Abstract
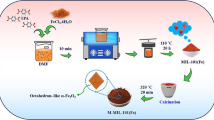
Here, we prepared a series of Fe-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs), including MIL-53(Fe), NH2-MIL-53(Fe), MIL-88B(Fe) and NH2-MIL-88B(Fe), via an oil bath process and used them to remove methylene blue under visible light. A comparative study of NH2-MILs and Fe-MILs was conducted. The experimental results showed that the presence of amino groups could improve the adsorption capacities of NH2-MILs, which was attributed to hydrogen bonding interactions and π–π stacking between the amino groups of the dye molecules and the amino-functionalized MOFs. The photocatalytic activities of NH2-MILs under visible light were higher than those of Fe-MILs, owing to the enhancement of visible-light absorption, the decrease in the band gap and the improvement of the adsorption capacity. After several photodegradation experiments, the catalytic activities decreased and could be restored by irradiating the catalysts with ultraviolet light. This study indicated that the amino-functionalized materials had great potential for wastewater treatment and resource utilization.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brillas E, Martínez-Huitle CA (2015) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods. Appl Catal B Environ 166:603–643
Tawfik A, Zaki DF, Zahran MK (2014) Degradation of reactive dyes wastewater supplemented with cationic polymer (Organo Pol.) in a down flow hanging sponge (DHS) system. J Ind Eng Chem 20:2059–2065
Castellanos NJ, Rojas ZM, Camargo HA et al (2019) Congo red decomposition by photocatalytic formation of hydroxyl radicals (·OH) using titanium metal–organic frameworks. Transit Met Chem 44:77–87
Liu L, Zhang J, Tan Y et al (2014) Rapid decolorization of anthraquinone and triphenylmethane dye using chloroperoxidase: catalytic mechanism, analysis of products and degradation route. Chem Eng J 244:9–18
Khansorthong S, Hunsom M (2009) Remediation of wastewater from pulp and paper mill industry by the electrochemical technique. Chem Eng J 151:228–234
Huo SH, Yan XP (2012) Metal–organic framework MIL-100 (Fe) for the adsorption of malachite green from aqueous solution. J Mater Chem 22:7449–7455
Feng L, Ren G, Wang F et al (2019) Two bimetallic metal–organic frameworks capable of direct photocatalytic degradation of dyes under visible light. Transit Met Chem 44:275–281
Meehan C, Bjourson AJ, McMullan G (2001) Paenibacillus azoreducens sp. nov., a synthetic azo dye decolorizing bacterium from industrial wastewater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1681–1685
Jia Y, Jin Q, Li Y et al (2015) Investigation of the adsorption behaviour of different types of dyes on MIL-100 (Fe) and their removal from natural water. Anal Methods 7:1463–1470
Haque E, Jun JW et al (2011) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with a metal–organic framework material, iron terephthalate (MOF-235). J Hazard Mater 185:507–511
Liu H, Ren X, Chen L (2016) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal–organic framework for the adsorptive removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. J Ind Eng Chem 34:278–285
Li JX, Qin ZB, Li YH et al (2018) Sonochemical synthesis and properties of two new nanostructured silver (I) coordination polymers. Ultrason Sonochem 48:127–135
Hao SY, Li YH, Zhu J et al (2018) Structures, luminescence and photocatalytic properties of two nanostructured cadmium (II) coordination polymers synthesized by sonochemical process. Ultrason Sonochem 40:68–77
Lee JY, Farha OK, Roberts J et al (2009) Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem Soc Rev 38:1450–1459
Yao SL, Liu SJ, Tian XM et al (2019) A ZnII-based metal–organic framework with a rare tcj topology as a turn-on fluorescent sensor for acetylacetone. Inorg Chem 58:3578–3581
Keskin S, Kızılel S (2011) Biomedical applications of metal organic frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:1799–1812
Kumar P, Vellingiri K, Kim KH et al (2017) Modern progress in metal–organic frameworks and their composites for diverse applications. Micropor Mesopor Mater 253:251–265
Shi L, Wang T, Zhang H et al (2015) An amine-functionalized iron (III) metal–organic framework as efficient visible-light photocatalyst for Cr(VI) reduction. Adv Sci 2:1–8
Kang WC, Li YH, Qin ZB et al (2018) Synthesis, structures and characterization of two cobalt (II) coordination polymers with 2,5-dichloroterephthalic acid and flexible bis (benzimidazole) ligands. Transit Met Chem 43:563–570
Liang R, Chen R, Jing F et al (2015) Multifunctional polyoxometalates encapsulated in MIL-100 (Fe): highly efficient photocatalysts for selective transformation under visible light. Dalton Trans 44:18227–18236
Laurier KGM, Vermoortele F, Ameloot R et al (2013) Iron (III)-based metal–organic frameworks as visible light photocatalysts. J Am Chem Soc 135:14488–14491
Tan F, Liu M, Li K et al (2015) Facile synthesis of size-controlled MIL-100 (Fe) with excellent adsorption capacity for methylene blue. Chem Eng J 281:360–367
Ai L, Zhang C, Li L et al (2014) Iron terephthalate metal–organic framework: revealing the effective activation of hydrogen peroxide for the degradation of organic dye under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 148:191–200
Li X, Guo W, Liu Z et al (2016) Fe-based MOFs for efficient adsorption and degradation of acid orange 7 in aqueous solution via persulfate activation. Appl Surf Sci 369:130–136
Wang D, Jia F, Wang H et al (2018) Simultaneously efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by Fe-based MOFs. J Colloid Interface Sci 519:273–284
Liu Y, Gao P, Huang C et al (2015) Shape-and size-dependent catalysis activities of iron-terephthalic acid metal–organic frameworks. Sci China Chem 58:1553–1560
Lin S, Song Z, Che G et al (2014) Adsorption behavior of metal–organic frameworks for methylene blue from aqueous solution. Micropor Mesopor Mat 193:27–34
Du JJ, Yuan YP, Sun JX et al (2011) New photocatalysts based on MIL-53 metal–organic frameworks for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J Hazard Mater 190:945–951
Liu YL, Zhao XJ, Yang XX et al (2013) A nanosized metal–organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH2 as a novel peroxidase mimic used for colorimetric detection of glucose. Analyst 138:4526–4531
Alqadami AA, Naushad M, Alothman ZA et al (2018) Adsorptive performance of MOF nanocomposite for methylene blue and malachite green dyes: kinetics, isotherm and mechanism. J Environ Manage 223:29–36
Naushad M, Za AlOthman, Awual MR et al (2016) Adsorption of rose Bengal dye from aqueous solution by amberlite Ira-938 resin: kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin Water Treat 57:13527–13533
Li C, Xiong Z, Zhang J et al (2015) The strengthening role of the amino group in metal–organic framework MIL-53 (Al) for methylene blue and malachite green dye adsorption. J Chem Eng Data 60:3414–3422
Liu B, Yang F, Zou Y et al (2014) Adsorption of phenol and p-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions on metal–organic frameworks: effect of hydrogen bonding. J Chem Eng Data 59:1476–1482
Acknowledgements
This project was granted financial support from the Henan Province program for science and technology development (16210221247) and the Program of Henan Province Department of Education (15A430053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Zhang, L., Wang, X. et al. Simultaneous efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue over iron(III)-based metal–organic frameworks: a comparative study. Transit Met Chem 44, 789–797 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-019-00349-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-019-00349-9