Abstract
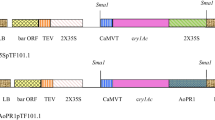
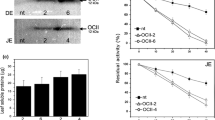
Insect-resistant transgenic plants have been suggested to have unpredictable effects on the biodiversity of the agro-ecosystem, including potential effects on insect natural enemies, beneficial in control of crop pests. Whilst carnivorous as adults, many of these predators may also consume plant tissues, in particular plant pollen and nectar. Coleoptera are important in terms of agro-ecological research not only because of the large number of species in this order, but also because of their role as biological control agents. Thus any detrimental impact on this group of insects would be highly undesirable. The effects of potato expressing the coleopteran-specific Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin Cry3A (Bt Cry3A) on the ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis and the carabid beetle Nebria brevicollis were investigated via the bitrophic interaction of the adult ladybird with potato flowers and the tritrophic interaction of the carabid consuming a non-target potato pest. Immunoassays confirmed accumulation of the transgene product in potato leaves and floral tissues (at levels of up to 0.01% (pollen) and 0.0285% (anthers) of total soluble protein). Despite H. axyridis and N. brevicollis belonging to the targeted insect order, no significant effects upon survival or overall body mass change of either beetle were observed. Furthermore, Bt Cry3A had no detrimental effects on reproductive fitness of either beetle species, either in terms of fecundity or subsequent egg viability. Behavioural analysis revealed no significant impact of Bt Cry3A on beetle activity or locomoter behaviour. Ligand blots indicate that this is due to either the absence of Bt-binding sites in brush border membrane vesicles (BBMV) isolated from Nebria brevicollis, or in the case of Harmonia axyridis, the binding did not functionally lead to behavioural or physical effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABE (Agricultural Biotechnology in Europe) (2002) The Environmental Impact of Agricultural Biotechnolgy. Issue Paper 3
Anderson PL, Hellmich II RL, Sears MK, Sumerford DV, Lewis LC (2004) Effects of Cry1Ab-expressing corn anthers on monarch butterfly larvae. Environ Entomol 33:1109–1115
Banks DJ, Hua G, Adang MJ (2003) Cloning of a Heliothis virescens 110 kDa aminopeptidase N and expression in Drosophila S2 cells. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:499–508
Barrett KL, Grandy N, Harrison EG, Hassan S, Oomen P (eds) (1994) Guidance document on regulatory testing procedures for pesticides with non-target arthropods. SETAC-Europe 51 pp
Betz FS, Hammond BG, Fuchs RL (2000) Safety and advantages of Bacillus thuringiensis-protected plants to control insect pests. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 32(2):156–173
Boucias DG, Pendland JC (1998) Principles of insect pathology. Kluwer Academic Publishers Group, Dordrecht
Broderick N, Raffa FK, Handelsman J (2006) Midgut bacteria required for Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15196–15199
de Maagd RA, Bravo A, Crickmore N (2001) How Bacillus thringiensis has evolved specific toxins to colonize the insect world. Trends Genet 17(4):193–199
Dorsch JA, Candas M, Griko NB, Maaty WSA, Midboe EG, Vadlamudi RK, Bulla LA Jr (2002) Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis bind specifically to a region adjacent to the membrane-proximal extracellular domain of BT-R1 in Manduca sexta: involvement of a cadherin in the entomopathogenicity of Bacillus thuringiensis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:1025–1036
Duffield SJ, Jepson PC, Wratten SD, Sotherton NW (1996) Spatial changes in invertebrate predation rate in winter wheat following treatment with dimethoate. Entomol Exp Appl 78:9–17
Ferry N, Edwards MG, Gatehouse JA, Gatehouse AMR (2004) Plant–insect interactions: molecular approaches to insect resistance. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(2):155–161
Ferry N, Edwards MG, Mulligan EA, Emami K, Petrova A, Frantescu M, Davison GM, Gatehouse AMR (2003) Engineering resistance to insect pests. In: Christou P, Klee H (eds) Handbook of plant biotechnology. John Wiley & Sons
Ferry N, Mulligan EA, Stewart CN, Tabashnik BE, Port GR, Gatehouse AMR (2006) Prey-mediated effects of transgenic canola on a predatory beetle. Transgenic Res 15:501–514
Gahan LJ, Gould F, Heckel DG (2001) Identification of a gene associated with Bt resistance in Heliothis virescens. Science 293(5531):857–860
