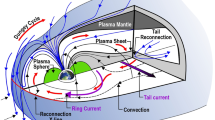
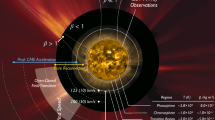
Abstract
The concept of geomagnetic storm-producing solar plasma flows has evolved and advanced considerably over the last 100 years or so. This particular field of study began in an effort to understand geomagnetic disturbances and the aurora. The purpose of this paper is try to follow the ways in which early concepts evolved to later ones, not to review each concept in detail. It is fascinating to see a step-by-step buildup of these concepts, from the earliest idea of flow of solar electrons to coronal mass ejections (CMEs). The time line, though tentative, of the studies of geomagnetic storm-producing plasma flows is presented. The author hopes that this paper will serve young researchers in particular to consider how they plan to advance further this scientific field. There is still much uncertainty about geomagnetic storm-producing solar plasma flows. Some of the major questions are listed from the point of view of a geophysicist in the summary sections by grouping them in terms of the quiet-time solar wind, solar streams from corona holes and CMEs associated with solar flares.



















































Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.-I. Akasofu, The neutral hydrogen flux in the solar plasma flow–I. Planet. Space Sci. 12, 905–913 (1964)
S.-I. Akasofu, Energy coupling between the solar wind and the magnetosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 28, 121 (1981)
S.-I. Akasofu, A comprehensive review of solar-terrestrial relationships in terms of a chain of four dynamo-powered plasma acceleration processes. Planet. Space Sci. 31, 25 (1983)
S.-I. Akasofu, New scheme provides a first step toward geomagnetic storm prediction. Eos 77, 225 (1996)
S.-I. Akasofu, Exploring the Secrets of the Aurora, 2nd edn. (Springer, Berlin, 2007)
S.-I. Akasofu, The choice of the concept of magnetic field lines or of electric current lines: Alfven medal lecture. Ann. Geophys. 29, 1215 (2011)
S.-I. Akasofu, S. Chapman, The ring current geomagnetic disturbance, and the Van Allen radiation belts. J. Geophys. Res. 66, 1321 (1961)
S.-I. Akasofu, S. Chapman, The development of the main phase of magnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 125 (1963)
S.-I. Akasofu, S. Chapman, Solar-Terrestrial Physics (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1972), pp. 901
S.-I. Akasofu, D.N. Covey, Magnetic configuration of the heliosphere in interstellar space. Planet. Space Sci. 29, 313 (1981)
S.-I. Akasofu, C.D. Fry, Heliospheric current sheet and its solar cycle variations. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 13679 (1986)
S.-I. Akasofu, L.-H. Lee, Modeling of an interplanetary disturbance event tracked by the interplanetary scintillation method. Planet. Space Sci. 37, 73 (1989)
S.-I. Akasofu, L.-H. Lee, Modeling of a series of interplanetary events in September, 1978. Planet. Space Sci. 38, 575 (1990)
S.-I. Akasofu, S. Yoshida, The structure of the solar plasma flow generated by solar flares. Planet. Space Sci. 15, 39 (1967)
H. Alfven, Cosmical Electrodynamics (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1950), pp. 237
H. Alfven, Electric currents cosmic plasmas. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 15, 271 (1977)
H. Alfven, Cosmic Plasma (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1981)
H.W. Babcock, The solar magnetograph. Astrophys. J. 118, 387 (1953)
H.W. Babcock, H.D. Babcock, The sun’s magnetic field, 1952–1954. Astrophys. J. 121, 349 (1955)
M. Banaszkiewicz, W.I. Axford, J.F. McKenzie, Astron. Astrophys. 337, 940 (1998)
J. Bartels, Terrestrial-magnetic activity and its relations to solar phenomena. Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. 37, 1 (1932)
L. Biermann, Kometenscheite und solar korpskularhlung. Z. Astrophys. 29, 274 (1951)
L. Biermann, Physical processes in comet tails and their relation to solar activity. Memoires de lat Societe Royale des Sciences de Liege Quatrrime Serie, Tome XIII, Fasc. I–II, 291 (1953)
D.E. Billings, W.O. Roberts, The origin of M-region geomagnetic storms. Astrophys. Nor., 9, 148–149 (1964)
K. Birkeland, The Norwegian Auroral Polaris Expedition, 1902–1903 (H. Aschehoug, Christinia, 1908), pp. 801
