) RNA interference. Nature 418:244–251. doi:10.1038/418244a
Hayakawa T, Zhu YF, Itoh K, Kimura Y, Izawa T, Shmamoto K, Toriyama S (1992) Genetieally engineered rice resistant to rice stripe virus, an insect-transmitted virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9865–9869
Kogenezawa H, Doi Y, Yora K (1996) Purification of rice stripe virus. Annu Phytopathol Soc Jpn 41:148–164
Lindbo JA, Silva-Rosales L, Proebsting WM, Dougherty WG (1993) Induction of a highly specific antiviral state in transgenic plant: Implications for regulation of gene expression and virus resistance. Plant Cell 5:1749–1759. doi:10.1105/tpc.5.12.1749
Liu XC, Pan CX, Song YZ, Chen HL, Wen FJ (1995) A simple procedure of DNA isolation from monocotyledonous plants and its application. J Shandong Agric Univ (Natural science) 26:491–495
Ma J, Song YZ, Li KD, Zhu CX, Wen FJ (2008) The analysis of molecular variability of rice stripe virus isolate (RSV-SD-JN2) in Jining Shandong. Zhi Wu Bao Hu Xue Bao 35:415–420
Matzke M, Matzke AJ, Kooter JM (2001) RNA: guiding gene silencing. Science 293:1080–1083
Nicola-Negri ED, Brunetti A, Tavazza M, Iiardi V (2005) Hairpin RNA-mediated silencing of Plum pox virus P1 and HC-Pro genes for efficient and predictable resistance to the virus. Transg Res 14:989–994. doi:10.1007/s11248-005-1773-y
Ramesh SV, Mishra AK, Praveen S (2007) Hairpin RNA-mediated strategies for silencing of tomato leaf curl virus AC1 and AC4 genes for effective resistance in plants. Oligonucleotides 17:251–257. doi:10.1089/oli.2006.0063
Ramirez BC, Haenni AL (1994) Molecular biology of tenuiviruses, a remarkable group of plant viruses. J Gen Virol 75:467–475. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-75-3-467
Sambrook J, Fristsch EF, Maniatis T (2001) Molecular cloning: a libratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sanford JC, Johnson SA (1985) The concept of parasite-derived resistance: deriving resistance genes from the parasite own genome. J Theor Biol 115:395–405. doi:10.1016/S0022-5193
Shimizu T, Yoshii M, Wei T, Hirochik H, Omura T (2009) Silencing by RNAi of the gene for Pns12, a viroplasm matrix protein of Rice dwarf virus, results in strong resistance of transgenic rice plants to the virus. Plant Biotechnol J 7:24–32. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00366.x
Smith NA, Singh SP, Wang M, Stoutjesdijk P, Green A, Waterhouse PM (2000) Gene expression: total silencing by intron-spliced hairpin RNAs. Nature 407:319–320. doi:10.1038/35030305
Song E, Lee SK, Dykxhoorn DM, Novina C, Zhang D, Crawford K, Cerny J, Sharp PA, Lieberman J, Manjunath N, Shankar P (2003) Sustained small interfering RNA-mediated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibition in primary macrophages. J Virol 77:7174–7181. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.13.7174-7181.2003
Takahashi M, Toriyama S, Hamamatsu C, Ishihama A (1993) Nucleotide sequence and possible ambisense coding strategy of rice stripe virus RNA segment 2. J Gen Virol 74:769–773. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-74-4-769
Toki S, Hara N, Ono K, Onodera H, Tagiri A, Oka S, Tanaka H (2006) Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. Plant J 47:969–976. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02836.x
Toriyama S (1986) Rice stripe virus: prototype of a new group of viruses that replicate in plants and insects. Microbiol Sci 3:347–351
Toriyama S, Takahashi M, Sano Y, Shimizu T, Ishihama A (1994) Nucleotide sequence of RNA1, the largest genomic segment of rice stripe virus, the proto type of the Tenuiviruses. J Gen Virol 75:3569–3579. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-75-12-3569
Vaucheret H, Beclin C, Fagard M (2001) Post transcriptional gene silencing in plants. J Cell Sci 114:3083–3091
Wang MB, Abbott DC, Waterhouse PM (2000) A single copy of a virus-derived transgene encoding hairpin RNA gives immunity to barley yellow dwarf virus. Mol Plant Pathol 1:347–356. doi:10.1046/j.1364-3703.2000.00038.x
Waterhouse PM, Graham MW, Wang MB (1998) Virus resistance and gene silencing in Plants can be induced by simultaneous expression of sense and antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13959–13964. doi:0027-8424/98/9513959-6$2.00/0
Wei TY, Yang JG, Liao FL, Gao FL, Lu LM et al (2009) Genetic diversity and population structure of rice stripe virus in China. J Gen Virol 90:1025–1034. doi:10.1099/vir.0.006858-0
Wu SJ, Zhong H, Zuo H, Gu MH, Liang GH (2006) Research progress in molecular biology of rice stripe virus and gene engineering of virus resistance. Acta Agric Jiangxi 18:72–77
Xie L (1986) Research on rice virus disease in China. Trop Agric Res Ser 19:45–50
Xue DW, Ma LL, Jiang H, Hua ZH, Guo LB, Huang DN, Qian Q (2005) Safety assessment of herbicide-tolerant transgenic rice. J Agric Biotechnol 13:723–727
Zhou T, Wang L, Chen ZB, Fan YJ, Zhou YJ (2009) Mechanism and inheritance of resistance to rice stripe disease in the japonica rice cultivar Zhendao 88. Sci Agric Sin 42:103–109
Zhu Y, Hayakawa T, Toriyama S, Takahashi M (1991) Complete nucleotide sequence of RNA3 of rice stripe virus: an ambisense coding strategy. J Gen Virol 72:763–767
Zhu Y, Hayakawa T, Toriyama S (1992) Complete nucleotide sequence of RNA4 of rice stripe virus isolate T and comparison with another isolate and with maize stripe virus. J Gen Virol 73:1309–1312. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1309
Zhu JH, Zhu XP, Wen FJ, Bai QR, Zhu CX, Song YZ (2004) Effect of cDNA fragments in different length derived from Potato Virus Y coat protein gene on the induction of RNA-mediated virus resistance. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 47:382–388. doi:10.1360./03yc0066
Zhu CX, Song YZ, Yin GH, Wen FJ (2009) Induction of RNA-mediated multiple virus resistance to potato virus Y, tobacco mosaic virus and cucumber mosaic virus. J Phytopathol 157:101–107. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0434.2008.01449.x
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in part by the National High Technology Research and Develop Program of China (No.2007AA10Z417) and National Special Grad Project of the Genetically Modified New Seeds Cultivation (No. 2008ZX08001-002). We acknowledged Zhou Yijun, researcher, and Zhou Tong from Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences for the help with the RSV-resistance analysis. We thank Professor Xiu-Qing Li from Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) Potato Research Centre for revising the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Song, Y., Wu, B. et al. Production of transgenic rice new germplasm with strong resistance against two isolations of Rice stripe virus by RNA interference. Transgenic Res 20, 1367–1377 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-011-9502-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-011-9502-1