Abstract
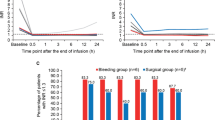
Major bleeding is a serious and potentially fatal complication of treatment with vitamin K antagonists (VKAs). Prothrombin complex concentrates (PCCs) can substantially shorten the time needed to reverse VKA effects. To determine the efficacy and safety of 3-factor PCCs for the rapid reversal of VKAs in patients with major bleeding. Patients receiving VKAs and suffering from acute major bleeding were eligible for this prospective cohort study if their international normalized ratio (INR) was higher than or equal to 2.0. Stratified 35–50 IU kg−1 PCC doses were infused based on initial INR. A total of 126 patients (62 males; mean age: 74 years, range 37–96 years) were enrolled. The mean INR at presentation was 3.3 (range 2–11). At 30 min after PCC administration the mean INR was 1.4 (range: 0.9–3.1), declining to less than or equal to 1.5 in 75 % of patients. The benefit of PCC was maintained for a long time, since in 97 % of all post-infusion time points through 96 h the mean INR remained lower than or equal to 1.5 (mean: 1.19; range: 0.9–2.3). During hospitalization neither thrombotic complications nor significant adverse events were observed and 12 patients died (10 %); none of the deaths was judged to be related to PCC administration. 3-factor PCC administration is an effective, rapid ad safe treatment for the urgent reversal of VKAs in patients with acute major bleeding. Broader use of PCC in this clinical setting appears to be appropriate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A et al (2012) Oral anticoagulant therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (9th Edition). Chest 141:e44S–e88S
Palareti G, Leali N, Coccheri S et al (1996) Bleeding complications of oral anticoagulant treatment: an inception-cohort, prospective collaborative trial (ISCOAT). Lancet 348:423–428
Ageno W, Garcia D, Aguilar MI et al (2009) Prevention and treatment of bleeding complications in patients receiving vitamin K antagonists, part 2: treatment. Am J Hematol 84:584–588
Nicolini A, Ghirarduzzi A, Iorio A et al (2002) Intracranial bleeding: epidemiology and relationships with antithrombotic treatment in 241 cerebral hemorrhages in Reggio Emilia. Haematologica 87:948–956
Baldi G, Altomonte F, Altomonte M et al (2006) Intracranial haemorrhage in patients on antithrombotics: clinical presentation and determinants of outcome in a prospective multicentric study in Italian emergency departments. Cerebrovasc Dis 22:286–293
Garcia DA, Regan S, Crowther M, Hylek EM (2006) The risk of hemorrhage among patients with warfarin-associated coagulopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:804–808
Go AS, Hylek EM, Chang Y et al (2003) Anticoagulation therapy for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: how well do randomized trials translate into clinical practice? JAMA 290:2685–2692
Rosand J, Eckman MH, Knudsen KA et al (2004) The effect of warfarin and intensity of anticoagulation on outcome of intracerebral hemorrhage. Arch Intern Med 164:880–884
Aguilar MI, Hart RG, Kase CS et al (2007) Treatment of warfarin-associated intracerebral hemorrhage: literature review and expert opinion. Mayo Clin Proc 82:82–92
Makris M, Greaves M, Phillips W et al (1997) Emergency oral anticoagulant reversal: the relative efficacy of infusion of fresh frozen plasma and clotting factor concentrate on correction of the coagulopathy. Thromb Haemost 77:477–480
Boulis NM, Bobek MP, Schmaier A, Hoff JT (1999) Use of factor IX complex in warfarin-related intracranial hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 45:1113–1118
Yasaka M, Sakata T, Minematsu K, Naritomi H (2002) Correction of INR by prothrombin complex concentrate and vitamin K in patients with warfarin related hemorrhagic complications. Thromb Res 108:25–30
Riess HB, Meier-Hellmann A, Motsch J et al (2007) Prothrombin complex concentrate (octaplex) in patients requiring immediate reversal of oral anticoagulation. Thromb Res 121:9–16
Lorenz R, Kienast J, Otto U et al (2007) Successful emergency reversal of phenprocoumon anticoagulation with prothrombin complex concentrate: a prospective clinical study. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 18:565–570
Leissinger CA, Blatt PM, Hoots WK, Ewenstein B (2008) Role of prothrombin complex concentrates in reversing warfarin anticoagulation: a review of the literature. Am J Hematol 83:137–143
Marietta M, Pedrazzi P, Girardis M, Torelli G (2007) Intracerebral haemorrage: an often neglected medical emergency. Intern Emerg Med 2:38–45
Yasaka M, Sakata T, Naritomi H, Minematsu K (2005) Optimal dose of prothrombin complex concentrate for acute reversal of oral anticoagulation. Thromb Res 115:455–459
Fredriksson K, Norrving B, Stromblad LG (1992) Emergency reversal of anticoagulation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 23:972–977
Cartmill M, Dolan G, Byrne JL, Byrne PO (2000) Prothrombin complex concentrate for oral anticoagulant reversal in neurosurgical emergencies. Br J Neurosurg 14:458–461
Huttner HB, Schellinger PD, Hartmann M et al (2006) Hematoma growth and outcome in treated neurocritical care patients with intracerebral hemorrhage related to oral anticoagulant therapy: comparison of acute treatment strategies using vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, and prothrombin complex concentrates. Stroke 37:1465–1470
