Abstract
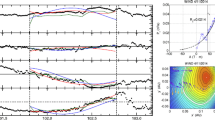
Magnetic clouds (MCs) are a subset of interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) which exhibit signatures consistent with a magnetic flux rope structure. Techniques for reconstructing flux rope orientation from single-point in situ observations typically assume the flux rope is locally cylindrical, e.g., minimum variance analysis (MVA) and force-free flux rope (FFFR) fitting. In this study, we outline a non-cylindrical magnetic flux rope model, in which the flux rope radius and axial curvature can both vary along the length of the axis. This model is not necessarily intended to represent the global structure of MCs, but it can be used to quantify the error in MC reconstruction resulting from the cylindrical approximation. When the local flux rope axis is approximately perpendicular to the heliocentric radial direction, which is also the effective spacecraft trajectory through a magnetic cloud, the error in using cylindrical reconstruction methods is relatively small (≈ 10∘). However, as the local axis orientation becomes increasingly aligned with the radial direction, the spacecraft trajectory may pass close to the axis at two separate locations. This results in a magnetic field time series which deviates significantly from encounters with a force-free flux rope, and consequently the error in the axis orientation derived from cylindrical reconstructions can be as much as 90∘. Such two-axis encounters can result in an apparent ‘double flux rope’ signature in the magnetic field time series, sometimes observed in spacecraft data. Analysing each axis encounter independently produces reasonably accurate axis orientations with MVA, but larger errors with FFFR fitting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bothmer, V., Schwenn, R.: 1998, The structure and origin of magnetic clouds in the solar wind. Ann. Geophys. 16, 1 – 24.
Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, Magnetic clouds: Constant alpha force-free configurations. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7217 – 7224.
Burlaga, L.F., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673 – 6684.
Cane, H.V., Richardson, I.G.: 2003, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections in the near-Earth solar wind during 1996 – 2002. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1156. doi: 10.1029/2002JA009817 .
Cremades, H., Bothmer, V.: 2004, On the three-dimensional configuration of coronal mass ejections. Astron. Astrophys. 422, 307 – 322. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20035776 .
Dungey, J.W.: 1961, Interplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47.
Farrugia, C.J., Osherovich, V.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, Magnetic flux rope versus the spheromak as models for interplanetary magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 12293. doi: 10.1029/95JA00272 .
Gosling, J.T.: 1993, The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18937 – 18950. doi: 10.1029/93JA01896 .
Gosling, J.T., Baker, D.N., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C., Zwickl, R.D.: 1987, Bidirectional solar wind electron heat flux events. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 8519 – 8535.
Gulisano, A.M., Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P.: 2007, Estimation of the bias of the minimum variance technique in the determination of magnetic clouds global quantities and orientation. Adv. Space Res. 40, 1881 – 1890. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.09.001 .
Hidalgo, M.A., Cid, C., Vinas, A.F., Sequeiros, J.: 2002, A non-force-free approach to the topology of magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1002 – 1009. doi: 10.1029/2001JA900100 .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.O.: 2001, Reconstruction of magnetic flux ropes in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 1443.
Hundhausen, A.J.: 1993, Sizes and locations of coronal mass ejections – SMM observations from 1980 and 1984 – 1989. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 13177 – 13200.
Klein, L.W., Burlaga, L.F.: 1982, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 613 – 624.
Lavraud, B., Borovsky, J.E.: 2008, Altered solar wind-magnetosphere interaction at low Mach numbers: Coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A00B08. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013192 .
Lavraud, B., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P.: 2011, In situ signatures of interchange reconnection between magnetic clouds and open magnetic fields: A mechanism for the erosion of polar coronal holes? Solar Phys. 270, 285 – 296. doi: 10.1007/s11207-011-9717-6 .
Lepping, R.P., Jones, J.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957 – 11965.
Lynch, B.J., Gruesbeck, J.R., Zurbuchen, T.H., Antiochos, S.K.: 2005, Solar cycle dependent helicity transport by magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A08107. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011137 .
Marubashi, K., Lepping, R.P.: 2007, Long-duration magnetic clouds: A comparison of analyses using torus- and cylinder-shaped flux rope models. Ann. Geophys. 25, 2453 – 2477. doi: 10.5194/angeo-25-2453-2007 .