Gebhardt C, Valkonen JPT (2001) Organization of genes controlling disease resistance in the potato genome. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:79–102
Gill M, Ellar D (2002) Transgenic Drosophila reveals a functional in vivo receptor for the Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac1. Insect Mol Biol 11(6):619–625
Gonzalez-Cabrera J, Farinos GP, Caccia S, Diaz-Mendoza M, Castanera P, Leonardi MG, Giordana B, Ferre J (2006) Toxicity and mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis cry proteins in the Mediterranean corn borer, Sesamia nonagrioides (Lefebvre). Appl Environ Microbiol 72(4):2594–2600
Griffits JS, Hasla SM, Yang TL, Garczynski SF, Mulloy B, Morris H, Cremer PS, Dell A, Adang MJ, Aroian RV (2005) Glycolipids as receptors for Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin. Science 307(5711):922–925
Groot AT, Dicke M (2002) Insect-resistant transgenic plants in a multi-trophic context. Plant J 31(4):387–406
Harwood JD, Aaron Samson R, Obrycki JJ (2006) No evidence for uptake of Cry1Ab Bt-endotoxins by the generalist predator Scarites subterraneus (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in laboratory and field experiments. Biocontrol Sci Technol 16(4):377–388
Harwood JD, Wallin WG, Obrycki JJ (2005) Uptake of Bt endotoxins by nontarget herbivores and higher order arthropod predators: molecular evidence from a transgenic corn agroecosystem. Mol Ecol 14(9):2815–2823
Heimbach U (1992) Laboratory method to test effects of pesticides on Poecilus cupreus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). IOBC/WPRS Bull 15(3):103–109
Hilbeck A, Baumgartner M, Fried PM, Bigler F (1998) Effects of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis corn-fed prey on mortality and development of immature Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Environ Entomol 27(2):480–487
James C (2005) Global status of commercialized transgenic crops. ISAAA Briefs No. 34. ISAAA, Ithaca, NY
Karim S, Riazuddin S, Gould F, Dean DH (2000) Determination of receptor binding properties of Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxins to Cotton Bollworm (Heliocoverpa zea) and Pink Bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) midgut brush border membrane vesicles. Pestic Biochem Physiol 67:198–216
Kromp B (1999) Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture: a review on pest control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement. Agric Ecosyst Environ 74:187–228
Li HR, Oppert B, Higgins RA, Huang FN, Buschman LL, Gao JR, Zhu KY (2005) Characterization of cDNAs encoding three trypsin-like proteinases and mRNA quantitative analysis in Bt-resistant and -susceptible strains of Ostrinia nubilalis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35(8):847–860
Loseva O, Ibrahim M, Candas M, Koller CN, Bauuer LS, Bull LA Jr (2002) Changes in protease activity and Cry3A toxin binding in the Colorado potato beetle: implications for insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 32:567–577
Losey JE, Rayor LS, Carter ME (1999) Transgenic pollen harms monarch larvae. Nature 399(6733):214–214
Lundgren JG, Weidenmann RN (2002) Tritrophic Interactions among Bt (CryMb1) corn, aphid prey, and the predator Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ Entomol 34(6):1621–1625
Lundgren JG, Weidenmann RN (2005) Coleopteran-specific Cry3Bb toxin from transgenic corn pollen does not affect the fitness of a non-target species, Coleomegilla maculata DeGeer (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ Entomol 31(6):1213–1218
Ma G, Roberts H, Sarjan M, Featherstone N, Lahnstein J, Akhurst R, Schmidt O (2005) Is the mature endotoxin Cry1Ac from Bacillus thuringiensis inactivated by a coagulation reaction in the gut lumen of resistant Helicoverpa armigera larvae? Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35:729–739
MacIntosh SC, Stone TB, Sims SR, Hunst PL, Greenplate JT, Marrone PG, Perlak FJ, Fischhoff DA, Fuchs RL (1990) Specificity and efficacy of purified Bacillus thuringiensis proteins against agronomically important insects. J Invertebr Pathol 56:258–266
Majerus MEN (1994) The new naturalist library, a survey of British Natural History, Ladybirds. Harper-Collins Somerset, UK
McNall RJ, Adang MJ (2003) Identification of novel Bacillus thuringiensis Cry 1Ac binding proteins in Manduca sexta midgut through proteomic analysis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:999–1010
Meier MS, Hilbeck A (2001) Influence of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis corn-fed prey on prey preference of immature Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Basic Appl Ecol 2(1):35–44
