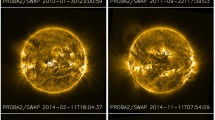
Abstract
Co-temporal Doppler images from Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)/Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) and Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)/Helioseismic Magnetic Imager (HMI) have been analyzed to extract quantitative information about global properties of the spatial and temporal characteristics of solar supergranulation. Preliminary comparisons show that supergranules appear to be smaller and have stronger horizontal velocity flows within HMI data than was measured with MDI. There appears to be no difference in their evolutionary timescales. Supergranule sizes and velocities were analyzed over a ten-day time period at a 15-minute cadence. While the averages of the time-series retain the aforementioned differences, fluctuations of these parameters first observed in MDI data were seen in both MDI and HMI time-series, exhibiting a strong cross-correlation. This verifies that these fluctuations are not instrumental, but are solar in origin. The observed discrepancies between the averaged values from the two sets of data are a consequence of instrument resolution. The lower spatial resolution of MDI results in larger observed structures with lower velocities than is seen in HMI. While these results offer a further constraint on the physical nature of supergranules, they also provide a level of calibration between the two instruments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deans, S.R.: 1983, The Radon Transform and Some of Its Applications, Wiley, New York.
DeRosa, M.L., Toomre, J.: 2004, Evolution of solar supergranulation. Astrophys. J. 616, 1242 – 1260. doi: 10.1086/424920 .
Doerr, H.-P., Roth, M.: 2011, Localized averaging kernels for probing the deep meridional flow with data from GONG, MDI and HMI. J. Phys. CS-271(1), 012057. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/271/1/012057 .
Dravins, D.: 1982, Photospheric spectrum line asymmetries and wavelength shifts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 20, 61 – 89. doi: 10.1146/annurev.aa.20.090182.000425 .
Duvall, T.L. Jr.: 1980, The equatorial rotation rate of the supergranulation cells. Solar Phys. 66, 213 – 221. doi: 10.1007/BF00150578 .
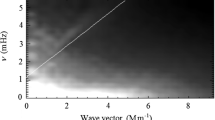
Gizon, L., Duvall, T.L., Schou, J.: 2003, Wave-like properties of solar supergranulation. Nature 421, 43 – 44. doi: 10.1038/nature01287 .
Goldbaum, N., Rast, M.P., Ermolli, I., Sands, J.S., Berrilli, F.: 2009, The intensity profile of the solar supergranulation. Astrophys. J. 707, 67 – 73. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/707/1/67 .
Hagenaar, H.J., Schrijver, C.J., Title, A.M.: 1997, The distribution of cell sizes of the solar chromospheric network. Astrophys. J. 481, 988. doi: 10.1086/304066 .
Hathaway, D.H.: 1987, Spherical harmonic analysis of steady photospheric flows. Solar Phys. 108, 1 – 20. doi: 10.1007/BF00152073 .
Hathaway, D.H.: 1988, Temporal filters for isolating steady photospheric flows. Solar Phys. 117, 1 – 12. doi: 10.1007/BF00148567 .
Hathaway, D.H.: 1992, Spherical harmonic analysis of steady photospheric flows. II. Solar Phys. 137, 15 – 32. doi: 10.1007/BF00146573 .
Hathaway, D.H., Williams, P.E., Cuntz, M.: 2006, Supergranule superrotation identified as a projection effect. Astrophys. J. 644, 598 – 602. doi: 10.1086/498842 .
Hathaway, D.H., Beck, J.G., Bogart, R.S., Bachmann, K.T., Khatri, G., Petitto, J.M., Han, S., Raymond, J.: 2000, The photospheric convection spectrum. Solar Phys. 193, 299 – 312. ADS: 2000SoPh..193..299H , doi: 10.1023/A:1005200809766 .
Hathaway, D.H., Beck, J.G., Han, S., Raymond, J.: 2002, Radial flows in supergranules. Solar Phys. 205, 25 – 38. ADS: 2002SoPh..205...25H , doi: 10.1023/A:1013881213279 .
Hathaway, D.H., Williams, P.E., Dela Rosa, K., Cuntz, M.: 2010, The advection of supergranules by the Sun’s axisymmetric flows. Astrophys. J. 725, 1082 – 1090. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/725/1/1082 .
Hirzberger, J., Gizon, L., Solanki, S.K., Duvall, T.L.: 2008, Structure and evolution of supergranulation from local helioseismology. Solar Phys. 251, 417 – 437. doi: 10.1007/s11207-008-9206-8 .
Howe, R., Jain, K., Hill, F., Komm, R., González Hernández, I., Bogart, R.: 2011a, Comparison of HMI Dopplergrams with GONG and MDI data. J. Phys. CS-271(1), 012060. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/271/1/012060 .
Howe, R., Tripathy, S., González Hernández, I., Komm, R., Hill, F., Bogart, R., Haber, D.: 2011b, Ring-diagram parameter comparisons for GONG, MDI and HMI. J. Phys. CS-271(1), 012015. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/271/1/012015 .
Leighton, R.B., Noyes, R.W., Simon, G.W.: 1962, Velocity fields in the solar atmosphere. I. Preliminary report. Astrophys. J. 135, 474. doi: 10.1086/147285 .
McIntosh, S.W., Leamon, R.J., Hock, R.A., Rast, M.P., Ulrich, R.K.: 2011, Observing evolution in the supergranular network length scale during periods of low solar activity. Astrophys. J. Lett. 730, L3. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/730/1/L3 .