Guidelines of the FCSA (2003) A guide to oral anticoagulant treatment. Haematologica 88(suppl .2): 1–47
Baglin TP, Keeling DM, Watson HG (2006) Guidelines on oral anticoagulation (warfarin): third edition—2005 update. Br J Haematol 132:277–285
Steiner T, Kaste M, Forsting M et al (2006) Recommendations for the management of intracranial haemorrhage—part I: spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage. The European Stroke Initiative Writing Committee and the Writing Committee for the EUSI Executive Committee. Cerebrovasc Dis 22:294–316
Freilone R, Polio B, Delios G et al (2009) Efficacy and safety of prothrombin complex concentrate (Uman complex) and vitamin K in a cohort of 56 patients with anticoagulation-related acute intracranial haemorrhage: clinical features and outcomes at three months. Haematologica 94(s4):114–115
Tiraferri E, Galletti M, Argento A (2004) Emergency use of prothrombin complex concentrates in oral anticoagulant therapy. Rapid reversal. Haematologica 89:177
Van Aart L, Eijkhout HW, Kamphuis JS et al (2007) Individualized dosing regimen for prothrombin complex concentrate more effective than standard treatment in the reversal of oral anticoagulant therapy: an open, prospective randomized controlled trial. Thromb Res 119:15–16
Imberti D, Barillari G, Biasioli C et al (2009) Prothrombin complex concentrates for urgent anticoagulation reversal in patients with intracranial haemorrhage. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 36:259–265
Evans G, Luddington R, Baglin T (2001) Beriplex P/N reverses severe warfarin induced overcoagulation immediately and completely in patients presenting with major bleeding. Br J Haematol 115:998–1001
Preston FE, Laidlaw ST, Sampson B, Kitchen S (2002) Rapid reversal of oral anticoagulation with warfarin by a prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex): efficacy and safety in 42 patients. Br J Haematol 116:619–624
Lankiewicz MW, Hays J, Friedman KD et al (2006) Urgent reversal of warfarin with prothrombin complex concentrate. J Thromb Haemost 4:967–970
Pabinger I, Brenner B, Kalina U et al (2008) Beriplex P/N anticoagulation reversal study group. Prothrombin complex concentrate (Beriplex P/N) for emergency anticoagulation reversal: a prospective multinational clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost 6:622–631
Viguè M, Ract C, Tremey B et al (2007) Ultra-rapid management of oral anticoagulant therapy-related surgical intracranial haemorrhage. Intensive Care Med 33:721–725
Imberti D, Barillari G, Biasioli C et al (2011) Emergency reversal of anticoagulation with a three-factor prothrombin complex concentrates in patients with intracranial haemorrhage. Blood Transfus 9:148–155
Dentali F, Marchesi C, Pierfranceschi MG et al (2011) Safety of prothrombin complex concentrates for rapid anticoagulation reversal of vitamin K antagonists. A meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost 106(3):429–438
Kessler CM (2006) Urgent reversal of warfarin with prothrombin complex concentrate: where are the evidence-base data? J Thromb Haemost 4:963–966
Holland L, Warkentin TE, Refaai M et al (2009) Suboptimal effect of a three-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (Profilnine-SD) in correcting supratherapeutic international normalized ratio due to warfarin overdose. Transfusion 49:1171–1177
Sorensen B, Johansen P, Nielsen GL et al (2003) Reversal of the International Normalized Ratio with recombinant activated factor VII in central nervous system bleeding during warfarin thromboprophylaxis: clinical and biochemical aspects. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 14:469–477
Freeman WD, Brott TG, Barrett KM et al (2004) Recombinant factor VIIa for rapid reversal of warfarin anticoagulation in acute intracranial hemorrhage. Mayo Clin Proc 7:1495–1500
Brody DL, Aiyagari V, Shackeford AM, Diringer MN (2005) Use of recombinant factor VIIa in patients with warfarin-associated intracranial hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 2:263–267
Dickneite G (2007) Prothrombin complex concentrate versus recombinant factor VIIa for reversal of coumarin anticoagulation. Thromb Res 119:643–651
Tanaka KA, Szlam F, Dickneite G, Levy JH (2008) Effects of prothrombin complex concentrate and recombinant activated factor VII on vitamin K antagonist induced anticoagulation. Thromb Res 122:117–123
Sørensen B, Spahn DR, Innerhofer P et al (2011) Clinical review: prothrombin complex concentrates–evaluation of safety and thrombogenicity. Crit Care 15(2):409
Franchini M, Lippi G (2010) Prothrombin complex concentrates: an update. Blood Transfus 8:149–154
Conflict of interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imberti, D., Magnacavallo, A., Dentali, F. et al. Emergency reversal of anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists with 3-factor prothrombin complex concentrates in patients with major bleeding. J Thromb Thrombolysis 36, 102–108 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0817-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0817-4