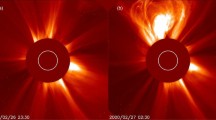
Abstract
The trajectories of coronal mass ejection (CME) are often observed to deviate from radial propagation from the source while within the coronagraph field of view (\(\mbox{R} <15\,\mbox{--}\,30~\mbox{R}_{\mathrm{sun}}\)). To better understand nonradial propagation within the corona, we first analyze the trajectories of five CMEs for which both the source and 3D trajectory (latitude, longitude, and velocity) can be well determined from solar imaging observations, primarily using observations from the twin Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory (STEREO) spacecraft. Next we analyze the cause of any nonradial propagation using a potential field source surface (PFSS) model to determine the direction of the magnetic pressure forces exerted on the CME at various heights in the corona. In two cases, we find that the CME deviation from radial propagation primarily occurs before it reaches the coronagraph field of view (below 1.5 solar radii). Based on the observations and the magnetic pressure forces calculated from the PFSS model, we conclude that for these cases the deviation is the result of strong active-region fields causing an initial asymmetric expansion of the CME that gives rise to the apparent rapid deflection and nonradial propagation from the source. Within the limitations of the PFSS model, the magnetic fields for all five cases appear to guide the CMEs out of the corona through the weak-field region around the heliospheric current sheet even when the current sheet is inclined and warped.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrne, J., Maloney, S.A., McAteer, J., Refoio, J.M., Gallagher, P.T.: 2010, Nat. Commun. 1, 74. DOI .
Colaninno, R., Vourlidas, A., Wu, C.C.: 2013, J. Geophys. Res. 118, 6866. DOI .
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V.: 2004, Astron. Astrophys. 422, 307.
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V., Tripathi, D.: 2006, Adv. Space Res. 38, 461.
DeForest, C.E., Howard, T.A., McComas, D.J.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 769, 43. DOI .
Gopalswamy, N., Mäkelä, P., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S.: 2009, J. Geophys. Res. 114, A00A22.
Gui, B., Shen, C., Wang, Y., Ye, P., Liu, J., Wang, S., Zhao, X.: 2011, Solar Phys. 271, 111. DOI .
Howard, R.A., Sheeley, N.R. Jr., Koomen, M.J., Michels, D.J.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 8173.
Howard, R.A., Moses, J.D., Vourlidas, A., Newmark, J.S., Socker, D.G., Plunkett, S.P., Korendyke, C.M., Cook, J.W., Hurley, A., Davila, J.M., et al.: 2008, Space Sci. Rev. 136, 67.
Hundhausen, A.J.: 1993, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 13177.
Kay, C., Opher, M., Evans, R.M.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 775, 5. DOI .
Kilpua, E.K.J., Pomoell, J., Vourlidas, A., Vainio, R., Luhmann, J., Li, Y., et al.: 2009, Ann. Geophys. 27, 4491.
Liewer, P.C., Hall, J.R., De Jong, E.M., Socker, D.G., Howard, R.A., Crane, P.C., Reiser, P., Rich, N., Vourlidas, A.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15903.
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D., Vourlidas, A., Petrie, G.J.D.: 2009, Astrophys. J. Lett. 698, L51.
Liu, Y., Davies, J.A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Bale, S.D., Lin, R.P.: 2010a, Astrophys. J. Lett. 710, L82.
Liu, Y., Thernisien, A., Luhmann, J.G., Vourlidas, A., Davies, J.A., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D.: 2010b, Astrophys. J. 722, 1762.
Liu, W., Nitta, N.V., Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M., Tarbell, T.D.: 2010c, Astrophys. J. 723, L53.
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Bale, S., Lin, R.P.: 2011, Astrophys. J. 734, 84. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Roussev, I.I.: 2011, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1187. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Vourlidas, A., Roussev, I.I., Morgan, H.: 2009, Solar Phys. 256, 269. DOI .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J., Davies, J.A., Möstl, C., Davis, C.J., Roussev, I.I., Temmer, M.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 759, 68. DOI .