J.D. Bohlin, An observational definition of coronal holes, in Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams, ed. by J.B. Zirker (Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, 1977), pp. 27–69
J.C. Brandt, D.M. Hunten, On ejection of neutral hydrogen from the Sun and the terrestrial consequences. Planet. Space Sci. 14, 95 (1966)
L. Burlaga, Interplanetary Magneto Hydrodynamics (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1995)
L. Burlaga, E. Sittler, F. Mariani, R. Schwenn, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673–6684 (1981)
L.J. Cahill, P.G. Amazeen, The boundary of the geomagnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 1835 (1963)
R.C. Carrington, Description of a singular appearance seen in the Sun on September 1, 1859. Mon. Not. R. Astron. 20, 13–15 (1860)
S. Chapman, An outline of a theory of magnetic storms. Proc. R. Soc. 97, 61 (1918)
S. Chapman, Solar streams of corpuscles: their geometry, absorption of light and penetration. Mon. Not. R. Atron. 89, 456–470 (1929)
S. Chapman, Note on the solar corona and the terrestrial ionosphere. Smithson. Contrib. Astrophys. 2, 1 (1957)
S. Chapman, J. Bartels, Geomagnetism, vol. I (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1940)
S. Chapman, V.C.A. Ferraro, A new theory of magnetic storms. Terr. Magn. Atmos. Electr. 36, 77 (1931)
J. Chen, Prominence eruptions and geoeffective solar wind structure, in Magnetic Storms. Geophysical Monograph, vol. 98 (American Geophys. Union, Washington, 1997), pp. 45–58
J. Chen, J. Krall, Acceleration of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1410 (2003) doi:10.1029/2003JA009849
M.R. Collier et al., Observations of neutral atoms from the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 24893 (2001)
N. Crooker, A.A. Joselyn, J. Feynman (eds.), Coronal Mass Ejections, Geophysical Monograph Series, vol. 99 (American Geophysical Union, Washington, 2009). p. 299
M. Dryer, Interplanetary shock waves: Recent developments. Space Sci. Rev. 17, 277 (1975)
M. Dryer, Z. Smith, C.D. Fry, W. Sun, C.S. Deehr, S.-I. Akasofu, Real-time shock arrival predictions during the “Halloween 2003 epoch”. Space Weather (2004) doi:10.1029/2004SW000087
J.W. Dungey, Cosmic Electrodynamics (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1958), p. 183
J.W. Dungey, Inteplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zone. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47 (1961)
D.H. Fairfield, L.J. Cahill, J. Geophys. Res. 71, 155 (1966)
C.D. Fry, M. Dryer, C.S. Deehr, W. Sun, S.-I. Akasofu, Z. Smit, Forecasting solar wind structure and shock arrival times using an ensemble of models. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1070 (2003) doi:10.029/2002JA009474
T. Gold, Discussion on shock waves and rarefied gas dynamics, in Gas Dynamics of Cosmic Clouds, July 6–11, 1953, Cambridge, England (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1955), p. 103
T. Gold, Motions in the magnetosphere of the Earth. J. Geophys. Res. 64, 1219 (1959)
J.T. Gosling, V. Pizzo, S.J. Bame, Anomalous low proton temperatures in the solar wind following interplanetary shock waves—evidence of magnetic bottles? J. Geophys. Res. 78, 2001 (1973)
J.T. Gosling, J.R. Asbridge, S.J. Bame, W.C. Feldman, R.D. Zwickl, Observations of large fluxes of He+ in the solar wind following an interplanetary shock. J. Geophys. Res. 85, 3431 (1980)
J.T. Gosling, D.N. Baker, S.J. Bame, D.Z. Zwickle, Bidirectional solar wind electron heat flux and hemispherically symmetric polar rain. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 11352 (1986)
J.T. Gosling, D.J. McComas, J.L. Phillips, S.J. Bame, Geomagnetic activity associated with Earth passage of interplanetary shock disturbances and coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 7831 (1991)
K. Hakamada, Long-term variations of the solar magnetic dipole. Inf. Sci. J. 17, 97 (2010) (in Japanese)
K. Hakamada, S.-I. Akasofu, Simulation of three-dimensional solar wind disturbances and resulting geomagnetic storms. Space Sci. Rev. 31, 3 (1982)
K. Harvey, F. Recely, Polar coronal holes during Cycles 22 and 23. Sol. Phys. 211, 31 (2002)
A. Hewish, S.J. Tappin, G.R. Faggen, Origin of strong interplanetary shocks, Nature, 314 (1985)
J. Hirshberg, A. Alksne, D.S. Colburn, S.J. Bame, A.J. Hundhausen, Observations of a solar flare induced interplanetary shock and helium-enriched driver gas. J. Geophys. Res. 75, 1 (1970)
