Abstract
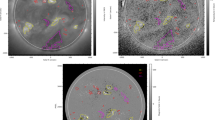
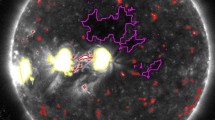
The temperature variations of the corona and its individual surface features as a function of the solar cycle are an interesting and important aspect of understanding the physics of the Sun. To study the temperature variations, we have used the full-disk soft X-ray images of the corona obtained from Hinode/X-Ray Telescope (XRT) in different filters. A sophisticated algorithm has been developed in Python to segment the different coronal features such as the active regions (ARs), coronal holes (CHs), background regions (BGs), and X-ray bright points (XBPs), derived the total intensity of all the features, and generated the temperature maps of the corona using the filter ratio method. Due to the XRT straylight issue in some filters and unavailability of a good pair of images, we used for our analysis the filter combinations of Ti-poly and Al-mesh for the period from February 01, 2008 to May 08, 2012 and Al-poly and Al-mesh for the period from May 09, 2012 to June 30, 2021, in total for 14 years which covers Solar Cycle 24. The first analysis in using the XRT intensity values of the coronal features from segmented solar disk and their relation to solar activity is presented. We discuss the temperature variations of a full-disk corona and all features (ARs, CHs, BGs, and XBPs). Our time series plots of the average temperature of the full-disk and all the features show temperature fluctuations synchronized with the solar cycle (sunspot number). Although the temperature of all features varies, but the mean temperature estimated for the whole observed period of the full-disk is around 1.29 ± 0.16 MK and active regions (ARs) are around 1.76 ± 0.32 MK, whereas BGs, CHs, and XBPs are 1.27 ± 0.15 MK, 1.23 ± 0.14 MK, and 1.37 ± 0.18 MK, respectively. In addition, we found that the mean temperature contribution estimated of the background regions (BGs) is around 93.2%, whereas ARs, CHs, and XBPs are 3.1%, 1.6% and 2.1%, respectively, to the average coronal temperature of the full-disk. The temperature values and their variations of all the features suggest that the features show a high variability in their temperature and that the heating rate of the emission features may be highly variable on solar cycle timescales. It is evident from the analysis that the filter-ratio method can be directly used for temperature analysis of coronal features and to study their surface temperature variability as a function of solar magnetic activity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adithya, H.N., Kariyappa, R., Shinsuke, I., Kanya, K., Zender, J., Damé, L., Gabriel, G., DeLuca, E., Weber, M.: 2021, Solar soft X-ray irradiance variability, I: segmentation of Hinode/XRT full-disk images and comparison with GOES (1 – 8 Å) X-ray flux. Solar Phys. 296, 71. DOI. ADS.
Golub, L., Deluca, E., Austin, G., Bookbinder, J., Caldwell, D., Cheimets, P., Cirtain, J., Cosmo, M., Reid, P., Sette, A., Weber, M., Sakao, T., Kano, R., Shibasaki, K., Hara, H., Tsuneta, S., Kumagai, K., Tamura, T., Shimojo, M., McCracken, J., Carpenter, J., Haight, H., Siler, R., Wright, E., Tucker, J., Rutledge, H., Barbera, M., Peres, G., Varisco, S.: 2007, The X-ray telescope (XRT) for the Hinode mission. Solar Phys. 243, 63. DOI. ADS.
Hara, H., Tsuneta, S., Lemen, J.R., Acton, L.W., McTiernan, J.M.: 1992, High-temperature plasmas in active regions observed with the soft X-ray telescope aboard YOHKOH. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 44, L135. ADS.
Kariyappa, R., Deluca, E.E., Saar, S.H., Golub, L., Damé, L., Pevtsov, A.A., Varghese, B.A.: 2011, Temperature variability in X-ray bright points observed with Hinode/XRT. Astron. Astrophys. 526, A78. DOI. ADS.
