Abstract
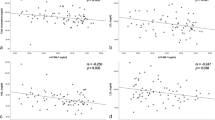
Tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interlekin-6 (IL-6) are key inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a disease also associated with endothelial perturbation and increased serum levels of adhesion molecules. As relationships between these processes and molecules are unclear, we tested the hypotheses (a) that TNF-α and IL-6 are linked to endothelial activation/damage and levels of soluble adhesion molecules, and (b) that intensive anti-inflammatory treatment improves levels of these indices. We recruited 66 patients with RA, 48 community controls (CC), and 25 disease controls (DC). Plasma TNF-α and IL-6 were compared to markers of vascular biology (vWF, sE-sel), soluble adhesion molecules (sICAM, sVCAM) and routine inflammatory markers (CRP and ESR). Blood was obtained at baseline and at 1 week and again 4 weeks after anti-inflammatory treatment in a subgroup of 29 patients with RA. With the exception of sE-selectin, RA patients had increased levels of all plasma markers compared to the HCs, whilst levels in the DCs were largely intermediate between RA and the CCs. Within the RA group, sEsel correlated with both CRP and ESR whilst TNF-α correlated with sVCAM (all r > 0.32, P < 0.01). After 1 week of combined anti-inflammatory therapy, only CRP, ESR, sEsel and sVCAM were significantly reduced (all P < 0.05). In RA, endothelial activation (as sEsel) correlates with classical markers of inflammation and is reduced by intensive anti-inflammatory medications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zvaifler NJ (1973) The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol 16:265–336. doi:10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60299-0
Scrivo R, Di Franco M, Spadaro A, Valesini G (2007) The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:312–322. doi:10.1196/annals.1422.033
Sfikakis PP, Tsokos GC (1997) Clinical use of the measurement of soluble cell adhesion molecules in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 4:241–246
Blann AD, Herrick A, Jayson MIV (1995) Soluble adhesion molecules E-selectin, ICAM and VCAM in the inflammatory vasculitides: relationship with disease severity and established laboratory indices. Br J Rheumatol 34:814–819. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/34.9.814
Ziff M (1989) Role of endothelium in chronic inflammation. Springer Semin Immunopathol 11:199–214. doi:10.1007/BF00197189
Rothschild BM, Masi AT (1982) Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: a vascular hypothesis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 12:11–31. doi:10.1016/0049-0172(82)90020-8
Del Rincón I, O’Leary DH, Freeman GL, Escalante A (2007) Acceleration of atherosclerosis during the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis 195:354–360. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.09.027
Hannawi S, Haluska B, Marwick TH, Thomas R (2007) Atherosclerotic disease is increased in recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: a critical role for inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 9:R116. doi:10.1186/ar2323
Bradley JR (2008) TNF-mediated inflammatory disease. J Pathol 214:149–160. doi:10.1002/path.2287
Smolen JS, Maini RN (2006) Interleukin-6: a new therapeutic target. Arthritis Res Ther 8(Suppl 2):S5. Erratum in: Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:407. doi:10.1186/ar1969
Maini RN, Brennan FM, Williams R, Chu CQ, Cope AP, Gibbons D, Elliott M, Feldmann M (1993) TNF-alpha in rheumatoid arthritis and prospects of anti-TNF therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol 11(Suppl 8):S173–S175
Haskard DO (1995) Cell adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 7:229–234. doi:10.1097/00002281-199505000-00012
Tervaert JW, Kallenberg CG (1997) Cell adhesion molecules in vasculitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 9:16–25
Volin MV (2005) Soluble adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Pharm Des 11:633–653. doi:10.2174/1381612053381972
Blann AD, Hopkins J, Winkles J, Wainwright AC (1992) Plasma and serum von Willebrand Factor antigen levels in connective tissue disorders. Ann Clin Biochem 29:67–71
Koch AE, Turkiewicz W, Harlow LA, Pope RM (1993) Soluble E-selectin in arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 69:29–35. doi:10.1006/clin.1993.1146
Blann AD (2000) Viewpoint: endothelial cell activation, injury, damage and dysfunction: separate entities or mutual terms? Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 11:623–630. doi:10.1097/00001721-200010000-00006
Cominacini L, Fratta Pasini A, Garbin U, Davoli A, De Santis A, Campagnola M, Rigoni A, Zenti MG, Moghetti P, Lo Cascio V (1995) Elevated levels of soluble E-selectin in patients with IDDM and NIDDM: relation to metabolic control. Diabetologia 38:1122–1124. doi:10.1007/BF00402185
Steiner M, Reinhardt KM, Krammer B, Ernst B, Blann AD (1994) Increased levels of soluble adhesion molecules in type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus are independent of glycaemic control. Thromb Haemost 72:979–984
Blann AD, Tse W, Maxwell SJ, Waite MA (1994) Increased levels of the soluble adhesion molecule E-selectin in essential hypertension. J Hypertens 12:925–928. doi:10.1097/00004872-199408000-00010
Blann AD, McCollum CN (1994) Circulating endothelial cell/leukocyte adhesion molecules in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 72:151–154
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324. doi:10.1002/art.1780310302
