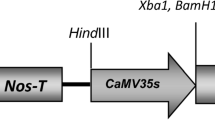
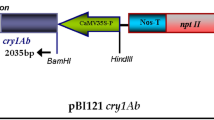
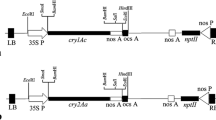
Abstract
Tomato leaf miner (Tuta absoluta) is a major pest of tomato in regions with hot climates such as South America and the Mediterranean. This insect feeds on almost every part of the plant and forms galleries while feeding on the plant’s inner tissues. Thus, it can cause plant death and is costly and difficult to control with chemical sprays. In this study, we transferred a modified Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ac gene to tomato plants via Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation. Introduction of the cry1Ac gene to the tomato genome was confirmed with PCR and Southern blot analysis in 12 independent events. Insertion sites of the transgene in the tomato genome were determined with TAIL-PCR (thermal asymmetric interlaced polymerase chain reaction) for four selected transgenic lines. Cry1Ac gene expression was verified at both the transcriptional and translational levels, with RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses, respectively. Expression of the Cry1Ac protein in tomato resulted in T. absoluta mortality rates of 38–100% depending on transgenic line. In addition, gallery formation was reduced in 57–100% of the transgenic plants. Moreover, it was found that a single copy of the gene in the hemizygous condition is sufficient to confer tolerance to leaf miner. This is the first reported development of tomato plants resistant to T. absoluta. These transgenic plants are promising for development of commercial tomato cultivars resistant to leaf miner, which will limit the use of environmentally harmful chemicals for control of this pest.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Abdallat AM, Ali-Sheikh-Omar MA, Alnemer LM (2015) Overexpression of two ATNAC3-related genes improves drought and salt tolerance in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:989–1001
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Chem 72:248–254
Bravo A, Gill S, Soberón M (2005) Bacillus thuringiensis mechanisms and use. In: Gilbert LL, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive molecular insect science, 6th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 175–205
Canedo V, Benavides J, Golmirzaie A, Cisneros F, Ghislain M, Lagnaoui A (1997) Assessing Bt-transformed potatoes for potato tuber moth, Phthorimaea operculella (Zeller), management. Program Rep 98:161–170
Cheng X, Sardana R, Kaplan H, Altosaar I (1998) Agrobacterium-transformed rice plants expressing synthetic cryIA (b) and cryIA (c) genes are highly toxic to striped stem borer and yellow stem borer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2767–2772
Delannay X, LaVallee BJ, Proksch RK, Fuchs RL, Sims SR, Greenplate JT, Marrone PG, Dodson RB, Augustine JJ, Layton JG, Fischhoff DA (1989) Field performance of transgenic tomato plants expressing the Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki insect control protein. Nat Biotechnol 7:1265–1269
Desneux N, Wajnberg E, Wyckhuys KA, Burgio G, Arpaia S, Narváez-Vasquez CA, González-Cabrera J, Ruescas DC, Tabone E, Frandon J, Pizzol J (2010) Biological invasion of European tomato crops by Tuta absoluta: ecology, geographic expansion and prospects for biological control. J Pest Sci 83:197–215
Desneux N, Luna MG, Guillemaud T, Urbaneja A (2011) The invasive South American tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta, continues to spread in Afro-Eurasia and beyond: the new threat to tomato world production. J Pest Sci 84:403–408
EPPO (European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization) (2005) EPPO reporting service. http://archives.eppo.int/EPPOReporting/2005/Rse-0509.pdf. Accessed 15 Sept 2015
Expósito-Rodríguez M, Borges AA, Borges-Pérez A, Pérez JA (2008) Selection of internal control genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies during tomato development process. BMC Plant Biol 8:131
Ferré J, Van Rie J, MacIntosh SC (2008) Insecticidal genetically modified crops and insect resistance management (IRM). In: Romeis J, Shelton AM, Kennedy GG (eds) Integration of insect-resistant genetically modified crops within IPM programs, 5th ed. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 41–85
Fischhoff DA, Bowdishi KS, Perlak FJ, Marrone PG, McCormick SM, Niedermeyer JG, Dean DA, Kusano-Kretzmer K, Mayer EJ, Rochester DE, Rogers SG (1987) Insect tolerant transgenic tomato plants. Nat Biotechnol 5:807–813
Frary A, Van Eck J (2004) Organogenesis from transformed tomato explants. In: Pena L (ed) Transgenic plants: methods and protocols. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 141–150
Gerszberg A, Hnatuszko-Konka K, Kowalczyk T, Kononowicz AK (2015) Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) in the service of biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:881–902
González-Cabrera J, Mollá O, Montón H, Urbaneja A (2010) Efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis (Berliner) in controlling the tomato borer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Biocontrol 56:71–80
James C (2007) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops, 2007, vol 37. ISAAA Ithaca, New York
Kılıç T (2010) First record of Tuta absoluta in Turkey. Phytoparasitica 38:243–244
Knowles BH, Dow JA (1993) The crystalδ-endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis: models for their mechanism of action on the insect gut. Bioessays 15:469–476
