Abstract
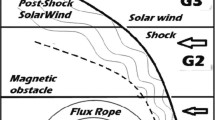
Interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) are important drivers of space-weather disturbances observed at the Earth. We use a parameterized ICME model to investigate the relation between the physical properties of an ICME and these disturbances. Compared to those studies focused on deriving a best set of ICME parameter values matched with observed disturbances, this study is aimed at investigating the role of each parameter in producing space-weather disturbances. Toward this end, we performed a series of three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulations with different sets of ICME parameter values. These parameters are the location, speed, mass, magnetic field strength, and magnetic field orientation of a spheromak-shaped ICME, which is injected into the solar wind reconstructed from near-Sun data and interplanetary scintillation (IPS) data via an MHD-IPS tomography method. By comparing simulation results to in situ observations near the Earth we discuss how the physical properties of an ICME affect space-weather disturbances at the Earth.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M.D., Newkirk, G.: 1969, Magnetic fields and the structure of the solar corona. I: Methods of calculating coronal fields. Solar Phys.9, 131. DOI . ADS .
Bobra, M.G., Sun, X., Hoeksema, J.T., Turmon, M., Liu, Y., Hayashi, K., Barnes, G., Leka, K.D.: 2014, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) vector magnetic field pipeline: SHARPs – Space-weather HMI active region patches. Solar Phys.289, 3549. DOI . ADS .
Brio, M., Wu, C.C.: 1988, An upwind differencing scheme for the equations of ideal magnetohydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys.75(2), 400. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock – Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res.86, 6673. DOI . ADS .
Cho, K.-S., Marubashi, K., Kim, R.-S., Park, S.-H., Lim, E.-K., Kim, S.-J., Kumar, P., Yurchyshyn, V., Moon, Y.-J., Lee, J.-O.: 2017, Impact of the ICME-Earth geometry on the strength of the associated geomagnetic storm: The September 2014 and March 2015 events. J. Korean Astron. Soc.50, 29. DOI . ADS .
Clyne, J., Rast, M.: 2005, A prototype discovery environment for analyzing and visualizing terascale turbulent fluid flow simulations. Proc. SPIE - Int. Soc. for Optical Eng.5669, 284. DOI .
Clyne, J., Mininni, P., Norton, A., Rast, M.: 2007, Interactive desktop analysis of high resolution simulations: application to turbulent plume dynamics and current sheet formation. New J. Phys.9(8), 301.
DeVore, C.R.: 2000, Magnetic helicity generation by solar differential rotation. Astrophys. J.539, 944. DOI . ADS .
Echer, E., Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T., Gonzalez, A.L.C.: 2008, Interplanetary conditions causing intense geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq -100~\mbox{nT}\)) during solar cycle 23 (1996 – 2006). J. Geophys. Res.113, A05221. DOI . ADS .
Filippov, B., Martsenyuk, O., Srivastava, A.K., Uddin, W.: 2015, Solar magnetic flux ropes. J. Astrophys. Astron.36, 157. DOI . ADS .
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1987, Criteria of interplanetary parameters causing intense magnetic storms (\(\mbox{D}_{st} < -100\) nT). Planet. Space Sci.35, 1101. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michałek, G., Kaiser, M.L., Howard, R.A., Reames, D.V., Leske, R., von Rosenvinge, T.: 2002, Interacting coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. Lett.572, L103. DOI . ADS .
Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S., Michalek, G., Stenborg, G., Vourlidas, A., Freeland, S., Howard, R.: 2009, The SOHO/LASCO CME catalog. Earth Moon Planets104, 295. DOI . ADS .
Hayashi, K., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2016, MHD-IPS analysis of relationship among solar wind density, temperature, and flow speed. J. Geophys. Res.121, 7367. DOI . ADS .
Hayashi, K., Zhao, X.P., Liu, Y.: 2006, MHD simulation of two successive interplanetary disturbances driven by cone-model parameters in IPS-based solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett.33, L20103. DOI . ADS .
Hayashi, K., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K.: 2003, MHD tomography using interplanetary scintillation measurement. J. Geophys. Res.108, 1102. DOI . ADS .
Hidalgo, M.A., Nieves-Chinchilla, T.: 2012, A global magnetic topology model for magnetic clouds. I. Astrophys. J.748(2), 109. DOI . ADS .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö.: 2002, Reconstruction of magnetic clouds in the solar wind: Orientations and configurations. J. Geophys. Res.107, 1142. DOI . ADS .
Inoue, S., Kusano, K., Magara, T., Shiota, D., Yamamoto, T.T.: 2011, Twist and connectivity of magnetic field lines in the solar active region NOAA 10930. Astrophys. J.738, 161. DOI . ADS .
Kang, J., Magara, T., Inoue, S., Kubo, Y., Nishizuka, N.: 2016, Distribution characteristics of coronal electric current density as an indicator for the occurrence of a solar flare. Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan68, 101. DOI . ADS .