MacQueen, R.M., Hundhausen, A.J., Conover, C.W.: 1986, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 31.
Manchester, W.B., Gombosi, T.I., Roussev, I., Ridley, A., De Zeeuw, D.L., Sokolov, I.V., Powell, K.G., Tóth, G.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, 2107.
Möstl, C., Amla, K., Hall, J.R., Liewer, P.C., De Jong, E.M., Colaninno, R.C., et al.: 2014, Astrophys. J. 787, 119. DOI .
Odstrcil, D.: 2004, J. Geophys. Res. 109, A02116. DOI .
Panasenco, O., 2015, Private communication.
Panasenco, O., Martin, S., Joshi, A.D., Srivastava, N.: 2011, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 73, 1129.
Panasenco, O., Martin, S., Velli, M., Vourlidas, A.: 2013, Solar Phys. 287, 391.
Plunkett, S.P., Thompson, B.J., St. Cyr, O.C., Howard, R.A.: 2001, J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 63, 389. DOI .
Pneuman, G.W.: 1984, Solar Phys. 94, 387.
Rouillard, A.P., Odstrcil, D., Sheeley, N.R., Tylka, A., Vourlidas, A., Mason, G., et al.: 2011, Astrophys. J. 735, 7. DOI .
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Astrophys. J. Lett. 714, L128. DOI .
Schrijver, C.J., DeRosa, M.L.: 2003, Solar Phys. 212, 165.
Schwenn, R.: 2000, Adv. Space Res. 26, 43.
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Gui, B., Ye, P., Wang, S.: 2011, Solar Phys. 269, 389.
Shen, C., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Liu, T., Liu, R., Vourlidas, A., Miao, B., Ye, P., Liu, J., Zhou, Z.: 2012, Nat. Phys. 8, 923. DOI .
Subramanian, P., Dere, K.P., Rich, N.B., Howard, R.A.: 1999, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 22321.
Thernisien, A.: 2011, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 194, 33.
Thernisien, A.F.R., Howard, R.A., Vourlidas, A.: 2006, Astrophys. J. 652, 763. DOI .
Thernisien, A.F.R., Vourlidas, A., Howard, R.A.: 2009, Solar Phys. 256, 111.
Tun, S., Vourlidas, A.: 2013, Astrophys. J. 766, 130.
Wang, Y.-M.: 2015, Astrophys. J. 805, L12. DOI .
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley, N.R., Rich, N.B.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 27, 149.
Wood, B.E., Wu, C.-C., Howard, R.A., Socker, D.G., Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, Astrophys. J. 729, 70.
Xie, H., Odstrcil, D., Mays, L., St. Cyr, O.C., Gopalswamy, N., Cremades, H.: 2012, J. Geophys. Res. 117, A04105. DOI .
Zhou, Y.F., Feng, X.S.: 2013, J. Geophys. Res. 118, 6007. DOI .
Zuccarello, F.P., Bemporad, A., Jacobs, C., Mierla, M., Poedts, S., Zuccarello, F.: 2012, Astrophys. J. 744, 66. DOI .
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank R.A. Howard, N. Sheeley, M. Velli and V. Pizzo for useful discussions on various aspects of this research. We also thank the referee for very useful comments that have improved the article. The work of PCL was conducted at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology under a contract from NASA. The work of OP was supported by a subcontract from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The work of AV and RC was supported by NASA contract S-136361-Y to the Naval Research Laboratory. AV is also supported by internal JHU/APL funds. The STEREO/SECCHI data used here are produced by an international consortium of the Naval Research Laboratory (USA), Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Lab (USA), NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (USA) Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK), University of Birmingham (UK), Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung (Germany), Centre Spatiale de Liège (Belgium), Institut d’Optique Théorique et Appliquée (France), Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale (France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liewer, P., Panasenco, O., Vourlidas, A. et al. Observations and Analysis of the Non-Radial Propagation of Coronal Mass Ejections Near the Sun. Sol Phys 290, 3343–3364 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0794-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-015-0794-9