Koul B, Srivastava S, Sanyal I, Tripathi B, Sharma V, Amla DV (2014) Transgenic tomato line expressing modified Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ab gene showing complete resistance to two lepidopteran pests. Springerplus 3:84–96
Kumar H, Kumar V (2004) Tomato expressing Cry1A(b) insecticidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis protected against tomato fruit borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) damage in the laboratory, greenhouse and field. Crop Prot 23:135–139
Li XQ, Wei JZ, Tan A, Aroian RV (2007) Resistance to root-knot nematode in tomato roots expressing a nematicidal Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein. Plant Biotechnol J 5:455–464
Lietti MMM, Botto E, Alzogaray RA (2005) Insecticide resistance in Argentine populations of Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Neotrop Entomol 34:113–119
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Maluf WR, Silva VD, Cardoso MD, Gomes LAA, Neto ACG, Maciel GM, Nizio DAC (2010) Resistance to the South American tomato pinworm Tuta absoluta in high acylsugar and/or high zingiberene tomato genotypes. Euphytica 176:113–123
Mandaokar A et al (2000) Transgenic tomato plants resistant to fruit borer (Helicoverpa armigera Hubner). Crop Prot 19:307–312
Metwali EM, Soliman HI, Fuller MP, Almaghrabi OA (2015) Improving fruit quality in tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum Mill) under heat stress by silencing the vis 1 gene using small interfering RNA technology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 121:153–166
Pillai MM, Venkataraman GM, Kosak S, Torok-Storb B (2008) Integration site analysis in transgenic mice by thermal asymmetric interlaced (TAIL)-PCR: segregating multiple-integrant founder lines and determining zygosity. Transgenic Res 17:749–754
Ponti L, Gutierrez AP, Altieri MA (2015) Holistic approach in invasive species research: the case of the tomato leaf miner in the Mediterranean Basin. Agroecol and Sust Food 39:436–468
Riquelme V, Botto E, Lafalce C (2006) Efficacy of insecticides against the "tomato moth", Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) and their residual effects on the parasitoid Trichogrammatoidea bactrae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Rev Soc Entomol Argent 65(3–4):57–65
Roditakis E, Vasakis E, Grispou M, Stavrakaki M, Nauen R, Gravouil M, Bassi A (2015) First report of Tuta absoluta resistance to diamide insecticides. J Pest Sci 88:9–16
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (1999) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Misener S, Krawetz S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 365–386
Saker MM, Salama HS, Salama M, El-Banna A, Abdel Ghany NM (2011) Production of transgenic tomato plants expressing Cry 2Ab gene for the control of some lepidopterous insects endemic in Egypt. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 9:149–155
Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P (2011) Bacillus thuringiensis: a century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J 9:283–300
Shah SH, Ali S, Jan SA, Ali GM (2015) Piercing and incubation method of in planta transformation producing stable transgenic plants by overexpressing DREB1A gene in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 120:1139–1157
Sharada MS, Kumari A, Pandey AK, Sharma S, Sharma P, Sreelakshmi Y, Sharma R (2017) Generation of genetically stable transformants by Agrobacterium using tomato floral buds. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 129:299–312
Silva GA, Picanco MC, Bacci L, Crespo AL, Rosado JF, Guedes RN (2011) Control failure likelihood and spatial dependence of insecticide resistance in the tomato pinworm, Tuta absoluta. Pest Manag Sci 67:913–920
Siqueira HÁA, Guedes RNC, Picanço MC (2000) Insecticide resistance in populations of Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Agric For Entomol 2:147–153
Spannagl M, Noubibou O, Haase D, Yang L, Gundlach H, Hindemitt T, Klee K, Haberer G, Schoof H, Mayer KF (2007) MIPSPlantsDB—plant database resource for integrative and comparative plant genome research. Nucleic Acids Res 35(suppl 1):D834–D840
Stewart CN Jr, Via LE (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR applications. Biotechniques 14:748–750
Urbaneja A, Gonzalez-Cabrera J, Arno J, Gabarra R (2012) Prospects for the biological control of Tuta absoluta in tomatoes of the Mediterranean basin. Pest Manag Sci 68:1215–1222
Yang C, Zhang D, Yang L (2013) Development of event-specific PCR detection methods for genetically modified tomato Huafan No. 1. J Sci Food Agric 93:652–660
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. I. Altosaar, University of Ottawa, Canada for the cry gene construct. This work was supported by a grant from Izmir Institute of Technology (2014-IYTE-32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HS transformed plants, performed molecular analyses and drafted paper with AF; FD and NM designed and performed insect bioassays; SD and AF devised and oversaw experimental work.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jose M. Segui-Simarro.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selale, H., Dağlı, F., Mutlu, N. et al. Cry1Ac-mediated resistance to tomato leaf miner (Tuta absoluta) in tomato. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 131, 65–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1262-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1262-z