Meunier, N., Roudier, T.: 2007, The superrotation of solar supergranules. Astron. Astrophys. 466, 691 – 696. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066790 .
Meunier, N., Roudier, T., Rieutord, M.: 2008, Supergranules over the solar cycle. Astron. Astrophys. 488, 1109 – 1115. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20078835 .
Meunier, N., Tkaczuk, R., Roudier, T.: 2007, Intensity variations inside supergranules. Astron. Astrophys. 463, 745 – 753. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20066314 .
Meunier, N., Tkaczuk, R., Roudier, T., Rieutord, M.: 2007, Velocities and divergences as a function of supergranule size. Astron. Astrophys. 461, 1141 – 1147. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20065625 .
Norton, A.A., Graham, J.P., Ulrich, R.K., Schou, J., Tomczyk, S., Liu, Y., Lites, B.W., López Ariste, A., Bush, R.I., Socas-Navarro, H., Scherrer, P.H.: 2006, Spectral line selection for HMI: a comparison of Fe i 6173 Å and Ni i 6768 Å. Solar Phys. 239, 69 – 91. doi: 10.1007/s11207-006-0279-y .
Norton, A.A., Graham, J.P., Ulrich, R.K., Schou, J., Tomczyk, S., Liu, Y., Lites, B.W., López Ariste, A., Bush, R.I., Socas-Navarro, H., Scherrer, P.H.: 2011, On the formation height of the SDO/HMI Fe i 6173 Å Doppler signal. Solar Phys. 271, 27 – 40. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9783-9 .
Pesnell, W.D., Thompson, B.J., Chamberlin, P.C.: 2012, The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 3 – 15. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9841-3 .
Raju, K.P., Singh, J.: 2002, Dependence of supergranular length-scales on network magnetic fields. Solar Phys. 207, 11 – 16. ADS: 2002SoPh..207...11R , doi: 10.1023/A:1015585010078 .
Rast, M.P.: 2003, Supergranulation: new observation, possible explanation. In: Sawaya-Lacoste, H. (ed.) GONG+ 2002. Local and Global Helioseismology: The Present and Future SP-517, ESA, Noordwijk, 163 – 172.
Rast, M.P.: 2010, Is there such a thing as quiet Sun? In: Cranmer, S.R., Hoeksema, J.T., Kohl, J.L. (eds.) SOHO-23: Understanding a Peculiar Solar Minimum CS-428, Astron. Soc. Pac., San Francisco, 87.
Rieutord, M., Rincon, F.: 2010, The Sun’s supergranulation. Living Rev. Solar Phys. 7(2). doi: 10.12942/lrsp-2010-2 .
Rieutord, M., Roudier, T., Rincon, F., Malherbe, J.-M.: 2000, On mesogranulation, network formation and supergranulation. Astron. Astrophys. 357, 1063.
Scherrer, P.H., Bogart, R.S., Bush, R.I., Hoeksema, J.T., Kosovichev, A.G., Schou, J., Rosenberg, W., Springer, L., Tarbell, T.D., Title, A., Wolfson, C.J., Zayer, I., MDI Engineering Team: 1995, The solar oscillations investigation – Michelson Doppler imager. Solar Phys. 162, 129 – 188. doi: 10.1007/BF00733429 .
Scherrer, P.H., Schou, J., Bush, R.I., Kosovichev, A.G., Bogart, R.S., Hoeksema, J.T., Liu, Y., Duvall, T.L., Zhao, J., Title, A.M., Schrijver, C.J., Tarbell, T.D., Tomczyk, S.: 2012, The Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) investigation for the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Solar Phys. 275, 207 – 227. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9834-2 .
Simon, G.W., Leighton, R.B.: 1964, Velocity fields in the solar atmosphere. III. Large-scale motions, the chromospheric network, and magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 140, 1120. doi: 10.1086/148010 .
Thompson, W.T.: 2002, Standardized coordinate systems for solar image data. Adv. Space Res. 29, 2093 – 2098. doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00155-2 .
Williams, P.E., Pesnell, W.D.: 2011, Comparisons of supergranule characteristics during the solar minima of Cycles 22/23 and 23/24. Solar Phys. 270, 125 – 136. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9718-5 .
Williams, P.E., Pesnell, W.D.: 2013, Time-series analysis of supergranule characteristics at solar minimum. Solar Phys., accepted.
Wolff, C.: 1995, Oscillation-convection coupling: cause of supergranulation. Astrophys. J. 443, 423 – 433. doi: 10.1086/175535 .
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an appointment to the NASA Postdoctoral Program at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, administered by Oak Ridge Associated Universities through a contract with NASA via the Solar Dynamics Observatory. SDO is part of NASA’s Living With a Star (LWS) program. HMI was designed and assembled at Stanford University and Lockheed Martin Solar and Astrophysics Laboratory. SOHO is a project of international cooperation between ESA and NASA. The authors wish to thank the referee for the comments that further enhanced the contents of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, P.E., Pesnell, W.D., Beck, J.G. et al. Analysis of Supergranule Sizes and Velocities Using Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)/Helioseismic Magnetic Imager (HMI) and Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO)/Michelson Doppler Imager (MDI) Dopplergrams. Sol Phys 289, 11–25 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0330-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-013-0330-8