J. Hirshberg, J.R. Asbridge, D.E. Robbins, The helium-enriched interplanetary plasma from proton flares of August/September, 1966. Sol. Phys. 18, 313 (1971)
J. Hirshberg, S.J. Bame, D.E. Robbines, Solar flares and solar wind enrichments: July 1965–July 1967. Sol. Phys. 23, 467 (1972)
D. Hovestadt, G. Gloeckler, H. Hofner, B. Klecker, F.M. Ipavich, C.Y. Fan, L.A. Fisk, J.J. O’Gallagher, M. Scholer, Singly charged energetic helium emitted in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 246, L81 (1981)
R.A. Howard, D.J. Michels, N.R. Sheeley Jr., M.J. Koomen, The observation of a coronal transient directed at Earth. Astrophys. J. 263, L101 (1982)
A.J. Hundhausen, Coronal Expansion and Solar Wind (Springer, New York, 1972), pp. 238
A.J. Hundhausen, R.A. Gentry, Numerical simulation of flare-generated disturbances in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 74, 2908 (1969)
B.V. Jackson, Heliographic observations of solar disturbances and their potential role in the origin of geomagnetic storms, in Magnetic Storms. Geophysical Monograph, vol. 98 (American Geophys. Union, Washington, 1997), p. 59
J.A. Joselyn, P.S. McIntosh, Disappearing solar filaments: a useful prediction of geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4555 (1981)
W.T. Kelvin, President’s address, 1892–93. Proc. R. Soc. 52, 299–310 (1892)
A.S. Krieger, A.F. Timothy, E.C. Roelof, A coronal hole and its identification as the source of a high velocity solar wind stream. Sol. Phys. 29, 505 (1973)
H. Kunow, N.U. Crooker, J.A. Linker, R. Schween, R. von Steiger (eds.), Coronal Mass Ejections (Springer, Berlin, 2006)
Liepman, Gas Dynamics of Cosmic Clouds, July 6–11, 1953, Cambridge, England (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1955)
F.A. Lindemann, Note on the theory of magnetic storms. Philos. Mag. 38, 669 (1919)
N. Lugas, A. Vourlidas, I.I. Roussev, H. Morgan, Solar-terrestrial simulation in the STEREO era: the 24–25 January 2007 eruptions. Sol. Phys. 256, 269 (2009)
P.K. Manoharan, Ooty interplanetary scintillation-remote-sensing observations and analysis of coronal mass ejections in the heliosphere, in Remote Sensing of the Inner Heliosphere, ed. by M.M. Bisi, A.R. Breen (Springer, Berlin, 2010)
E.W. Maunder, Magnetic disturbances, 1882–1903, as recorded at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, and their association with sunspots. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 65, 2 (1905)
D.J. McComas, H.A. Elliott, N.A. Schwadron, J.T. Gosling, R.M. Skoug, B.E. Goldstein, Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 24 (2003). doi:10.1029/2003GL017136
S.M.P. McKenna-Lawlor, M. Dryer, M.D. Kartalev, Z. Smith, C.D. Fry, W. Sun, S.C. Deer, K. Keccskemety, K. Kudela, Near real-time predictions of the arrival at Earth of flare-related shocks during solar cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A11103 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011162
T. Nagata, Characteristics of the solar flare effect (Sqa) on geomagnetic field at Huancayo (Peru) and at Kakioka (Japan). J. Geophys. Res. 57, 1 (1952)
N.F. Ness, C.S. Scearce, J.B. Seek, Initial results of the Imp 1 magnetic field experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 69, 3571 (1964)
M. Neugebauer, C.W. Snyder, Solar plasma experiment. Science 138, 1095 (1962)
M.W. Neupert, V. Pizzo, Solar corornal holes as sources of recurrent geomagnetic disturbances. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 3701 (1974)
H.W. Newton, Solar flares and magnetic storms. Mon. Not. R. Astro. Soc. 103, 244 (1943)
D. Odstrcil, D.P. Riley, X.P. Zhao, Numerical simulation of the 12 May 1997 interplanetary CME event. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A02116 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JA010135
E.N. Parker, Dynamics of the interplanetary gas and magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 128, 664 (1958)
E.N. Parker, Sudden expansion of the corona following a large solar flare and the attendant magnetic field and cosmic ray effects. Astrophys. J. 133, 1014 (1961)
J.C. Pecker, W.O. Roberts, Solar corpuscles responsible for geomagnetic disturbances. J. Geophys. Res. 60, 33 (1955)
