Abstract
The generalized linear model (GLM) is a class of regression models where the means of the response variables and the linear predictors are joined through a link function. Standard GLM assumes the link function is fixed, and one can form more flexible GLM by either estimating the flexible link function from a parametric family of link functions or estimating it nonparametically. In this paper, we propose a new algorithm that uses P-spline for nonparametrically estimating the link function which is guaranteed to be monotone. It is equivalent to fit the generalized single index model with monotonicity constraint. We also conduct extensive simulation studies to compare our nonparametric approach for estimating link function with various parametric approaches, including traditional logit, probit and robit link functions, and two recently developed link functions, the generalized extreme value link and the symmetric power logit link. The simulation study shows that the link function estimated nonparametrically by our proposed algorithm performs well under a wide range of different true link functions and outperforms parametric approaches when they are misspecified. A real data example is used to illustrate the results.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
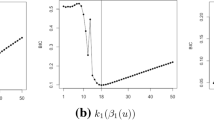
In nonlinear case 1, when the true model is probit, the boundary values are \(10^{-5}\) and \(10^{11}\), since there are nonpositive definite problem in solve.QR() when the \(\lambda \) are too large.
References
Aranda-Ordaz, F.J.: On two families of transformations to additivity for binary response data. Biometrika 68(2), 357–363 (1981)
Bollaerts, K., Eilers, P.H., Aerts, M.: Quantile regression with monotonicity restrictions using P-splines and the L1-norm. Stat. Model. 6(3), 189–207 (2006)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Czado, C., Santner, T.J.: The effect of link misspecification on binary regression inference. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 33(2), 213–231 (1992)
De Boor, C.: A Practical Guide to Splines. Springer, New York (2001)
Eilers, P.H., Marx, B.D.: Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties. Stat. Sci. 11(2), 89–121 (1996)
Eilers, P.H., Li, B., Marx, B.D.: Multivariate calibration with single-index signal regression. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 96(2), 196–202 (2009)
Eilers, P.H., Marx, B.D., Durbán, M.: Twenty years of P-splines. SORT Stat. Oper. Res. Trans. 39(2), 149–186 (2015)
Härdle, W.K., Müller, M., Sperlich, S., Werwatz, A.: Nonparametric and Semiparametric Models. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R.: Generalized Additive Models. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1990)
He, X., Shi, P.: Monotone B-spline smoothing. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 93(442), 643–650 (1998)
Ichimura, H.: Semiparametric least squares (SLS) and weighted SLS estimation of single-index models. J. Econom. 58(1), 71–120 (1993)
Jiang, X., Dey, D.K., Prunier, R., Wilson, A.M., Holsinger, K.E.: A new class of flexible link functions with application to species co-occurrence in cape floristic region. Ann. Appl. Stat. 7(4), 2180–2204 (2013)
Kim, S., Chen, M.H., Dey, D.K.: Flexible generalized t-link models for binary response data. Biometrika 95(1), 93–106 (2008)
Klein, R.W., Spady, R.H.: An efficient semiparametric estimator for binary response models. Econometrica 61(2), 387–421 (1993)
Leitenstorfer, F., Tutz, G.: Generalized monotonic regression based on B-splines with an application to air pollution data. Biostatistics 8(3), 654–673 (2007)
Liu, C.: Robit regression: a simple robust alternative to logistic and probit regression. In: Applied Bayesian Modeling and Causal Inference from Incomplete-data Perspectives, pp. 227–238. Wiley, London (2004)
Mallick, B.K., Gelfand, A.E.: Generalized linear models with unknown link functions. Biometrika 81(2), 237–245 (1994)
Marx, B.D., Eilers, P.H., Li, B.: Multidimensional single-index signal regression. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 109(2), 120–130 (2011)
McCullagh, P., Nelder, J.A.: Generalized Linear Models. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1989)
Muggeo, V.M., Ferrara, G.: Fitting generalized linear models with unspecified link function: a P-spline approach. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52(5), 2529–2537 (2008)
Pregibon, D.: Goodness of link tests for generalized linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 29(1), 15–23 (1980)
Ramsay, J.: Estimating smooth monotone functions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 60(2), 365–375 (1998)
Ramsay, J.O.: Monotone regression splines in action. Stat. Sci. 3(4), 425–441 (1988)
Roy, V.: Efficient estimation of the link function parameter in a robust Bayesian binary regression model. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 73, 87–102 (2014)
Wang, L., Yang, L.: Spline estimation of single-index models. Stat. Sin. 19(2), 765–783 (2009)
Wang, W., Small, D.S.: Monotone B-spline smoothing for a generalized linear model response. Am. Stat. 69(1), 28–33 (2015)
Wang, X., Dey, D.K.: Generalized extreme value regression for binary response data: an application to B2B electronic payments system adoption. Ann. Appl. Stat. 4(4), 2000–2023 (2010)
Wang, Z.: An algorithm for generalized monotonic smoothing. J. Appl. Stat. 27(4), 495–507 (2000)
Weisberg, S., Welsh, A.: Adapting for the missing link. Ann. Stat. 22(4), 1674–1700 (1994)
Wood, S.: Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2006)
Wood, S.N.: Fast stable direct fitting and smoothness selection for generalized additive models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 70(3), 495–518 (2008)
Ypma, J.: Introduction to nloptr: an R interface to NLopt. Tech. rep. (2014)
Yuan, Y.: Prediction Performance of Survival Models. University of Waterloo, Waterloo (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Roy, V. & Zhu, Z. A new algorithm to estimate monotone nonparametric link functions and a comparison with parametric approach. Stat Comput 28, 1083–1094 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-017-9781-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11222-017-9781-3