Meissle M, Vojtech E, Poppy GM (2005) Effects of Bt maize-fed prey on the generalist predator Poecilus cupretis L. (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Transgenic Res 14(2):123–132
Mullin CA, Saunders MC, Leslie TW, Biddinger DJ, Fleischer SJ (2005) Toxic and behavioural effects to Carabidae of seed treatments used on Cry3BbI and Cry1Ab/c protected corn. Environ Entomol 34(6):1626–1636
Nechols JR, Obrycki JJ (1989) Comparative behavioural and ecological studies in relation to biological control: an overview. J Kans Entomol Soc 62:146–147
Newell CA, Rozman R, Hinchee MA, Lawson EC, Haley L, Sanders P, Kaniewski W, Tumer NE, Horsch RB, Fraley RT (1991) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Solanum tuberosum L.cv. ‘Russet Burbank’. Plant Cell Rep 10:30–34
Perlak FJ, Stone TB, Muskopf YM, Petersen LJ, Parker GB, McPherson SA, Wyman J, Love S, Reed G, Biever D, Fischhoff DA (1993) Genetically improved potatoes: protection from damage by Colorado potato beetles. Plant Mol Biol 22:313–321
Poppy GM (1997) Tritrophic interactions: improving ecological understanding and biological control? Endeavour 21:61–65
Reed GL, Jensen AS, Riebe J, Head G, Duan JJ (2001) Transgenic Bt potato and conventional insecticides for Colorado potato beetle management: comparative efficacy and non-target impacts. Entomol Exp Appl 100:89–100
Riddick EW, Barbosa P (1998) Impact of Cry-3A-intoxicated Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and pollen on consumption, development, and fecundity of Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 91(3):303–307
Riddick EW, Dively G, Barbosa P (1998) Effect of a seed-mix deployment of Cry3A-transgenic and non-transgenic potato on the abundance of Lebia grandis (Coleoptera: Carabidae) and Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am 91(5):647–653
Rodrigo-Simón A, de Maagd RA, Avilla C, Bakker PL, Molthoff J, González-Zamora JE, Ferré J (2006) Lack of detrimental effects of Bacillus thuringiensis cry toxins on the insect predator Chrysoperla carnea: a toxicological, histopathological, and biochemical analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(2):1595–1603
Romeis J, Dutton A, Bigler F (2004). Bacillus thuringiensis toxin (Cry1Ab) has no direct effect on larvae of the green lacewing Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). J Insect Physiol 50:175–183
Shi H, Zhang LF, Hua BZ, Mi XC, Wei W, Zhang YJ, Ma KP (2006) Insecticidal activity of residual Bt protein at the second trophic level. Chin Sci Bull 51(8):946–951
Sing SR (2001) The behaviour of the ladybird, Coccinella septumpunctata, in response to sub-lethal doses of insecticide. Thesis, University of Newcastle Upon Tyne
Slaney AC, Loidl Robbins H, English L (1992) Mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin CryIIIA: an analysis of toxicity in Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say) and Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi Barber. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 22(1):9–18
Strong DR, Lawton JH, Southwood TRE (1984) Insects on plants—community patterns and mechanisms. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Thiele HU, Weiss HE (1976) Die Carabiden eines Auenwaldgebietes als Bioindikatoren für anthropgen bedingte Änderungen des Mikroklimas. Schriftens. Vegetationskd 10:359–374
Wallin H, Chiverton PA, Ekbom BS, Borg A (1992) Diet, fecundity and egg size in some polyphagous predatory carabid beetles. Entomol Exp Appl 65:129–140
Wolfenbarger LL, Phifer PR (2000) Biotechnology and ecology—the ecological risks and benefits of genetically engineered plants. Science 290(5499):2088–2093
Wolfersberge M, Leuthy P, Maurer A, Parenti P, Sacchi FV, Giordana B, Hanozet GM (1987) Preparation and partial characterisation of amino acid transporting brush border membrane vesicles from the larval midgut of the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicase). Comp Biochem Physiol 86A:301–308
Zhang GF, Wan FH, Lovei GL, Liu WX, Guo JY (2006) Transmission of Bt toxin to the predator Propylaea japonica (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) through its aphid prey feeding on transgenic Bt corn. Environ Entomol 35(1):143–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferry, N., Mulligan, E.A., Majerus, M.E.N. et al. Bitrophic and tritrophic effects of Bt Cry3A transgenic potato on beneficial, non-target, beetles. Transgenic Res 16, 795–812 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-007-9088-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-007-9088-9