Kataoka, R., Ebisuzaki, T., Kusano, K., Shiota, D., Inoue, S., Yamamoto, T.T., Tokumaru, M.: 2009, Three-dimensional MHD modeling of the solar wind structures associated with 13 December 2006 coronal mass ejection. J. Geophys. Res.114, A10102. DOI . ADS .
Klein, L.W., Burlaga, L.F.: 1982, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.87, 613. DOI . ADS .
Kliem, B., Török, T., Thompson, W.T.: 2012, A parametric study of erupting flux rope rotation. Modeling the “Cartwheel CME” on 9 April 2008. Solar Phys.281, 137. DOI . ADS .
Lee, H., Magara, T.: 2018, MHD simulation for investigating the dynamic state transition responsible for a solar eruption in active region 12158. Astrophys. J.859, 132. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Jones, J.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.95, 11957. DOI . ADS .
Lim, E.-K., Jeong, H., Chae, J., Moon, Y.-J.: 2007, A check for consistency between different magnetic helicity measurements based on the helicity conservation principle. Astrophys. J.656(2), 1167. DOI . ADS .
Linker, J.A., Caplan, R.M., Downs, C., Riley, P., Mikic, Z., Lionello, R., Henney, C.J., Arge, C.N., Liu, Y., Derosa, M.L., Yeates, A., Owens, M.J.: 2017, The open flux problem. Astrophys. J.848, 70. DOI . ADS .
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Müller-Mellin, R., Schroeder, P.C., Wang, L., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D., Li, Y., Acuña, M.H., Sauvaud, J.-A.: 2008, A comprehensive view of the 2006 December 13 CME: From the Sun to interplanetary space. Astrophys. J.689, 563. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Manchester, W.B. IV, Gombosi, T.I.: 2005, Numerical simulation of the interaction of two coronal mass ejections from Sun to Earth. Astrophys. J.634, 651. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Downs, C., Shibata, K., Roussev, I.I., Asai, A., Gombosi, T.I.: 2011, Numerical investigation of a coronal mass ejection from an anemone active region: Reconnection and deflection of the 2005 August 22 eruption. Astrophys. J.738, 127. DOI . ADS .
Lynch, B.J., Gruesbeck, J.R., Zurbuchen, T.H., Antiochos, S.K.: 2005, Solar cycle-dependent helicity transport by magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res.110, A08107. DOI . ADS .
Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I., Roussev, I., Ridley, A., de Zeeuw, D.L., Sokolov, I.V., Powell, K.G., Tóth, G.: 2004, Modeling a space weather event from the Sun to the Earth: CME generation and interplanetary propagation. J. Geophys. Res.109, A02107. DOI . ADS .
Manchester, W.B., Ridley, A.J., Gombosi, T.I., Dezeeuw, D.L.: 2006, Modeling the Sun-to-Earth propagation of a very fast CME. Adv. Space Res.38, 253. DOI . ADS .
Manchester, I., Ward, B., Vourlidas, A., Tóth, G., Lugaz, N., Roussev, I.I., Sokolov, I.V., Gombosi, T.I., De Zeeuw, D.L., Opher, M.: 2008, Three-dimensional MHD simulation of the 2003 October 28 coronal mass ejection: Comparison with LASCO coronagraph observations. Astrophys. J.684, 1448. DOI . ADS .
Marubashi, K., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Gopalswamy, N., Cho, K.-S., Park, Y.-D.: 2015, Geometrical relationship between interplanetary flux ropes and their solar sources. Solar Phys.290, 1371. DOI . ADS .
Moriguchi, T., Nakamizo, A., Tanaka, T., Obara, T., Shimazu, H.: 2008, Current systems in the Jovian magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res.113, A05204. DOI . ADS .
Nakamizo, A., Tanaka, T., Kubo, Y., Kamei, S., Shimazu, H., Shinagawa, H.: 2009, Development of the 3-D MHD model of the solar corona-solar wind combining system. J. Geophys. Res.114, A07109. DOI . ADS .
Odstrcil, D., Riley, P., Zhao, X.P.: 2004, Numerical simulation of the 12 May 1997 interplanetary CME event. J. Geophys. Res.109, A02116. DOI . ADS .
Parker, E.N.: 1958, Dynamics of the interplanetary gas and magnetic fields. Astrophys. J.128, 664. DOI . ADS .
Schatten, K.H., Wilcox, J.M., Ness, N.F.: 1969, A model of interplanetary and coronal magnetic fields. Solar Phys.6, 442. DOI . ADS .
Schmidt-Voigt, M.: 1989, Time-dependent MHD simulations for cometary plasmas. Astron. Astrophys.210, 433. ADS .
Shen, F., Feng, X.S., Wang, Y., Wu, S.T., Song, W.B., Guo, J.P., Zhou, Y.F.: 2011, Three-dimensional MHD simulation of two coronal mass ejections’ propagation and interaction using a successive magnetized plasma blobs model. J. Geophys. Res.116, A09103. DOI . ADS .
