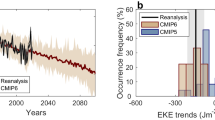
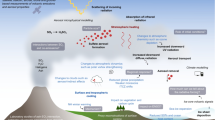
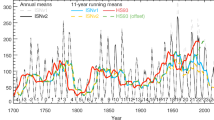
Abstract
This paper provides a comprehensive update on sporadic E layers that is placed in the context of atmosphere-ionosphere coupling, exemplified here by the fundamental windshear theory processes that govern sporadic E layer formation and variability. Some basics of windshear theory are provided first, followed by a summary of key experimental results, their interpretation and physical understanding. The emphasis is placed on the wind shear control of the diurnal and sub-diurnal variability and altitude descent of sporadic E layers and the key role behind these properties of the diurnal and semidiurnal tides. Furthermore, the paper summarizes recent observations that establish a role also for the planetary waves in sporadic E layer occurrence and long-term variability. The possible mechanisms behind this interaction are examined and evidence is presented which shows that planetary waves affect sporadic E layers indirectly though the amplitude modulation of tides at lower altitudes in the MLT region. Only a brief mention is made about gravity wave effects on sporadic E, which apparently exist but cannot be as crucial in layer forming as thought in the past. There is now enough evidence to suggest that mid- and low-latitude sporadic E is not as “sporadic” as the name implies but a regularly occurring ionospheric phenomenon. This may suggest that the sporadic E layer physics can be incorporated in large-scale atmosphere-ionosphere coupling models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.I. Axford, The formation and vertical movement of dense ionized layers in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 769 (1963)
C. Arras, C. Jacobi, J. Wickert, Semidiurnal tidal signature in sporadic E occurrence rates derived from GPS radio occultation measurements at higher midlatitudes. Ann. Geophys. 27, 2555–2563 (2009)
R.L. Bishop, G.D. Earle, Metallic ion transport associated with midlatitude intermediate layer development. J. Geophys. Res. 108(A1), 1019 (2003)
G. Chimonas, W.I. Axford, Vertical movement of temperate zone sporadic E layer. J. Geophys. Res. 73, 111 (1968)
G. Chimonas, Enhancement of sporadic E by horizontal transport within the layer. J. Geophys. Res. 76, 4578 (1971)
N. Christakis, C. Haldoupis, Q. Zhou, C. Meek, Seasonal variability and descent of mid-latitude sporadic E layers at Arecibo. Ann. Geophys. 27, 923–931 (2009)
R.R. Clark, M.D. Burrage, S.J. Franke, A.H. Manson, C.E. Meek, N.J. Mitchel, H.G. Muller, Observations of 7-day planetary waves with MLT radars and UARS/HRDI instrument. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 64, 1217 (2002)
F.T. Djuth, M.P. Sulzer, S.A. Gonzales, J.D. Mathews, J.H. Elder, A continuum of gravity waves in the Arecibo thermosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L16801 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003GL019376
G.D. Earle, T.J. Kane, R.F. Pfaff, S.R. Bounds, Ion layer separation and equilibrium zonal winds in midlatitude sporadic E. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(4), 461–464 (2000). doi:10.1029/1999GL900572
J.M. Forbes, Tidal and planetary waves, in The Upper Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere, a Review of Experiment and Theory, ed. by R.M. Johnson, T.L. Killen (1994), p. 67
J.M. Forbes, M.E. Hagan, S. Miyahara, F. Vial, A.H. Manson, C.E. Meek, Yu. Portnyagin, Quasi-16-day oscillation in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 9149 (1995)
S. Fukao, M. Yamamoto, R.T. Tsunoda, H. Hayakawa, T. Mukai, The SEEK (Sporadic-E Experiment from Kyushu) campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1761–1764 (1998)
C. Haldoupis, D.T. Farley, K. Schlegel, Type 1 echoes from the midlatitude E region ionosphere. Ann. Geophys. 15, 908–917 (1997)
C. Haldoupis, D. Pancheva, Planetary waves and midlatitude sporadic E layers: Strong experimental evidence for a close relationship. J. Geophys. Res. 107 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JA000212
C. Haldoupis, D. Pancheva, N.J. Mitchell, A study of tidal and planetary wave periodicities present in midlatitude sporadic E layers. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A02302 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003JA010253
C. Haldoupis, C. Meek, N. Christakis, D. Pancheva, A. Bourdillon, Ionogram height-time intensity observations of descending sporadic E layers at mid-latitude. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 68, 539 (2006)
C. Haldoupis, D. Pancheva, Terdiurnal tidelike variability in sporadic E layers. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A07303 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011522
C. Haldoupis, D. Pancheva, W. Singer, C. Meek, J. MacDougall, An explanation for the seasonal dependence of midlatitude sporadic E layers. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A06315 (2007). doi:10.1029/2007JA012322
C. Haldoupis, A tutorial review on sporadic E layers, in Aeronomy of the Earth’s Atmosphere and Ionosphere. IAGA Special Sopron Book series, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0326-1-29 (Springer, Berlin, 2011)
R.M. Harper, Tidal winds in the 100- to 200-km region at Arecibo. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 3243 (1977)
