Abstract
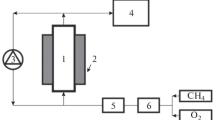
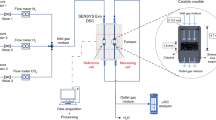
The catalytic partial oxidation of methane (CPO) over flame-made 2.5%Rh–2.5%Pt/Al2O3 and 2.5%Rh/Al2O3 in 6%CH4/3%O2/He shows the potential of in situ studies using miniaturized fixed-bed reactors, the importance of spatially resolved studies and its combination with infrared thermography and on-line mass spectrometry. This experimental strategy allowed collecting data on the structure of the noble metal (oxidation state) and the temperature along the catalyst bed. The reaction was investigated in a fixed-bed quartz microreactor (1–1.5 mm diameter) following the catalytic performance by on-line gas mass spectrometry (MS). Above the ignition temperature of the catalytic partial oxidation of methane (310–330 °C), a zone with oxidized noble metals was observed in the inlet region of the catalyst bed, accompanied by a characteristic hot spot (over-temperature up to 150 °C), while reduced noble metal species became dominant towards the outlet of the bed. The position of both the gradient in oxidation state and the hot spot were strongly dependent on the furnace temperature and the gas flow (residence time). Heating as well as a higher flow rate caused a migration of the transition zone of the oxidation state/maximum in temperature towards the inlet. At the same time the hydrogen concentration in the reactor effluent increased. In contrast, at low temperatures a movement of the transition zone towards the outlet was observed at increasing flux, except if the self-heating by the exothermic methane oxidation was too strong. The results indicate that in the oxidized zone mainly combustion of methane occurs, whereas in the reduced part direct partial oxidation and reforming reactions prevail. The results demonstrate how spatially resolved spectroscopy can help in understanding catalytic reactions involving different reaction zones and gradients even in micro scale fixed-bed reactors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao E, Firth S, McMillan PF, Gavriilidis A (2007) Catal Today 126:119
Chan EM, Marcus MA, Fakra S, ElNaggar M, Mathies RA, Paul Alivisatos A (2007) J Phys Chem A 111:12210
Beato P, Kraehnert R, Engelschalt S, Frank T, Schlögl R (2008) Chem Eng J 135S:247
Clausen BS, Steffensen G, Fabius B, Villadsen J, Feidenhans’l R, Topsøe H (1991) J Catal 132:524
Ehrfeld W, Hessel V, Löwe H (2000) Microreactors: new technology for modern chemistry. Wiley-VCH, New York
Gavriilidis A, Angeli P, Cao E, Yeong KK, Wan YSS (2002) Chem Eng Res Des 80A:3
Schroer CG, Kuhlmann M, Gunzler TF, Lengeler B, Richwin M, Griesebock B, Lutzenkirchen-Hecht D, Frahm R, Ziegler E, Mashayekhi A, Haeffner DR, Grunwaldt JD, Baiker A (2003) Appl Phys Lett 82:3360
Grunwaldt J-D, Hannemann S, Schroer CG, Baiker A (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:8674
Bergwerff JA, van de Water LGA, Visser T, de Peinder P, Leliveld BRG, de Jong KP, Weckhuysen BM (2005) Chem Eur J 11:4592
Holzwarth A, Schmidt H-W, Maier WF (1998) Angew Chem Int Ed 37:2644
Grunwaldt J-D, Kimmerle B, Hannemann S, Baiker A, Boye P, Schroer CG (2007) J Mater Chem 17:2603
Busch OM, Brijoux W, Thomson S, Schuth F (2004) J Catal 222:174
Stavitski E, Kox MHF, Swart I, de Groot FMF, Weckhuysen BM (2008) Angew Chem Int Ed 47:3543
Hickman DA, Haupfear EA, Schmidt LD (1993) Catal Lett 17:223
Tyulenin YP, Savkin VV, Sinev MY, Korchak VN (2002) Kin Catal 43:847
Mallens EPJ, Hoebink J, Marin GB (1997) J Catal 167:43
Hickman DA, Schmidt LD (1992) J Catal 138:267
