Abstract
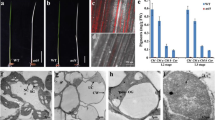
Two albino mutants (ab1 and ab2) have been derived from long-term shoot proliferation of Bambusa edulis. Based on transmission electronic microscopy data, the chloroplasts of these mutants were abnormal. To study the mutation of gene regulation in the aberrant chloroplasts, we designed 19 pairs of chloroplast-encoded gene primers for genomic and RT-PCR. Only putative NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase chain 4L (ndhE; DQ908943) and ribosomal protein S7 (rps7; DQ908931) were conserved in both the mutant and wild-type plants. The deletions in the chloroplast genome of these two mutants were different: nine genes were deleted in the chloroplast genomic aberration in ab1 and 11 genes in ab2. The chloroplast genes, NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase chain 4 (ndhD; DQ908944), chloroplast 50S ribosomal protein L14 (rpl14; DQ908934), and ATP synthase beta chain (atpB; DQ908948) were abnormal in both mutants. The gene expressions of 18 of these 20 genes were correlated with their DNA copy number. The two exceptions were: ATP synthase CF0 A chain (atpI; DQ908946), whose expression in both mutants was not reduced even though the copy number was reduced; ribosomal protein S19 (rps19; DQ908949), whose expression was reduced or it was not expressed at all even though there was no difference in genomic copy number between the wild-type and mutant plants. The genomic PCR results showed that chloroplast genome aberrations do occur in multiple shoot proliferation, and this phenomenon may be involved in the generation of albino mutants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caredda S, Devaux P, Sangwan RS, Proult I, Clément C (2004) Plastid ultrastructure and DNA related to albinism in androgenetic embryos of various barley (Hordeum vulgare) cultivars. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 76:35–43
Chen YR, Lin TL, Huang YF (1988) Variations in the plastids of albino plants derived from rice anther culture. Proc Natl Sci Counc B 12:62–68
Damasco OP, Graham GC, Henry RJ, Adkins SW, Smith MK (1996) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) detection of dwarf off-types in micropropagated Cavendish (Musa spp. AAA) bananas. Plant Cell Rep 16:118–123
Day A, Ellis THN (1984) Chloroplast DNA deletions associated with wheat plant regenerated from pollen: possible basis for maternal inheritance of chloroplasts. Cell 39:359–368
Duncan DB (1955) Multiple range and multiple F test. Biometrics 11:1–42
Dunford R, Walden RM (1991) Plastid genome structure and plastid-related transcript levels in albino barley plants derived from anther culture. Curr Genet 20:339–347
Genovesi AD, Magill CW (1979) Improved rate of callus and green plant production from rice anther culture following cold shock. Crop Sci 19:662–664
Hager M, Biehler K, Illerhaus J, Ruf S, Bock R (1999) Targeted inactivation of the smallest plastid genome-encoded open reading frame reveals a novel and essential subunit of the cytochrome b 6 f complex. EMBO J 18:5834–5842
Harada T, Ishikawa R, Niizeki M, Saito KI (1992) Pollen-derived rice calli that have large deletions in plastid DNA do not require protein synthesis in plastids for growth. Mol Gen Genet 233:145–150
Harada T, Sato T, Asaka D, Matsukawa I (1991) Large-scale deletions of rice plastid DNA in anther culture. Theor Appl Genet 81:157–161
Kubis S, Baldwin A, Patel R, Razzaq A, Dupree P, Lilley K, Kurth J, Leister D, Jarvis P (2003) The Arabidopsis ppi1 mutant is specifically defective in the expression, chloroplast import, and accumulation of photosynthetic proteins. Plant Cell 15:1859–1871
Lin CS, Chang WC (1998) Micropropagation of Bambusa edulis through nodal explants of field-grown culms and flowering of regenerated plantlets. Plant Cell Rep 17:617–620
Lin CS, Lin CC, Chang WC (2004) Effect of thidiazuron on vegetative tissue-derived somatic embryogenesis and flowering of Bambusa edulis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 76:75–82
Martin W, Stoebe B, Goremykin V, Hansmann S, Hasegawa M, Kowallik K (1998) Gene transfer to the nucleus and the evolution of chloroplasts. Nature 393:162–165
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 55:541–552
Rout GR, Das P (1994) Somatic embryogenesis and in vitro flowering of 3 species of bamboo. Plant Cell Rep 13:683–686
Ruf S, Biehler K, Bock R (2000) A small chloroplast-encoded protein as a novel architectural component of the light-harvesting antenna. J Cell Biol 149:369–377
Ruf S, Kössel H, Bock R (1997) Targeted inactivation of a tobacco intron–containing open reading frame reveals a novel chloroplast-encoded photosystem I–related gene. J Cell Biol 139:95–102
Sheu JJ, Yu TS, Tong WF, Yu SM (1996) Carbohydrate starvation stimulates differential expression of rice α-amylase genes that is modulated through complicated transcriptional and posttranscriptional processes. J Biol Chem 27:26998–27004
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Rev 26:31–43
Yu JJ, Vermaas WFJ (1990) Transcript levels and synthesis of photosystem II components in cyanobacterial mutants with inactivated photosystem II genes. Plant Cell 2:315–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, NT., Jane, WN., Tsay, HS. et al. Chloroplast genome aberration in micropropagation-derived albino Bambusa edulis mutants, ab1 and ab2 . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 88, 147–156 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9182-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9182-3