Abstract
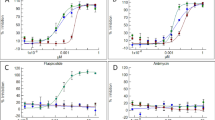
Although transgenic crops expressing either Cry1Ab or Cry1Ac, both derived from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), have been used commercially, the evolution of insects resistance to these CRY proteins has become a challenge. Thus, it has been proposed that co-expression of two Bt proteins with different modes of action may delay the development of resistance to Bt. However, few Bt proteins have been identified as having different modes of action from those of Cry1Ab or Cry1Ac. In this study, transgenic lines of maize over-expressing either Cry1Ie or Cry1Ac gene have been developed. Several independent transgenic lines with one copy of the foreign gene were identified by Southern blot analysis. Bioassays in the laboratory showed that the transgenic plants over-expressing Cry1Ie were highly toxic against the wild-type cotton bollworm (Heliothis armigera), producing mortality levels of 50 % after 6 days of exposure. However, the mortality caused by these plants was lower than that caused by the Cry1Ac transgenic plants (80 %) and MON810 plants expressing Cry1Ab (100 %), which both exhibited low toxicity toward the Cry1Ac-resistant cotton bollworm. In contrast, three transgenic maize lines expressing Cry1Ie induced higher mortality against this pest and were also highly toxic to the Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) in the field. These results indicate that the Cry1Ie protein has a different mode of action than the Cry1Ab and Cry1Ac proteins. Therefore, the use of transgenic plants expressing Cry1Ie might delay the development of Bt-resistant insects in the field.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates SL, Zhao JZ, Roush RT, Shelton AM (2005) Insect resistance management in GM crops: past, present and future. Nat Biotechnol 23(1):57–62
Bergamasco V, Goncalves J, Polanczyk R, Desiderio J, Lemon M (2011) Expression of a new Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ia gene in Escherichia coli with strong activity against cotton pests. Aust J Bas Appl Sci 5(12):526–533
Bravo A, Soberon M (2008) How to cope with insect resistance to Bt toxins? Trends Biotechnol 26(10):573–579
Chitkowski RL, Turnipseed SG, Sullivan MJ, Bridges WC Jr (2003) Field and laboratory evaluations of transgenic cottons expressing one or two Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki Berliner proteins for management of noctuid (Lepidoptera) pests. J Econ Entomol 96(3):755–762
Choi SK, Shin BS, Kong EM, Rho HM, Park SH (2000) Cloning of a new Bacillus thuringiensis cry1I-type crystal protein gene. Curr Microbiol 41(1):65–69
Ferre J, Van Rie J (2002) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 47:501–533
Gatehouse JA (2008) Biotechnological prospects for engineering insect-resistant plants. Plant Physiol 146(3):881–887
He K, Wang Z, Zhou D, Wen L, Song Y (2000) Methodologies and criterions for evaluating maize resistance to Asian maize borer. J Shenyang Agric Univ 31:439–443
James C (2013) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2012. ISAAA Brief 44-2012
Jurat-Fuentes JL, Karumbaiah L, Jakka SR, Ning C, Liu C, Wu K, Jackson J, Gould F, Blanco C, Portilla M, Perera O, Adang M (2011) Reduced levels of membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase are common to lepidopteran strains resistant to Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. PLoS One 6(3):e17606
Kota M, Daniell H, Varma S, Garczynski SF, Gould F, Moar WJ (1999) Overexpression of the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry2Aa2 protein in chloroplasts confers resistance to plants against susceptible and Bt-resistant insects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(5):1840–1845
Koziel MG, Beland GL, Bowman C, Carozzi NB, Crenshaw R, Crossland L, Dawson J, Desai N, Hill M, Kadwell S, Launis K, Lewis K, Maddox D, McPherson K, Meghji MR, Merlin E, Rhodes R, Warren GW, Wright M, Evola SV (1993) Field performance of elite transgenic maize plants expressing an insecticidal protein derived from Bacillus thuringiensis. Nat Biotechnol 11(2):194–200
Lian Y, Jia Z, He K, Liu Y, Song F, Wang B, Wang G (2008) Transgenic tobacco plants expressing synthetic Cry1Ac and Cry1Ie genes are more toxic to cotton bollworm than those containing one gene. Chin Sci Bull 53:1381–1387
