Abstract
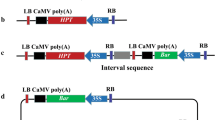
A binary vector, designated PROGMO, was constructed to assess the potential of the Zygosaccharomyces rouxii R/Rs recombination system for generating marker- and backbone-free transgenic potato (Solanum tuberosum) plants with high transgene expression and low copy number insertion. The PROGMO vector utilises a constitutively expressed plant-adapted R recombinase and a codA-nptII bi-functional, positive/negative selectable marker gene. It carries only the right border (RB) of T-DNA and consequently the whole plasmid will be inserted as one long T-DNA into the plant genome. The recognition sites (Rs) are located at such positions that recombinase enzyme activity will recombine and delete both the bi-functional marker genes as well as the backbone of the binary vector, leaving only the gene of interest flanked by a copy of Rs␣and RB. Efficiency of PROGMO transformation was tested by introduction of the GUS reporter gene into potato. It was shown that after 21 days of positive selection and using 300 mgl−1 5-fluorocytosine for negative selection, 29% of regenerated shoots carried only the GUS gene flanked by a copy of Rs and RB. The PROGMO vector approach is simple and might be widely applicable for the production of marker- and backbone-free transgenic plants of many crop species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Breitler JC, Meynard D, Van Boxtel J, Royer M, Bonnot F, Cambillau L, Guiderdoni E (2004) A novel two T-DNA binary vector allows efficient generation of marker-free transgenic plants in three elite cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Transgenic Res 13:271–287
De Buck S, Jacobs A, Van Montagu M, Depicker A (1999) The DNA sequences of T-DNA junctions suggest that complex T-DNA loci are formed by a recombination process resembling T-DNA integration. Plant J 20:295–304
Dietze J, Blau A, Willmitzer L (1995) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of potato (Solanum tuberosum). In: Potrykus I, Spangenberg G (eds), Gene Transfer to Plants Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 24–29
Dóczi R, Csanaki C, Bánfalvi Z (2002) Expression and promoter activity of the desiccation-specific Solanum tuberosum gene, StDS2. Plant Cell Environ 25:1197–1203
Endo S, Sugita K, Sakai M, Tanaka H, Ebinuma H (2002) Single-step transformation for generating marker-free transgenic rice using the ipt-type MAT vector system. Plant J 30:115–122
Gittins JR, Pellny TK, Hiles ER, Rosa C, Biricolti S, James DJ (2000) Transgene expression driven by heterologous ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase small-subunit gene promoters in the vegetative tissues of apple (Malus pumila mill.). Planta 210:232–240
Gleave AP, Mitra DS, Mudge SR, Morris BA (1999) Selectable marker-free transgenic plants without sexual crossing: transient expression of cre recombinase and use of a conditional lethal dominant gene. Plant Mol Biol 40:223–235
Goldsbrough A, Bevan M (1991) New patterns of gene activity in plants detected using an Agrobacterium vector. Plant Mol Biol 16:263–269
Hare PD, Chua N-H (2002) Excision of selectable marker genes from transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 20:113–122
Hood EE, Helmer GL, Fraley RT, Shilton MD (1986) The hypervirulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens A281 is encoded in a region of pTiBo542 outside of the T-DNA. J Bacteriol 168:1291–1304
Horsch RB, Klee HJ (1986) Rapid assay of foreign gene expression in leaf discs transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens: role of T-DNAs borders in the transfer process. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4428–4432
Huang S, Gilbertson LA, Adams TH, Malloy KP, Reisenbigler EK, Birr DH, Snyder MW, Zhang Q, Luethy MH (2004) Generation of marker-free transgenic maize by regular two-border Agrobacterium transformation vectors. Transgenic Res 13:451–461
Janssen BJ, Gardner RC (1990) Localized transient expression of GUS in leaf discs following cocultivation with Agrobacterium. Plant Mol Biol 14:61–72
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Miki B, McHugh S (2004) Selectable marker genes in transgenic plants: applications, alternatives and biosafety. J Biotechnol 107:193–232
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plantarum 15:473–497
Narasimhulu SB, Deng XB, Sarria R, Gelvin SB (1996) Early transcription of Agrobacterium T-DNA genes in tobacco and maize. Plant Cell 8:873–886
Onouchi H, Nishihama R, Kudo M, Machida Y, Machida C (1995) Visualization of site-specific recombination catalyzed by a recombinase from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 247:653–660
Onouchi H, Yokoi K, Machida C, Matsuzaki H, Oshima Y, Matsuoka K, Nakamura K, Machida Y (1991) Operation of an efficient site-specific recombination system of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in tobacco cells. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6373–6378
Outchkourov NS, Peters J, de Jong J, Rademakers W, Jongsma MA (2003) Novel rubisco small subunit promoter from chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora L) yields high foreign gene expression levels in plants. Planta 21:1003–1012
Rommens CM, Humara JM, Ye J, Yan H, Richael C, Zhang L, Perry R, Swords K (2004) Crop improvement through modification of the plant’s own genome. Plant Physiol 135:421–431
Samac DA, Tesfaye M, Dornbusch M, Saruul P, Temple SJ (2004) A comparison of constitutive promoters for expression of transgenes in alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Transgenic Res 13:349–361
Schaart JG, Krens FA, Pelgrom KTB, Mendes O, Rouwendal GJ (2004) Effective production of marker-free transgenic strawberry plants using inducible site-specific recombination and a bifunctional selectable marker gene. Plant Biotechnol J 2:233–240
Shure M, Wessler S, Fedoroff N (1983) Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell 35:225–233
Sugita K, Kasahara T, Matsunaga E, Ebinuma H (2000) A transformation vector for the production of marker-free transgenic plants containing a single copy transgene at high frequency. Plant J 22:461–469
Toriyama K, Chiba A, Nakagawa Y (2003) Visualization of somatic deletions mediated by R/RS site-specific recombination and induction of germinal deletions caused by callus differentiation and regeneration in rice. Plant Cell Rep 21:605–610
Tzfira T, Li J, Lacroix B, Citovsky V (2004) Agrobacterium T-DNA integration: molecules and models. Trends Genet 20:375–83
Vancanneyt G, Schmidt R, Oçonner-Sanchez A, Willmitzer L, Rocha-Sosa M (1990) Construction of an intron-containing marker gene: Splicing of the intron in transgenic plants and its use in monitoring early events in Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Mol Gen Genet 220:245–250
de Vetten N, Wolters AM, Raemakers K, van der Meer I, ter Stege R, Heeres E, Heeres P, Visser R (2003) A transformation method for obtaining marker-free plants of a cross-pollinating and vegetatively propagated crop. Nat Biotechnol 21:439–442
Waters VL, Guiney DG (1993) Processes at the nick region link conjugation, T-DNA transfer and rolling circle replication. Mol Microbiol 9:1123–1130
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Rouwendal (Plant Research International, Wageningen University and Research Center, Wageningen, The Netherlands) for the PROGMO plasmid, promoters and cloning strategy development, and M. Kiss for technical assistance. M.K. had a fellowship from the Netherlands Ministry of Agriculture, Nature Management and Fisheries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondrák, M., van der Meer, I.M. & Bánfalvi, Z. Generation of Marker- and Backbone-Free Transgenic Potatoes by Site-Specific Recombination and a Bi-Functional Marker Gene in a Non-Regular One-Border Agrobacterium Transformation Vector. Transgenic Res 15, 729–737 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-006-9021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-006-9021-7