Abstract
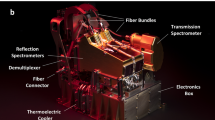
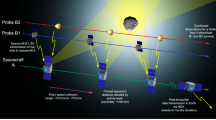
The design of an advanced Net Flux Radiometer (NFR), for inclusion as a payload on a future Ice Giants probe mission, is given. The Ice Giants NFR (IG-NFR) will measure the upward and downward radiation flux (hence net radiation flux), in seven spectral bands, spanning the range from solar to far infra-red wavelengths, each with a \(5^{\circ}\) Field-Of-View (FOV) and in five sequential view angles (\(\pm 80^{\circ}\), \(\pm 45^{\circ}\), and \(0^{\circ}\)) as a function of altitude. IG-NFR measurements within either Uranus or Neptune’s atmospheres, using dedicated spectral filter bands will help derive radiative heating and cooling profiles, and will significantly contribute to our understanding of the planet’s atmospheric heat balance and structure, tropospheric 3-D flow, and compositions and opacities of the cloud layers. The IG-NFR uses an array of non-imaging Winston cones integrated to a matched thermopile detector Focal Plane Assembly (FPA), with individual bandpass filters, housed in a diamond windowed vacuum micro-vessel. The FPA thermopile detector signals are read out in parallel mode, amplified and processed by a multi-channel digitizer application specific integrated circuit (MCD ASIC) under field programmable gate array (FPGA) control. The vacuum micro-vessel rotates providing chopping between FOV’s of upward and downward radiation fluxes. This unique design allows for small net flux measurements in the presence of large ambient fluxes and rapidly changing ambient temperatures during the probe descent to \({\geq} 10\) bar pressure.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Allison, R.F. Beebe, B.J. Conrath, D.P. Hinson, A.P. Ingersoll, Uranus atmospheric dynamics and circulation, in Uranus (1991), pp. 253–295
S. Aslam, A. Akturk, G. Quilligan, A radiation hard multi-channel digitizer ASIC for operation in the harsh Jovian environment, in Extreme Environment Electronics, ed. by J.D. Cressler, H.A. Mantooth (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2012), ISBN: 978-1-4398-7430-1
S. Aslam et al., Net flux radiometer for a Saturn probe, in European Planetary Science Congress, Nantes, France, 27th Sept.–2nd Oct. (2015)
S. Aslam et al., Dual-telescope multi-channel thermal-infrared radiometer for outer planet fly-by missions. Acta Astronaut. 128, 628–639 (2016)
S. Aslam, R.K. Achterberg, V. Cottini, N. Gorius, T. Hewagama, P.G.J. Irwin, C.A. Nixon, A.A. Simon, G. Quilligan, G. Villanueva, Net flux radiometer for the ice giants, in 49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2018, (LPI Contrib. No. 2083, 2675), The Woodlands, TX, USA (2018)
S. Aslam, R.K. Achterberg, S.B. Calcutt, V. Cottini, N. Gorius, T. Hewagama, P.G.J. Irwin, C.A. Nixon, A.A. Simon, G. Quilligan, G. Villanueva, A compact, Versatile net flux radiometer for ice giant probes, in Proceedings of the International Planetary Probe Workshop, Oxford, UK (2019)
S.K. Atreya, A-S. Wong, Clouds of Neptune and Uranus, in Proceedings, International Planetary Probe Workshop, NASA Ames, CP-2004-213456 (2004)
S.K. Atreya, A.-S. Wong, Coupled clouds and chemistry of the giant planets—A case for multiprobes. Space Sci. Rev. 116, 121–136 (2005)
K.H. Baines, H.B. Hammel, Clouds, hazes, and the stratospheric methane abundance in Neptune. Icarus 109, 20–39 (1994)
K.H. Baines, M.E. Mickelson, L.E. Larson, D.W. Ferguson, The abundances of methane and ortho/para hydrogen on Uranus and Neptune: Implications of New Laboratory 4-0 H2 quadrupole line parameters. Icarus 114, 328–340 (1995)
J. Bishop, S.K. Atreya, P.N. Romani, G.S. Orton, B.R. Sandel, R.V. Yelle, in Neptune and Triton, ed. by D.P. Cruikshank, M. Shapley Matthews, A.M. Schumann (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1995), p. 427, ISBN 0-8165-1525-5
I. de Pater, S. Massie, Models of the millimeter-centimeter spectra of the giant planets. Icarus 62, 143–171 (1985)
I. de Pater, P.N. Romani, S.K. Atreya, Uranus’ deep atmosphere revealed. Icarus 82, 288–313 (1989)
I. de Pater, P.N. Romani, S.K. Atreya, Possible microwave absorption by H2S gas in Uranus’ and Neptune’s atmospheres. Icarus 91, 220–233 (1991)
I. de Pater, L.A. Sromovsky, P.M. Fry, H.B. Hammel, C. Baranec, K.M. Satanagi, Icarus 252, 121 (2015)
S.E. Dodson-Robinson, P. Bodenheimer, The formation of Uranus and Neptune in solid-rich feeding zones: Connecting chemistry and dynamics. Icarus 207, 491–498 (2010)