Emery P, Gabay C, Kraan M, Gomez-Reino J (2007) Evidence-based review of biologic markers as indicators of disease progression and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 27:793–806. doi:10.1007/s00296-007-0357-y
Williams B, Poulter NR, Brown MJ, Davis M, McInnes GT, Potter JF, Sever PS (2004) McG Thom S; British Hypertension Society. Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the fourth working party of the British Hypertension Society, 2004-BHS IV. J Hum Hypertens 18:139–185. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001683
British Cardiac Society, British Hypertension Society (2005) Diabetes UK; HEART UK; Primary Care Cardiovascular Society; Stroke Association. JBS 2: Joint British Societies’ guidelines on prevention of cardiovascular disease in clinical practice. Heart 91(Suppl 5):v1–v52. doi:10.1136/hrt.2005.079988
Sever PS, Dahlöf B, Poulter NR, Wedel H, Beevers G, Caulfield M, Collins R, Kjeldsen SE, McInnes GT, Mehlsen J, Nieminen M, O’Brien E, Ostergren J (2001) Rationale, design, methods and baseline demography of participants of the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial. ASCOT investigators. J Hypertens 19:1139–1147. doi:10.1097/00004872-200106000-00020
Tokuhira M, Hosaka S, Volin MV, Haines GKIII, Katschke KJ Jr, Kim S, Koch AE (2000) Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 mediation of monocyte chemotaxis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:1122–1133. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200005)43:5<1122::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-7
Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Alcocer-Varela J (1999) Interleukin-8, interleukin-10, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression levels are higher in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis than in osteoarthritis. Scand J Immunol 50:215–222. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.1999.00573.x
Kraan MC, Reece RJ, Barg EC, Smeets TJ, Farnell J, Rosenburg R, Veale DJ, Breedveld FC, Emery P, Tak PP (2000) Modulation of inflammation and metalloproteinase expression in synovial tissue by leflunomide and methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Findings in a prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-design clinical trial in thirty-nine patients at two centers. Arthritis Rheum 43:1820–1830. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1820::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-D
Littler AJ, Buckley CD, Wordsworth P, Collins I, Martinson J, Simmons DL (1997) A distinct profile of six soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, ICAM-3, VCAM-1, E-selectin, L-selectin and P-selectin) in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 36:164–169. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/36.2.164
Dessein PH, Joffe BI, Singh S (2005) Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction, cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R634–R643. doi:10.1186/ar1717
Marlor CW, Webb DL, Bombara MP, Greve JM, Blue ML (1992) Expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in fibroblast like synoviocytes after stimulation with tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol 140:1055–1060
Paleolog EM, Crossman DC, McVey JH, Pearson JD (1990) Differential regulation by cytokines of constitutive and stimulated secretion of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. Blood 75:688–695
van der Poll T, van Deventer SJ, Pasterkamp G, van Mourik JA, Büller HR, ten Cate JW (1992) Tumor necrosis factor induces von Willebrand factor release in healthy humans. Thromb Haemost 67:623–626
Becker JC, Dummer R, Hartmann AA, Burg G, Schmidt RE (1991) Shedding of ICAM-1 from human melanoma cell lines induced by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Functional consequences on cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol 147:4398–4401
Leeuwenberg JF, Smeets EF, Neefjes JJ, Shaffer MA, Cinek T, Jeunhomme TM, Ahern TJ, Buurman WA (1992) E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 are released by activated human endothelial cells in vitro. Immunology 77:543–549
Couffinhal T, Duplàa C, Labat L, Lamaziere JM, Moreau C, Printseva O, Bonnet J (1993) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates ICAM-1 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb 13:407–414
Scott DA, Stapleton JA, Wilson RF, Sutherland G, Palmer RM, Coward PY, Gustavsson G (2000) Dramatic decline in circulating intercellular adhesion molecule-1 concentration on quitting tobacco smoking. Blood Cells Mol Dis 26:255–258. doi:10.1006/bcmd.2000.0304
Blann AD, Steele C, McCollum CN (1997) The influence of smoking and of oral and transdermal nicotine on blood pressure, and haematology and coagulation indices. Thromb Haemost 78:1093–1096
Salat C, Boekstegers P, Holler E, Werdan K, Reinhardt B, Fateh-Moghadam S, Pihusch R, Kaul M, Beinert T, Hiller E (1996) Hemostatic parameters in sepsis patients treated with anti-TNF alpha-monoclonal antibodies. Shock 6:233–237. doi:10.1097/00024382-199610000-00001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, W., Carruthers, D., Lip, G.Y.H. et al. Inflammatory cytokines, endothelial markers and adhesion molecules in rheumatoid arthritis: effect of intensive anti-inflammatory treatment. J Thromb Thrombolysis 29, 437–442 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0370-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-009-0370-y