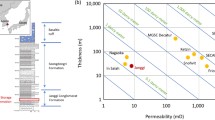
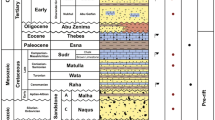
Abstract
This article presents the results of CO2/brine two-phase flow experiments in rocks at reservoir conditions. X-ray CT scanning is used to determine CO2 saturation at a fine scale with a resolution of a few pore volumes and provide 3D porosity and saturation maps that can be use to correlate CO2 saturations and rock properties. The study highlights the strong influence of sub-core scale heterogeneities on the spatial distribution of CO2 at steady state and provides useful relative permeability data on a sample originated from an actual storage site (CO2CRC-Otway project, Victoria, South-West Australia). Two different samples tested, although different in nature, present strong heterogeneities, but differ in the detail of the connectivity of high porosity layers. In both samples, the results of the investigations show that sub-core scale heterogeneities control the sweep efficiency and may cause channeling through the porous medium. In one of the samples, CO2 saturation appears uncorrelated to porosity close to the outlet end of the core. This observation is understood as a result of the position and the orientation of high porosity layers with respect to the inlet face of the core. Finally, in the operating conditions of the two experiments, the saturation maps demonstrate that gravity does not play a major role since no detectable buoyancy driven flow is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akin, S., Kovscek, A.R.: Computed tomography in petroleum engineering research. In: Akin, S., Kovscek, A.R. (eds.) Applications of X-Ray Computed Tomography in the Geosciences, vol. 215, pp. 23–38. Geological Society, London (2003) (Special Publications, 0305-8719/03/$15. © The Geological Society of London)
Bachu S., Bennion D.B.: Effects of in-situ conditions on relative permeability characteristics of CO2-brine systems. Environ. Geol. 54, 1707–1722 (2008)
Bennion, D.B., et al.: Relative Permeability Characteristics for Supercritical CO2 Displacing Water in a Variety of Potential Sequestration Zones in the Western Canada Sedimendary Basin. SPE 95547 (2005)
Bennion, D.B., et al.: Dependence on Temperature, Pressure, and Salinity of the IFT and Relative Permeability Displacement Characteristics of CO2 Injected in Deep Saline Aquifers. SPE 102138 (2006a)
Bennion, D.B., et al.: The Impact of Interfacial Tension and Pore Size Distribution/Capillary Pressure Character on CO2 Relative Permeability at Reservoir Conditions in CO2-Brine Systems. SPE 99325-MS (2006b)
Bennion, D.B., et al.: Spercritical CO2 and H2S-Brine Drainage and Imbibition Relative Permeability Relationships for Intergranular Sandstone and Carbonate Formations. SPE 99326 (2006c)
Benson, S.M., et al.: Core Scale and Pore Scale Studies of Carbon Dioxide Migration in Saline Formations. In: Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, IEA Greenhouse Gas Program, Trondheim, Norway (2006)
Caruana A., Dawe R.A.: Flow behaviour in the presence of wettability heterogeneities. Trans. Porous. Med. 25, 217–233 (1996)
Crotti, M.A., et al.: Relative Permeability Curves: The influence of Flow Direction and Heterogeneities. Dependence of End Point Saturations on Displacement Mechanisms. SPE 39657 (1998)
Honarpour, M., Koederitz, L., Harvey, A.H.: Relative Permeability of Petroleum Reservoir. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA (1986). ISBN 0-8493-5739-X
Huppler, H.D.: Numerical Investigation of the Effects of Core Heterogeneities on Waterflood Relative Permeability, vol. 249, p. 381. AIME (1970)
Perrin J.-C. et al.: Core-scale experimental study of relative permeability properties of CO2 and brine in reservoir rocks. Energy Procedia 1(1), 3515–3522 (2009)
Schembre J.M., Kovscek A.R.: A technique for measuring two-phase relative permeability in porous media via X-ray CT measurements. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 39, 159–174 (2003)
Shi J.-Q. et al.: History matching of CO2 core flooding CT scan saturation profiles with porosity dependant capillary pressure. Energy Procedia 1(1), 3205–3211 (2009)
Tetsuya S. et al.: Geological storage of carbon dioxide by residual gas and solubility trapping. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2, 58–64 (2008)
Wellington S.L., Vinegar H.J.: X-ray computerized tomography. J. Pet. Technol. 39, 885–898 (1987)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrin, JC., Benson, S. An Experimental Study on the Influence of Sub-Core Scale Heterogeneities on CO2 Distribution in Reservoir Rocks. Transp Porous Med 82, 93–109 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9426-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9426-x