Ice Giants Pre-Decadal Survey Mission Study Report (2017), (JPLD-100520), https://www.lpi.usra.edu/icegiants/mission_study/
P.G.J. Irwin, Giant Planets of Our Solar System. Giant Planets of Our Solar System: Atmospheres, Composition, and Structure. Springer Praxis Books (Springer, Berlin, 2009), ISBN: 978-3-540-85157-8
P.G.J. Irwin, N.A. Teanby, R. de Kok, L.N. Fletcher, C.J.A. Howett, C.C.C. Tsang, C.F. Wilson, S.B. Calcutt, C.A. Nixon, P.D. Parrish, The NEMESIS planetary atmosphere radiative transfer and retrieval tool. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 109, 1136–1150 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2007.11.006
P.G.J. Irwin, M.H. Wong, A.A. Simon, G.S. Orton, D. Toledo, HST/WFC3 observations of Uranus’ 2014 storm clouds and comparison with VLT/SINFONI and IRTF/Spex observations. Icarus 288, 99–119 (2017)
P.G.J. Irwin, D. Toledo, R. Garland, N.A. Teanby, L.N. Fletcher, G.S. Orton, B. Bézard, Detection of hydrogen sulfide above the clouds in Uranus’s atmosphere. Nat. Astron. 2, 420–427 (2018)
P.G.J. Irwin, D. Toledo, R. Garland, N.A. Teanby, L.N. Fletcher, G.S. Orton, B. Bézard, Probable detection of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) in Neptune’s atmosphere. Icarus 321, 550–563 (2019)
E. Karkoschka, M.G. Tomasko, Icarus 211, 780–797 (2011)
J.J. Lissauer, Formation of the outer planets. Space Sci. Rev. 116, 11–24 (2005)
O. Mousis et al., Scientific rationale for Uranus and Neptune in situ explorations. Planet. Space Sci. 155, 12–40 (2018)
J.C. Pearl, B.J. Conrath, R.A. Hanel, J.A. Pirraglia, A. Coustenis, The albedo, effective temperature, and energy balance of Uranus, as determined from Voyager IRIS data. Icarus 84, 12–28 (1990)
G. Quilligan, S. Aslam, Auto-zero Differential Amplifier. US Patent 9,685,913 B2 (2017)
G. Quilligan, S. Aslam, Gated CDS Integrator. US Patent 10,158,335 B2 (2018a)
G. Quilligan, S. Aslam, Gated CDS Integrator. US Patent 9,985,594 B2 (2018b)
G. Quilligan, S. Aslam, B. Lakew, J. DuMonthier, R. Katz, I. Kleyner, A 0.18 μm CMOS thermopile readout ASIC immune to 50 Mrad total ionizing dose (Si) and single event latchup to 174 MeV-cm2/mg, in International Workshop on Instrumentation for Planetary Missions (IPM-2014), Greenbelt, MD 20771, November (2014)
G. Quilligan, J. DuMonthier, S. Aslam, B. Lakew, I. Kleyner, R. Katz, Thermal radiometer signal processing using radiation hard CMOS application specific integrated circuits for use in harsh planetary environments, in European Planetary Science Congress 2015, Nantes, France, 27 Sept.–2 Oct. (2015)
L.A. Sromovsky, F.A. Best, H.E. Revercomb, J. Hayden, Galileo net flux radiometer experiment. Space Sci. Rev. 60, 233–262 (1992)
L.A. Sromovsky, A.D. Collard, P.M. Fry, G.S. Orton, M.T. Lemmon, M.G. Tomasko, R.S. Freedman, Galileo probe measurements of thermal and solar radiation fluxes in the Jovian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 22929–22977 (1998)
M.G. Tomasko, D. Buchhauser, M. Bushroe, L.E. Dafoe, L.R. Doose, A. Eible, C. Fellows, E. McFarlane, G.M. Prout, M.J. Pringle, B. Rizk, C. See, P.H. Smith, K. Tsetsenekos, The Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer (DISR) experiment on the Huygens entry probe of Titan. Space Sci. Rev. 104, 469–551 (2002)
D. Turrini et al., The comparative exploration of the ice giant planets with twin spacecraft: Unveiling the history of our Solar System. Planet. Space Sci. 104, 93–107 (2014)
G. Villanueva et al., Planetary Spectrum Generator (PSG): An online tool to synthesize spectra of comets, small bodies and (exo)planets, in Asteroids, Comets, Meteors (ACM) Conference, Montevideo (2017). https://psg.gsfc.nasa.gov
Vision and Voyages for Planetary Science in the Decade 2013-2022, (NRC 2011), https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/2013decadal/
Acknowledgements
We thank NASA Goddard Space Flight Center for research and development funds, and the NASA ROSES PICASSO program (NNH17ZDA001N-PICASSO) for supporting the design and technology maturation of the IG-NFR. We also wish to thank Ms. Maxine Alexandre-Strong, a 2019 NASA summer intern for proof reading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
In Situ Exploration of the Ice Giants: Science and Technology
Edited by Olivier J. Mousis and David H. Atkinson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, S., Achterberg, R.K., Calcutt, S.B. et al. Advanced Net Flux Radiometer for the Ice Giants. Space Sci Rev 216, 11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-019-0630-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-019-0630-x