Abstract
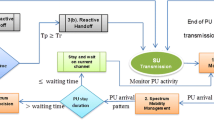
Cognitive radio networks use dynamic spectrum access of secondary users (SUs) to deal with the problem of radio spectrum scarcity . In this paper, we investigate the SU performance in cognitive radio networks with reactive-decision spectrum handoff. During transmission, a SU may get interrupted several times due to the arrival of primary (licensed) users. After each interruption in the reactive spectrum handoff, the SU performs spectrum sensing to determine an idle channel for retransmission. We develop two continuous-time Markov chain models with and without an absorbing state to study the impact of system parameters such as sensing time and sensing room size on several SU performance measures. These measures include the mean delay of a SU, the variance of the SU delay, the SU interruption probability, the average number of interruptions that a SU experiences, the probability of a SU getting discarded from the system after an interruption and the SU blocking probability upon arrival.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang, Y.-C., Chen, K.-C., Li, G. Y., & Mähönen, P. (2011). Cognitive radio networking and communications: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 60(7), 3386–3407.
Datla, D., Wyglinski, A. M., & Minden, G. J. (2009). A spectrum surveying framework for dynamic spectrum access networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(8), 4158–4168.
Federal Communications Commission. (2002) Spectrum Policy Task Force Report. Washington, DC: Federal Communications Commission. ET Docket No. 02–135.
Islam, M. H., Koh, C. L., Oh, S. W., Qing, X., Lai, Y. Y., Wang, C., Liang, Y.-C., Toh, B. E., Chin, F., Tan, G. L., & Toh, W. (2008). Spectrum survey in Singapore: occupancy measurements and analyses. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Communications, CrownCom 2008. Singapore: CrownCom. doi:10.1109/CROWNCOM.2008.4562457.
Mitola, J. (2000). Cognitive radio: An integrated agent architecture for software defined radio. PhD Dissertation, KTH, Stockholm.
Akyildiz, I. F., Lee, W.-Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2006). NeXt generation dynamic spectrum access cognitive radio wireless networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 50(13), 2127–2159.
Wang, C.-W., & Wang, L.-C. (2012). Analysis of reactive spectrum handoff in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 30(10), 2016–2028.
Huang, Y., & Wang, J. (2010). A multi-class preemptive priority cognitive radio system with random interruption discipline. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Queueing Theory and Network Applications, QTNA 2010 (pp. 162–168). Beijing: QTNA.
Wang, B., Ji, Z., Liu, K. J. R., & Clancy, T. C. (2009). Primary-prioritized Markov approach for dynamic spectrum allocation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Commununications, 8(4), 1854–1865.
Wong, E. W. A., & Foh, C. H. (2009). Analysis of cognitive radio spectrum access with finite user population. IEEE Communications Letters, 13(5), 294–296.
Pla, V., De Vuyst, S., De Turck, K., Bernal-Mor, E., Martinez-Bauset, J., & Wittevrongel, S. (2011). Saturation throughput in a heterogeneous multi-channel cognitive radio network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, ICC 2011. Kyoto: ICC. doi:10.1109/icc.2011.5963512.
Pacheco-Paramo, D., Pla, V., & Martinez-Bauset, J. (2009). Optimal admission control in cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Cognitive Radio Oriented Wireless Networks and Communications, CrownCom 2009. Hannover: CrownCom. doi:10.1109/CROWNCOM.2009.5189133.
Tang, S., & Mark, B. L. (2007). Performance analysis of a wireless network with opportunistic spectrum sharing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM 2007 (pp. 4636–4640). Washington: GLOBECOM.
Tang, S., & Mark, B. L. (2009). Modeling and analysis of opportunistic spectrum sharing with unreliable spectrum sensing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(4), 1934–1943.
Tang, S., & Mark, B. L. (2008). An analytical performance model of opportunistic spectrum access in a military environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, WCNC 2008 (pp. 2681–2686). Las Vegas: WCNC.
Sai Shankar, N. (2007). Squeezing the most out of cognitive radio: A joint MAC/PHY perspective. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP 2007 (Vol. IV, pp. 1361–1364). Honolulu: ICASSP.
Sai Shankar, N., Chou, C.-T., Challapali, K., & Mangold, S. (2005). Spectrum agile radio: Capacity and QoS implications of dynamic spectrum assignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM 2005 (pp. 2510–2516). St. Louis: GLOBECOM.
Chou, C.-T., Sai Shankar, N., Kim, H., & Shin, K. G. (2007). What and how much to gain by spectrum agility? IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 25(3), 576–588.
Wang, L.-C., & Chen, A. (2008). On the performance of spectrum handoff for link maintenance in cognitive radio. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Wireless Pervasive Computing, ISWPC 2008 (pp. 670–674). Santorini: ISWPC.
Song, Y., & Xie, J. (2011). Performance analysis of spectrum handoff for cognitive radio ad hoc networks without common control channel under homogeneous primary traffic. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2011 (pp. 3011–3019). Shanghai: INFOCOM.
Laourine, A., Chen, S., & Tong, L. (2010). Queuing analysis in multichannel cognitive spectrum access: A large deviation approach. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM 2010. San Diego: INFOCOM. doi:10.1109/INFCOM.2010.5461942.
Salameh, O. I., De Turck, K., Bruneel, H., Blondia, C., & Wittevrongel, S. (2014). On the performance of secondary users in a cognitive radio network. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Analytical and Stochastic Modelling Techniques and Applications, ASMTA 2014 (pp. 208–222). Budapest: ASMTA.
Li, B., Yang, P., Li, X.-Y., Wang, J., & Wu, Q. (2011). Finding optimal action point for multi-stage spectrum access in cognitive radio networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, ICC 2011. Kyoto: ICC. doi:10.1109/icc.2011.5962854.
Yuan, G., Grammenos, R. C., Yang, Y., & Wang, W. (2010). Performance analysis of selective opportunistic spectrum access with traffic prediction. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 59(4), 1949–1959.
Daigle, J. N. (2005). Queueing theory with applications to packet telecommunication. Boston: Springer.
Bolch, G., Greiner, S., de Meer, H., & Trivedi, K. S. (1998). Queueing networks and Markov chains. New York: Wiley.
Wolff, R. W. (1982). Poisson arrivals see time averages. Operations Research, 30(2), 223–231.
Kemeny, J. G., & Snell, J. L. (1976). Finite Markov chains. New York: Springer.
Golub, G. H., & Van Loan, C. F. (2013). Matrix computations. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Bright, L., & Taylor, P. G. (1995). Calculating the equilibrium distribution in level dependent quasi-birth-and-death processes. Communications in Statistics, 11(3), 497–525.
Bright, L., & Taylor, P. G. (1997). Equilibrium distributions for level-dependent Quasi-Birth-and-Death processes. Lecture Notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics, 183, 359–375.
Tang, S., & Mark, B. L. (2008). Modeling an opportunistic spectrum sharing system with a correlated arrival process. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, WCNC 2008 (pp. 3297–3302). Las Vegas: WCNC.
Acknowledgements
This research has been partly funded by the Interuniversity Attraction Poles Programme initiated by the Belgian Science Policy Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salameh, O., De Turck, K., Bruneel, H. et al. Analysis of secondary user performance in cognitive radio networks with reactive spectrum handoff. Telecommun Syst 65, 539–550 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0250-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0250-7