Kosugi, T., Matsuzaki, K., Sakao, T., Shimizu, T., Sone, Y., Tachikawa, S., Hashimoto, T., Minesugi, K., Ohnishi, A., Yamada, T., Tsuneta, S., Hara, H., Ichimoto, K., Suematsu, Y., Shimojo, M., Watanabe, T., Shimada, S., Davis, J.M., Hill, L.D., Owens, J.K., Title, A.M., Culhane, J.L., Harra, L.K., Doschek, G.A., Golub, L.: 2007, The Hinode (Solar-B) mission: an overview. Solar Phys. 243, 3. DOI. ADS.
Kumara, S.T., Kariyappa, R., Zender, J.J., Giono, G., Delouille, V., Chitta, L.P., Damé, L., Hochedez, J.-F., Verbeeck, C., Mampaey, B., Doddamani, V.H.: 2014, Segmentation of coronal features to understand the solar EUV and UV irradiance variability. Astron. Astrophys. 561, A9. DOI. ADS.
Lemaire, J.F.: 2011, Determination of coronal temperatures from electron density profiles. arXiv e-prints. arXiv. ADS.
Narukage, N., Sakao, T., Kano, R., Hara, H., Shimojo, M., Bando, T., Urayama, F., Deluca, E., Golub, L., Weber, M., Grigis, P., Cirtain, J., Tsuneta, S.: 2011, Coronal-temperature-diagnostic capability of the Hinode/ X-ray telescope based on self-consistent calibration. Solar Phys. 269, 169. DOI. ADS.
Narukage, N., Sakao, T., Kano, R., Shimojo, M., Winebarger, A., Weber, M., Reeves, K.K.: 2014, Coronal-temperature-diagnostic capability of the Hinode/X-ray telescope based on self-consistent calibration. II. Calibration with on-orbit data. Solar Phys. 289, 1029. DOI. ADS.
Takeda, A., Yoshimura, K., Saar, S.H.: 2016, The Hinode/XRT full-Sun image corrections and the improved synoptic composite image archive. Solar Phys. 291, 317. DOI. ADS.
Weber, M.A., Schmelz, J.T., DeLuca, E.E., Roames, J.K.: 2005, Isothermal bias of the “filter ratio” method for observations of multithermal plasma. Astrophys. J. Lett. 635, L101. DOI. ADS.
White, S.M., Thomas, R.J., Schwartz, R.A.: 2005, Updated expressions for determining temperatures and emission measures from goes soft X-ray measurements. Solar Phys. 227, 231. DOI. ADS.
Zender, J.J., Kariyappa, R., Giono, G., Bergmann, M., Delouille, V., Damé, L., Hochedez, J.-F., Kumara, S.T.: 2017, Segmentation of photospheric magnetic elements corresponding to coronal features to understand the EUV and UV irradiance variability. Astron. Astrophys. 605, A41. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgments
Hinode is a Japanese mission developed and launched by ISAS/JAXA, in collaboration with NAOJ as a domestic partner, NASA and STFC (UK) as international partners. The Hinode science team at ISAS /JAXA has conducted the scientific operation of the Hinode mission. This team mainly consists of scientists from different institutes in the partner countries. JAXA and NAOJ (Japan), STFC (U.K.), NASA (U.S.A.), ESA, and NSC (Norway) have provided the support for the post-launch operation. The Hinode team had contributed all their efforts in the design, build, and operation of the mission. RK wish to express his sincere thanks to all members of ISEE, Nagoya University for the support provided under the Programs of ISEE Joint International Research and Visiting Professorship. HNA had visited ISEE/Nagoya University for 3 months under the sponsership of SCOSTEP Visiting Scholar Program and the support of ISEE. Authors would like to thank Aki Takeda and Keiji Yoshimura for the useful suggestions on the use of the XRT images. The authors would like to express their deepest thanks to the referee who reviewed the manuscript very thoroughly and provided valuable comments and suggestions that greatly improved the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been contributed to this manuscript and it has been circulated to all the authors for their reviews.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adithya, H.N., Kariyappa, R., Kusano, K. et al. Solar Soft X-Ray Irradiance Variability, II: Temperature Variations of Coronal X-Ray Features. Sol Phys 298, 99 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02190-x