Mulligan, T., Russell, C.T.: 2001, Mulitspacecraft modeling of the flux rope structure of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: Cylindrical symmetric versus nonsymmetric topologies. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10581 – 10596.
Owens, M.J.: 2008, Combining remote and in situ observations of coronal mass ejections to better constrain magnetic cloud reconstruction. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A12102. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013589 .
Owens, M.J., Cargill, P.J.: 2004, Non-radial solar wind flows induced by the motion of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Ann. Geophys. 22, 4395 – 4397.
Owens, M.J., Crooker, N.U., Horbury, T.S.: 2009, The expected imprint of flux rope geometry on suprathermal electrons in magnetic clouds. Ann. Geophys. 27, 4057 – 4067. doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-4057-2009 .
Owens, M.J., Merkin, V.G., Riley, P.: 2006, A kinematically distorted flux rope model for magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A03104. doi: 10.1029/2005JA011460 .
Owens, M.J., Schwadron, N.A., Crooker, N.U., Hughes, W.J., Spence, H.E.: 2007, Role of coronal mass ejections in the heliospheric Hale cycle. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L06104. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028795 .
Rees, A., Forsyth, R.J.: 2004, Two examples of magnetic clouds with double rotations observed by the Ulysses spacecraft. Geophys. Res. Lett. 31, L06804. doi: 10.1029/2003GL018330 .
Riley, P., Crooker, N.U.: 2004, Kinematic treatment of CME evolution in the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 600, 1035 – 1042.
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Mikic, Z., Odstrcil, D., Hidalgo, M.A., Hu, Q., Lepping, R.P., Lynch, B.J., Rees, A.: 2004, Fitting flux-ropes to a global MHD solution: A comparison of techniques. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1321 – 1332.
Romashets, E., Vandas, M.: 2009, Linear force-free field of a toroidal symmetry. Astron. Astrophys. 499, 17 – 20. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/200911701 .
Russell, C.T., Mulligan, T.: 2002, On the magnetosheath thicknesses of interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Planet. Space Sci. 50, 527 – 534.
Savani, N.P., Owens, M.J., Rouillard, A.P., Forsyth, R.J., Davies, J.A.: 2010, Observational evidence of a coronal mass ejection distortion directly attributable to a structured solar wind. Astrophys. J. Lett. 714, L128 – L132. doi: 10.1088/2041-8205/714/1/L128 .
Sonnerup, B.U.O., Cahill, L.J.: 1967, Magnetopause structure and attitude from Explorer 12 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 72, 171.
Vandas, M., Romashets, E.P.: 2003, A force-free field with constant alpha in an oblate cylinder: A generalization of the Lundquist solution. Astron. Astrophys. 398, 801 – 807. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20021691 .
Vandas, M., Fischer, S., Geranios, A.: 1991, Spherical and cylindrical models of magnetized plasma clouds and their comparison with spacecraft data. Planet. Space Sci. 39, 1147 – 1154. doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(91)90166-8 .
Vandas, M., Fischer, S., Dryer, M., Smith, Z., Detman, T.: 1998, Propagation of a spheromak 2. Three-dimensional structure of a spheromak. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 23717 – 23726. doi: 10.1029/98JA01902 .
Wang, Y., Zhou, G., Ye, P., Wang, S., Wang, J.: 2006, A study of the orientation of interplanetary magnetic clouds and solar filaments. Astrophys. J. 651, 1245 – 1255. doi: 10.1086/507668 .
Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., Crooker, N.U., Balogh, A., Bothmer, V., Forsyth, R.J., Gazis, P., Gosling, J.T., Horbury, T., Kilchmann, A., Richardson, I.G., Riley, P., Rodriguez, L., von Steiger, R., Wurz, P., Zurbuchen, T.H.: 2006, Understanding interplanetary coronal mass ejection signatures. Space Sci. Rev. 123, 177 – 216. doi: 10.1007/s11214-006-9017-x .
Yamamoto, T.T., Kataoka, R., Inoue, S.: 2010, Helical lengths of magnetic clouds from the magnetic flux conservation. Astrophys. J. 710, 456 – 461. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/710/1/456 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owens, M.J., Démoulin, P., Savani, N.P. et al. Implications of Non-cylindrical Flux Ropes for Magnetic Cloud Reconstruction Techniques and the Interpretation of Double Flux Rope Events. Sol Phys 278, 435–446 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-9939-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-012-9939-2