Vernon PDF, Green MLH, Cheetham AK, Ashcroft AT (1990) Catal Lett 6:181
Heitnes K, Lindberg S, Rokstad OA, Holmen A (1995) Catal Today 24:211
Yang SW, Kondo JN, Hayashi K, Hirano M, Domen K, Hosono H (2004) Appl Catal A 277:239
Rabe S, Nachtegaal M, Vogel F (2007) Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:1461
Deutschmann O, Schmidt LD (1998) AIChE J 44:2465
Quiceno R, Deutschmann O, Warnatz J, Perez-Ramirez J (2007) Catal Today 119:311
Basini L, Aasberg-Petersen K, Guarinoni A, Ostberg M (2001) Catal Today 64:9
Grunwaldt J-D, Basini L, Clausen BS (2001) J Catal 200:321
Grunwaldt J-D, Kappen P, Basini L, Clausen BS (2002) Catal Lett 78:13
Nakagawa K, Ikenaga NO, Kobayashi T, Suzuki T (2001) Catal Today 64:31
Basile F, Fornasari G, Trifirò F, Vaccari A (2001) Catal Today 64:21
Horn R, Williams KA, Degenstein NJ, Schmidt LD (2007) Chem Eng Sci 62:1298
Grunwaldt J-D, Baiker A (2005) Catal Lett 99:5
Strobel R, Grunwaldt J-D, Camenzind A, Pratsinis SE, Baiker A (2005) Catal Lett 104:9
Hannemann S, Grunwaldt JD, Lienemann P, Gunther D, Krumeich F, Pratsinis SE, Baiker A (2007) Appl Catal A 316:226
Grunwaldt J-D, Caravati M, Hannemann S, Baiker A (2004) Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:3037
Clausen BS, Grabaek L, Topsoe H, Hansen LB, Stoltze P, Nørskov JK, Nielsen OH (1993) J Catal 141:368
Sankar G, Thomas JM, Chen J, Wright PA, Barrett PA, Greaves GN, Catlow CRA (1995) Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 97:37
Clausen BS, Topsoe H, Frahm R (1998) Adv Catal 42:315
Grunwaldt J-D, Clausen BS (2002) Topics Catal 18:37
Hsieh CK, Yeyinmen IM, Hsia JJG, Keskin I (1967) In: Touloukian YS (ed) Thermophysical properties of high temperature solid materials. Macmillan Company, New York, p 405
Frahm R (1989) Physica B 158:342
Newton MA, Jyoti B, Dent AJ, Fiddy SG, Evans J (2004) Chem Commun 2382
Hannemann S, Grunwaldt J-D, van Vegten N, Baiker A (2007) Catal Today 54
Bazin D, Rehr JJ (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:12398
York APE, Xiao TC, Green MLH (2003) Topics Catal 22:345
Gelin P, Primet M (2002) Appl Catal B 39:1
Freni S, Calogero G, Cavallaro S (2000) J Power Source 87:28
Williams KA, Leclerc CA, Schmidt LD (2005) AIChE J 51:247
Rabe S, Truong TB, Vogel F (2005) Appl Catal A 292:177
Hu YH, Ruckenstein E (2004) Adv Catal 48:297
Li BT, Kado S, Mukainakano Y, Miyazawa T, Miyao T, Naito S, Okumura K, Kunimori K, Tomishige K (2007) J Catal 245:144
Acknowledgements
We thank HASYLAB at DESY (Hamburg, Germany) for providing beamtime and support by Dr. Adam Webb, Mathias Herrmann and Bernd Reime throughout the measurements at the beamline X1. Furthermore, we are grateful to SLS (Villigen, Switzerland) for providing beamtime including support by Dr. C. Borca and Dr. D. Grolimund at the microXAS beamline. Pergam Suisse AG (Zurich, Switzerland) is thanked for lending the infrared camera and the help with its handling. Financial support for the spatially resolved XAS measurements is gratefully acknowledged by DESY/HASYLAB and the European Community – Research Infrastructure Action under the FP6: “Structuring the European Research Area” (“Integrating Activity on Synchrotron and Free Electron Laser Science” (IA-SFS) RII3-CT-2004-506008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hannemann, S., Grunwaldt, JD., Kimmerle, B. et al. Axial Changes of Catalyst Structure and Temperature in a Fixed-Bed Microreactor During Noble Metal Catalysed Partial Oxidation of Methane. Top Catal 52, 1360–1370 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9315-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9315-0