Shiota, D., Kataoka, R.: 2016, Magnetohydrodynamic simulation of interplanetary propagation of multiple coronal mass ejections with internal magnetic flux rope (SUSANOO-CME). Space Weather14, 56. DOI . ADS .
Snyder, C.W., Neugebauer, M., Rao, U.R.: 1963, The solar wind velocity and its correlation with cosmic-ray variations and with solar and geomagnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res.68, 6361. DOI . ADS .
Tanaka, T.: 1994, Finite volume TVD scheme on an unstructured grid system for three-dimensional MHD simulation of inhomogeneous systems including strong background potential fields. J. Comput. Phys.111, 381. DOI . ADS .
Tanaka, T.: 2015, Substorm auroral dynamics reproduced by advanced global magnetosphere-ionosphere (M-I) coupling simulation. In: Auroral Dynamics and Space Weather, 177. Chap. 13. DOI .
Tanaka, T., Murawski, K.: 1997, Three-dimensional MHD simulation of the solar wind interaction with the ionosphere of Venus: Results of two-component reacting plasma simulation. J. Geophys. Res.102, 19805. DOI . ADS .
Tanaka, T., Washimi, H.: 1999, Solar cycle dependence of the heliospheric shape deduced from a global MHD simulation of the interaction process between a nonuniform time-dependent solar wind and the local interstellar medium. J. Geophys. Res.104, 12605. DOI . ADS .
Thernisien, A.F.R., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Modeling of flux rope coronal mass ejections. Astrophys. J.652, 763. DOI . ADS .
Thompson, W.T.: 2006, Coordinate systems for solar image data. Astron. Astrophys.449, 791. DOI . ADS .
Török, T., Downs, C., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Titov, V.S., Mikić, Z., Riley, P., Caplan, R.M., Wijaya, J.: 2018, Sun-to-Earth MHD simulation of the 2000 July 14 “Bastille Day” eruption. Astrophys. J.856, 75. DOI . ADS .
Totten, T.L., Freeman, J.W., Arya, S.: 1995, An empirical determination of the polytropic index for the free-streaming solar wind using HELIOS 1 data. J. Geophys. Res.100, 13. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., Fischer, S., Pelant, P., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Detman, T.: 1997, Propagation of a spheromak 1. Some comparisons of cylindrical and spherical magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res.102, 24183. DOI . ADS .
Vemareddy, P., Cheng, X., Ravindra, B.: 2016, Sunspot rotation as a driver of major solar eruptions in the NOAA active region 12158. Astrophys. J.829, 24. DOI . ADS .
Vourlidas, A., Lynch, B.J., Howard, R.A., Li, Y.: 2013, How many CMEs have flux ropes? Deciphering the signatures of shocks, flux ropes, and prominences in coronagraph observations of CMEs. Solar Phys.284, 179. DOI . ADS .
Xie, H., Ofman, L., Lawrence, G.: 2004, Cone model for halo CMEs: Application to space weather forecasting. J. Geophys. Res.109, A03109. DOI . ADS .
Zhang, J., Richardson, I.G., Webb, D.F., Gopalswamy, N., Huttunen, E., Kasper, J.C., Nitta, N.V., Poomvises, W., Thompson, B.J., Wu, C.-C., Yashiro, S., Zhukov, A.N.: 2007, Solar and interplanetary sources of major geomagnetic storms (\(\mbox{Dst} \leq -100\) nT) during 1996 – 2005. J. Geophys. Res.112, A10102. DOI . ADS .
Zhou, Y.F., Feng, X.S., Wu, S.T., Du, D., Shen, F., Xiang, C.Q.: 2012, Using a 3-D spherical plasmoid to interpret the Sun-to-Earth propagation of the 4 November 1997 coronal mass ejection event. J. Geophys. Res.117, A01102. DOI . ADS .
Zurbuchen, T.H., Richardson, I.G.: 2006, In-situ solar wind and magnetic field signatures of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Space Sci. Rev.123, 31. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Kyung Hee University for general support of this work. J.A. thanks Gwangson Choe for his instructive comments. J.A. thanks Soojeong Jang and Jihye Kang for providing the data and information used in this work. J.A. also thanks Takashi Tanaka for providing the REPPU code and useful comments on the code. The CME catalog is generated and maintained at the CDAW Data Center by NASA and The Catholic University of America in cooperation with the Naval Research Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The authors used the synoptic charts of solar-surface magnetic fields provided by Wilcox Solar Observatory (WSO), Stanford University (http://wso.standford.edu). We also acknowledge use of NASA/GSFC Space Physics Data Facility OMNIWeb service, and OMNI data. Figure 3 was created using VAPOR (Clyne and Rast, 2005; Clyne et al., 2007). J.A. thanks the researchers at NICT for their detailed comments, suggestions, and constant support. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2017R1A2B4002383, PI: T. Magara), as well as the BK21 plus program through the NRF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, J., Magara, T., Hayashi, K. et al. Parametric Study of ICME Properties Related to Space Weather Disturbances via a Series of Three-Dimensional MHD Simulations. Sol Phys 294, 143 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1531-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-019-1531-6