Abstract
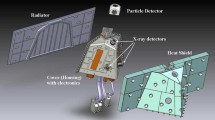
The MAVEN Solar Energetic Particle (SEP) instrument is designed to measure the energetic charged particle input to the Martian atmosphere. SEP consists of two sensors mounted on corners of the spacecraft deck, each utilizing a dual, double-ended solid-state detector telescope architecture to separately measure fluxes of electrons from 20 to 1000 keV and ions from 20–6000 keV, in four orthogonal look directions, each with a field of view of \(42^{\circ}\) by \(31^{\circ}\). SEP, along with the rest of the MAVEN instrument suite, allows the effects of high energy solar particle events on Mars’ upper atmospheric structure, temperatures, dynamics and atmospheric escape rates, to be quantified and understood. Given that solar activity was likely substantially higher in the early solar system, understanding the relationship between energetic particle input and atmospheric loss today will enable more confident estimates of total atmospheric loss over Mars’ history.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Agostinelli, J. Allison, K. Amako, J. Apostolakis, H. Araujo et al., GEANT4—a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 506, 250–303 (2003)
J. Allison, K. Amako, J. Apostolakis, H. Arauho, P. Arce Dubois et al., Geant4 developments and applications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 53, 270–278 (2006)
L. Andersson, R.E. Ergun, G. Delory, The Langmuir probe and waves experiment for MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0194-3
V. Angelopoulos, D. Sibeck, C.W. Carlson et al., First results from the THEMIS mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2008). doi:10.1007/s11214-008-9378-4
S. Barabash et al., The analyzer of space plasmas and energetic atoms (ASPERA-3) for the Mars express mission. Space Sci. Rev. 126, 113–164 (2006). doi:10.1007/s11214-006-9124-8
J.-L. Bertaux, F. Leblanc, O. Witasse, E. Quemerais, J. Lilensten, S.A. Stern, B. Sandel, O. Korablev, Discovery of an aurora on Mars. Nature 435, 790–794 (2005). doi:10.1038/nature03603
M.W. Chevalier, W.B. Peter, U.S. Inan, T.F. Bell, M. Spasojevic, Remote sensing of ionospheric disturbances associated with energetic particle precipitation using the South Pole VLF beacon. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A11306 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JA012425
J.E.P. Connerney, J. Espley, P. Lawton, S. Murphy, J. Odom, R. Oliversen, D. Sheppard, The Maven magnetic field investigation. Space Sci. Rev. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0169-4
A.V. Dmitriev, H.-C. Yeh, Geomagnetic signatures of sudden ionospheric disturbances during extreme solar radiation events. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 70, 1971–1984 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.05.008
F. Eparvier, P.C. Chamberlin, T.N. Woods, E.M.B. Thiemann, The solar extreme ultraviolet monitor for MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0195-2
J.R. Espley, W.M. Farrell, D.A. Brain, D.D. Morgan, B. Cantor, J.J. Plaut, M.H. Acuña, G. Picardi, Absorption of MARSIS radar signals: Solar energetic particles and the daytime ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L09101 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GL028829
Y. Futaana et al., Mars express and Venus express multi-point observations of geoeffective solar flare events in December 2006. Planet. Space Sci. 56(6), 873–880 (2008)
J.S. Halekas, E.R. Taylor, G. Dalton, G. Johnson, D.W. Curtis, J.P. McFadden, D.L. Mitchell, R.P. Lin, B.M. Jakosky, The solar wind ion analyzer for MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. (2013). doi:10.1007/s11214-013-0029-z
D.M. Hassler et al., The radiation assessment detector (RAD) investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 170, 503–558 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9913-1
D.M. Hassler et al., Mars’ surface radiation environment measured with the Mars science laboratory’s curiosity rover. Science 343 (2014). doi:10.1126/science.1244797
B.M. Jakosky, R.P. Lin, J.M. Grebowsky, J.G. Luhmann, D.F. Mitchell, G. Beutelschies et al., The Mars atmosphere and volatile evolution (MAVEN) mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0139-x
