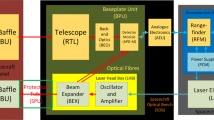
Abstract
Hayabusa2 was launched on 3 December 2014 on an H-IIA launch vehicle from the Tanegashima Space Center, and is, at the time of writing, cruising toward asteroid 162137 Ryugu (\(1999\mathrm{JU}_{3}\)). After reaching the asteroid, it will stay for about 1.5 years to observe the asteroid and collect surface material samples.
The light detection and ranging (LIDAR) laser altimeter on Hayabusa2 has a wide dynamic range, from 25 km to 30 m, because the LIDAR is used as a navigation sensor for rendezvous, approach, and touchdown procedures. Since it was designed for use in planetary explorers, its weight is a low 3.5 kg. The LIDAR can serve not only as a navigation sensor, but also as observation equipment for estimating the asteroid’s topography, gravity and surface reflectivity (albedo). Since Hayabusa2 had a development schedule of just three years from the start of the project to launch, minimizing development time was a particular concern. A key to shortening the development period of Hayabusa2’s LIDAR system was heritage technology from Hayabusa’s LIDAR and the SELENE lunar explorer’s LALT laser altimeter.
Given that the main role of Hayabusa2’s LIDAR is to serve as a navigation sensor, we discuss its development from an engineering viewpoint. However, detailed information about instrument development and test results is also important for scientific analysis of LIDAR data and for future laser altimetry in lunar and planetary exploration. Here we describe lessons learned from the Hayabusa LIDAR, as well as Hayabusa2’s hardware, new technologies and system designs based on it, and flight model evaluation results. The monolithic laser used in the laser module is a characteristic technology of this LIDAR. It was developed to solve issues with low-temperature storage that were problematic when developing the LIDAR system for the first Hayabusa mission. The new module not only solves such problems but also improves reliability and miniaturization by reducing the number of parts.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Abe, T. Mukai, N. Hirata, O.S. Barnouin-Jha, A.F. Cheng, H. Demura et al., Observing 25143 Itokawa using the light detection and ranging instrument (LIDAR) on the Hayabusa spacecraft: local topography and mass. Science 41(312), 1344–1347 (2006)
H. Araki, S. Tazawa, H. Noda, T. Tsubokawa, N. Kawano, S. Sasaki, Observation of the lunar topography by the laser altimeter LALT on board Japanese lunar explorer SELENE. Adv. Space Res. 42(2), 317–322 (2008)
J.F. Cavanaugh, J.C. Smith, X. Sun, A.E. Bartels, L. Ramos-Izquierdo, D.J. Krebs, J.F. McGarry, R. Trunzo, A.M. Novo-Gradac, J.L. Britt, J. Karsh, R.B. Katz, A.T. Lukemire, R. Szymkiewicz, D.L. Berry, J.P. Swinski, G.A. Neumann, M.T. Zuber, D.E. Smith, The mercury laser altimeter instrument for the MESSENGER mission. Space Sci. Rev. 131(1–4), 451–479 (2007)
T.D. Cole, M.T. Boies, A.S. El-Dinary, Laser radar instrument for the Near-Earth Asteroid Rendezvous (NEAR) mission. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2748, 122–139 (1996)
C.S. Dickinson, M. Daly, O. Bar-nouin, B. Bierhaus, D. Gaudreau, J. Tripp, M. Ilnicki, A. Hildebrand, An overview of the OSIRIS REx laser altimeter—OLA, in 43rd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2012)
Q. Huang, J.S. Ping, M.A. Wieczorek, J.G. Yan, X.L. Su, Improved global lunar topographic model by Chang’E-1 laser altimetry DATA, in 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2010)
J.A. Kamalakar, K.V.S. Bhaskar, A.S. Laxmi Prasad, R. Ranjith, K.A. Lohar, R. Venketeswaran, T.K. Alex, Lunar ranging instrument for Chandrayaan-1. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 114(6), 725–731 (2005)
T. Kase, T. Shiina, T. Imaoku, Y. Asakawa, T. Mizuno, Development of the laser oscillator for HAYABUSA2-LIDAR, in 30th Laser Sensing Symposium D-1, Shodoshima (2012)
T. Mizuno, K. Tshuno, E. Okumura, M. Nakayama, LIDAR for asteroid explorer Hayabusa: development and on board evaluation. J. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 54(634), 514–521 (2006)
T. Mizuno, K. Tsuno, E. Okumura, M. Nakayama, Evaluation of LIDAR system in rendezvous and touchdown sequence of Hayabusa mission. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 53(179), 47–53 (2010)
H. Noda, T. Mizuno, H. Kunimori, H. Takeuchi, N. Namiki, Alignment measurement with optical transponder system of Hayabusa2 LIDAR, in 18th International Workshop on Laser Ranging, 13-Po06, Fujiyoshida (2013)
S. Nozette, P. Rustan, L.P. Pleasance, J.F. Kordas, I.T. Lewis, H.S. Park, R.E. Priest, D.M. Horan, P. Regeon, C.L. Lichtenberg, E.M. Shoemaker, E.M. Eliason, A.S. McEwen, M.S. Robinson, P.D. Spudis, C.H. Acton, B.J. Buratti, T.C. Duxbury, D.N. Baker, B.M. Jakosky, J.E. Blamont, M.P. Corson, J.H. Resnick, C.J. Rollins, M.E. Davies, P.G. Lucey, E. Malaret, M.A. Massie, C.M. Pieters, R.A. Reisse, R.A. Simpson, D.E. Smith, T.C. Sorenson, R.W. Vorder Breugge, M.T. Zuber, The Clementine mission to the Moon: scientific overview. Science 266, 1835–1839 (1994)
L. Ramos-Izquierdo, J.L. Bufton, P. Hayes, Optical system design and integration of the Mars observer laser altimeter. Appl. Opt. 33(15), 307–322 (1994)
H. Riris, X. Sun, J.F. Cavanaugh, G.B. Jackson, L. Ramos-Izquierdo, D.E. Smith, M. Zuber, The Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA) on NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) mission, in Proceedings SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 6555 (2007), p. 65550
H. Senshu, S. Oshigami, M. Kobayashi, R. Yamada, N. Namiki, T. Mizuno, Hayabusa2 LIDAR science team, dust detection mode of Hayabusa2 LIDAR. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue)
F. Terui, N. Ogawa, Y. Mimasu, S. Yasuda, M. Uo, Guidance, navigation and control of Hayabusa2 in proximity of an asteroid, in 36th Annual American Astronautical Society Guidance & Control Conference, AAS 13-094, Colorado (2013)
N. Thomas, The BepiColombo laser altimeter (BELA): concept and baseline design. Planet. Space Sci. 55, 1398–1413 (2007)
R. Yamada, H. Senshu, N. Namiki, T. Mizuno, S. Abe, F. Yoshida, H. Noda, N. Hirata, S. Oshigami, H. Araki, Y. Ishihara, K. Matsumoto, Performance of Hayabusa2 LIDAR to observe normal albedo on the C-type asteroid. Space Sci. Rev. (2016, this issue)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuno, T., Kase, T., Shiina, T. et al. Development of the Laser Altimeter (LIDAR) for Hayabusa2. Space Sci Rev 208, 33–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-015-0231-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-015-0231-2