J. Roosen, The seasonal variation of geomagnetic disturbance amplitudes. Bull. Astr. Insts. Neth. 18, 295 (1966)
I.I. Roussev, N. Lugas, I. Sokolov, New physical insight on the changes in magnetic topology during coronal mass ejections: case studies for the 2002 April 21 and August 24 events. Astrophys. J. 668, L87 (2007)
T. Saito, S.-I. Akasofu, Is the Earth’s dipole actually inclined with respect to the rotation axis? Planet. Space Sci. 38, 1203 (1990)
T. Saito, T. Oki, S.-I. Akasofu, C. Olmstead, The sunspot cycle variations of the neutral line on the source surface. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 5453 (1989)
T. Saito, W. Sun, C.S. Deehr, S.-I. Akasofu, Transient equatorial magnetic flux loops on the Sun as a possible new source of geomagnetic storms. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A05102 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JA011941
K. Schatten, J.M. Wilcox, N.F. Ness, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Sol. Phys. 6, 442 (1969)
M. Schultz, Interplanetary sector structure and the heliospheric equator. Astrophys. Space Sci. 24, 371 (1973)
A. Schuster, Sun-spots and magnetic storms. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 65, 186 (1905)
A. Schuster, On the origin of magnetic storms. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 85, 44 (1911)
R. Schwenn, Solar wind sources and their variations over the solar cycle, in Solar Dynamics and Its Effects on the Heliosphere and the Earth, ed. by D.N. Baker et al. (Springer, Berlin, 2007), pp. 51–76, pp. 372
R.M. Skoug, S.J. Bames, W.C. Feldman, J.T. Gosling, D.J. McComas, J.T. Steinberg, R.L. Tokar, P. Reley, L.F. Burlaga, N.S. Ness, C.W. Smith, A prolonged He+ enhancement within a coronal mass ejection in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 161 (1999)
Z. Smith, M. Dryer, S.M.P. McKenna-Lawlor, C.D. Fry, C.S. Deehr, W. Sun, Operational validation of HAFv2’s predictions of interplanetary shock arrivals at Earth: declining phase of solar cycle 23. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A05106 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JA13836R
C.P. Sonett, E.J. Smith, A.R. Smith, in Proceedings of the First International Space Sciences Symposium, ed. by H.K. Kallman Biji (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1960), p. 921.
C. Stormer, The Polar Aurora (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 1955), pp. 403
W. Sun, C.S. Deehr, M. Dryer, Z.K. Smith, S.-I. Akasofu, Simulated solar mass ejection imager and “Solar Terrestrial Relations Observation-like” views of the solar wind following the solar flares of 27–29 May 2003. Space Weather 6, So3006 (2008). doi:10.1029/2006sSW000296
L. Svalgaard, J.M. Wilcox, Long term evolution of solar sector structure. Sol. Phys. 41, 461 (1975)
J.J. Thomson, G.P. Thomson, in Conduction of Electricity through Gases, I (Dover, New York, 1969), p. 30, pp. 491
V.S. Titov, P. Demoulin, Basic topology of twisted magnetic configurations in solar flares. Astron. Astrophys. 351, 707 (1999)
R. Tousey, The solar corona. Space Res. XIII 48, 714 (1973)
C.-Y. Tu, C. Zhou, E. Marsch, L.-D. Xia, L. Zhao, J.-X. Wang, K. Wilhelm, Solar wind origin in coronal funnels. Science 308, 519 (2005)
J.A. Van Allen, Radiation observations with satellite 1958. J. Geophys. Res. 64, 271 (1959)
J.M. Wilcox, N.F. Ness, Quasi-stationary corotating structure in the interplanetary medium. J. Geophys. Res. 70, 5793–5805 (1965)
S.T. Wu, S.M. Hans, M. Dryer, Two dimensional, time-dependent MHD description of interplanetary disturbances, 1. Simulation of high speed solar wind interactions. Planet. Space Sci. 27, 25 (1979)
S.T. Wu, W.P. Guo, D.J. Michels, L.F. Burlaga, MHD description of the dynamical relationships between a flux rope, streamer, coronal mass ejection, and magnetic cloud: An analysis of the January 1997 Sun-Earth connection event. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 14789 (1999)
J.B. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams (Colorado Associated Univ. Press, Boulder, 1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akasofu, SI. A Historical Review of the Geomagnetic Storm-Producing Plasma Flows from the Sun. Space Sci Rev 164, 85–132 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9856-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9856-y