M. Kaiser, The STEREO mission: An overview. Adv. Space Res. 36, 1483 (2005)
F. Leblanc, O. Witasse, J. Winningham, D. Brain, J. Lilensten, P.-L. Blelly, R.A. Frahm, J.S. Halekas, J.L. Bertaux, Origins of the Martian aurora observed by spectroscopy for investigation of characteristics of the atmosphere of mars (SPICAM) on board Mars express. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09313 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006JA011763
R.J. Lillis, D.A. Brain, G.T. Delory, D.L. Mitchell, J.G. Luhmann, R.P. Lin, Evidence for superthermal secondary electrons produced by SEP ionization in the Martian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 117, E03004 (2012). doi:10.1029/2011JE003932
R.J. Lillis, D.A. Brain, S.W. Bougher, F. Leblanc, J.G. Luhmann, B.M. Jakosky, R. Modolo, J. Fox, J. Deighan, X. Fang, Y.C. Wang, Y. Lee, C. Dong, Y. Ma, T. Cravens, L. Andersson, S.M. Curry, N. Schneider, M. Combi, I. Stewart, J. Clarke, J. Grebowsky, D.L. Mitchell, R. Yelle, A.F. Nagy, D. Baker, R.P. Lin, Characterizing atmospheric escape from Mars today and through time, with MAVEN. Space Sci. Rev. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0165-8
R.P. Lin et al., A 3-dimensional plasma and energetic particle investigation for the wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71(1–4), 125–153 (1995)
R.P. Lin, D.W. Curtis, D.E. Larson, J.G. Luhmann, S.E. McBride, M.R. Maier, T. Moreau, C.S. Tindall, P. Turin, L. Wang, The STEREO IMPACT suprathermal electron (STE) instrument. Space Sci. Rev. (2008). doi:10.1007/s11214-008-9330-7
P.R. Mahaffy, M. Benna, T. King et al., The neutral gas and ion mass spectrometer on the Mars atmosphere and volatile evolution mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0091-1
W.E. McClintock, N.M. Schneider, G.M. Holsclaw, J.T. Clarke, A.C. Hoskins, I. Stewart, F. Montmessin, R.V. Yelle, J. Deighan, The imaging ultraviolet spectrograph (IUVS) for the MAVEN mission. Space Sci. Rev. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0098-7
J. McFadden, O. Kortmann, G.J. Dalton, R. Abiad, D. Curtis, R. Sterling, K. Hatch, P. Berg, C. Tiu, M. Marckwordt, R. Lin, B. Jakosky, The MAVEN suprathermal and thermal ion composition (STATIC) instrument. Space Sci. Rev. (2015)
S.V. McKenna-Lawlor, V. Afonin, K.I. Gringauz, K. Kecskemety, E. Keppler, f.F. Kirsch, f.A. Richter, P. Rusznyak, K. Schwingenschuh, D. O’Sullivan, A.J. Somogyi, L. Szabo, A. Thompson, A. Varga, Ye. Yeroshenkoll, M. Witte, Energetic particle studies at Mars by SLED on Phobos-2. Adv. Space Res. 12(9), 231–241 (1992)
D.L. Mitchell, R.P. Lin, C. Mazelle, H. Rème, P.A. Cloutier, J.E.P. Connerney, M.H. Acuna, N.F. Ness, Probing Mars’ crustal magnetic field and ionosphere with the MGS electron reflectometer. J. Geophys. Res. 106(E10), 23419–23427 (2001). doi:10.1029/2000JE001435
D.D. Morgan, D.A. Gurnett, D.L. Kirchner, R.L. Huff, D.A. Brain, W.V. Boynton, M.H. Acuña, J.J. Plaut, G. Picardi, Solar control of radar wave absorption by the Martian ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L13202 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006GL026637
R. Müller-Mellin, S. Böttcher, J. Falenski, E. Rode, L. Duvet, T. Sanderson, B. Butler, B. Johlander, H. Smit, The solar electron and proton telescope for the STEREO mission. Space Sci. Rev. 136(1–4), 363–389 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11214-007-9204-4
J.B. Reagan, T.M. Watt, Simultaneous satellite and radar studies of the D region ionosphere during the intense solar particle events of August 1972. J. Geophys. Res. 81(25), 4579–4596 (1976). doi:10.1029/JA081i025p04579
C. Zeitlin, T. Cleghorn, F. Cucinotta, P. Saganti, V. Andersen, K. Lee, L. Pinsky, W. Atwell, R. Turner, G. Badhwar, Overview of the Martian radiation environment experiment. Adv. Space Res. 33(12), 2204–2210 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larson, D.E., Lillis, R.J., Lee, C.O. et al. The MAVEN Solar Energetic Particle Investigation. Space Sci Rev 195, 153–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-015-0218-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-015-0218-z