J.R. Holton, An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (Academic Press, San Diego, 1982)
G.G. Hussey, K. Schlegel, C. Haldoupis, Simultaneous 50-MHz coherent backscatter and digital ionosonde observations in the midlatitude E region. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 6991 (1998)
D.L. Hysell, M. Yamamoto, S. Fukao, Imaging radar observations and theory of type I and type II quasiperiodic echoes. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1360 (2002)
M.F. Larsen, A shear instability seeding mechanism for quasiperiodic echoes. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 24931 (2000)
M.C. Kelley, The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics, 2nd edn. (Academic Press, San Diego, 2009)
D.J. Livneh, I. Seker, F.T. Djuth, J.D. Mathews, Continuous quasiperiodic thermospheric waves over Arecibo. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A07313 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JA012225
J.W. MacDougall, 110 km neutral zonal wind patterns. Planet. Space Sci. 22, 545 (1974)
J.W. MacDougall, J.M. Plane, P.T. Jayachandran, Polar cap Sporadic E: part 2, modeling. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 62, 1169–1176 (2000)
J.D. Mathews, F.S. Bekeny, Upper atmosphere tides and the vertical motion of ionospheric sporadic layers at Arecibo. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2743–2750 (1979)
J.D. Mathews, M.P. Sulzer, P. Perillat, Aspects of layer electrodynamics from high-resolution ISR observations of the 80–270 km ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24(11), 1411–1414 (1997)
J.D. Mathews, Sporadic E: current views and recent progress. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 60, 413 (1998)
C.K. Meyer, J.M. Forbes, A 6.5-day westward propagating planetary wave: Origin and characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 26173 (1997)
K.L. Miller, L.G. Smith, Incoherent scatter radar observations of irregular structure in mid-latitude sporadic E layers. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 3761–3775 (1978)
D. Pancheva, Evidence for non-linear coupling of planetary waves and tides in the lower thermosphere over Bulgaria. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 62, 115 (2000)
D. Pancheva, C. Haldoupis, C.E. Meek, A.H. Manson, N.J. Mitchell, Evidence of a role for modulated atmospheric tides in the dependence of sporadic E on planetary waves, J. Geophys. Res. 108 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002JA009788
R.F. Pfaff, M. Yamamoto, P. Marioni, H. Mori, S. Fukao, Electric field measurements above and within a sporadic-E layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 1769–1772 (1998)
S. Shalimov, C. Haldoupis, M. Voiculescu, K. Schlegel, Midlatitude E region plasma accumulation driven by planetary wave horizontal wind shears. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 28207 (1999)
S. Shalimov, C. Haldoupis, A model of midlatitude E region plasma convergence inside a planetary wave cyclonic vortex. Ann. Geophys. 20, 1193 (2002)
L.G. Smith, A sequence of rocket observations of nighttime sporadic E. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 32, 1427 (1970)
E.P. Szuszczewicz, R.G. Roble, P.J. Wilkinson, R. Hanbaba, Coupling mechanisms in the lower ionospheric-thermospheric system and manifestations in the formation and dynamics of intermediate descending layers. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 57, 1483 (1995)
H. Teitelbaum, F. Vial, On the tidal variability induced by non-linear interaction with planetary waves. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 14169 (1991)
R. Tsunoda, M. Yamamoto, K. Igarashi, K. Hocke, S. Fukao, Quasiperiodic radar echoes from midlatitude sporadic E and role of the 5-day planetary wave. Geophys. Res. Lett. 25, 951 (1998)
M. Voiculescu, C. Haldoupis, K. Schlegel, Evidence for planetary wave effects on midlatitude backscatter and sporadic E layer occurrence. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 1105 (1999)
M. Voiculescu, C. Haldoupis, D. Pancheva, M. Ignat, K. Schlegel, S. Shalimov, More evidence for a planetary wave link with midlatitude E region coherent backscatter and sporadic E layers. Ann. Geophys. 18, 1182 (2000)
J.D. Whitehead, Recent work on midlatitude and equatorial sporadic E. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 51, 401 (1989)
J.D. Whitehead, The formation of the sporadic E layer in the temperate zones. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 20, 49 (1961)
P.J. Wilkinson, E.P. Szuszczewicz, R.G. Roble, Measurements and modelling of intermediate, descending, and sporadic layers in the lower ionosphere: Results and implications for global-scale ionospheric-thermospheric studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 19, 95 (1992)
X.M. Zuo, W.X. Wan, Planetary wave oscillations in sporadic E layer occurrence at Wuhan. Earth Planets Space 60, 647–652 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haldoupis, C. Midlatitude Sporadic E. A Typical Paradigm of Atmosphere-Ionosphere Coupling. Space Sci Rev 168, 441–461 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9786-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-011-9786-8