Liang GM, Wu KM, Yu HK, Li KK, Feng X, Guo YY (2008) Changes of inheritance mode and fitness in Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) along with its resistance evolution to Cry1Ac toxin. J Invertebr Pathol 97(2):142–149
Liu YJ, Song FP, He KL, Yuan Y, Zhang XX, Gao P, Wang JH, Wang GY (2004a) Expression of a modified Cry1Ie gene in E. coli and in transgenic tobacco confers resistance to corn borer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 36(4):309–313
Liu YJ, Yuan Y, Zheng J, Tao YZ, Dong ZG, Wang JH, Wang GY (2004b) Signal peptide of potato PinII enhances the expression of Cry1Ac in transgenic tobacco. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 36(8):553–558
Ruiz de Escudero I, Estela A, Porcar M, Martinez C, Oguiza JA, Escriche B, Ferre J, Caballero P (2006) Molecular and insecticidal characterization of a Cry1I protein toxic to insects of the families Noctuidae, Tortricidae, Plutellidae, and Chrysomelidae. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):4796–4804
Soberon M, Pardo-Lopez L, Lopez I, Gomez I, Tabashnik BE, Bravo A (2007) Engineering modified Bt toxins to counter insect resistance. Science 318(5856):1640–1642
Song F, Zhang J, Gu A, Wu Y, Han L, He K, Chen Z, Yao J, Hu Y, Li G, Huang D (2003) Identification of cry1I-type genes from Bacillus thuringiensis strains and characterization of a novel cry1I-type gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(9):5207–5211
Tabashnik BE, Gassmann AJ, Crowder DW, Carriere Y (2008) Insect resistance to Bt crops: evidence versus theory. Nat Biotechnol 26(2):199–202
Tabashnik BE, Unnithan GC, Masson L, Crowder DW, Li X, Carriere Y (2009) Asymmetrical cross-resistance between Bacillus thuringiensis toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in pink bollworm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(29):11889–11894
Tabashnik BE, Huang F, Ghimire MN, Leonard BR, Siegfried BD, Rangasamy M, Yang Y, Wu Y, Gahan LJ, Heckel DG, Bravo A, Soberon M (2011) Efficacy of genetically modified Bt toxins against insects with different genetic mechanisms of resistance. Nat Biotechnol 29(12):1128–1131
Tailor R, Tippett J, Gibb G, Pells S, Pike D, Jordan L, Ely S (1992) Identification and characterization of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin entomocidal to coleopteran and lepidopteran larvae. Mol Microbiol 6(9):1211–1217
Tohidfar M, Zare N, Jouzani G, Eftekhari S (2013) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) using a synthetic cry3a gene to enhance resistance against alfalfa weevil. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 113:227–235
Wu KM, Guo YY (2005) The evolution of cotton pest management practices in China. Annu Rev Entomol 50:31–52
Xu L, Wang Z, Zhang J, He K, Ferry N, Gatehouse A (2010) Cross-resistance of Cry1Ab-selected Asian corn borer to other Cry toxins. J Appl Entomol 134:429–438
Zhang X, Candas M, Griko NB, Taussig R, Bulla LA Jr (2006) A mechanism of cell death involving an adenylyl cyclase/PKA signaling pathway is induced by the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(26):9897–9902
Zhang S, Cheng H, Gao Y, Wang G, Liang G, Wu K (2009) Mutation of an aminopeptidase N gene is associated with Helicoverpa armigera resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 39(7):421–429
Zhang H, Yin W, Zhao J, Jin L, Yang Y, Wu S, Tabashnik BE, Wu Y (2011) Early warning of cotton bollworm resistance associated with intensive planting of Bt cotton in China. PLoS One 6(8):e22874
Zhao JZ, Cao J, Li Y, Collins HL, Roush RT, Earle ED, Shelton AM (2003) Transgenic plants expressing two Bacillus thuringiensis toxins delay insect resistance evolution. Nat Biotechnol 21(12):1493–1497
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the National Major Project for Transgenic Organism Breeding (2011ZX08003-001). We thank the editors from American Journal Experts for improving the English language in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yuwen Zhang and Yunjun Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Ren, Y. et al. Overexpression of a novel Cry1Ie gene confers resistance to Cry1Ac-resistant cotton bollworm in transgenic lines of maize. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 115, 151–158 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0348-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0348-5