Abstract
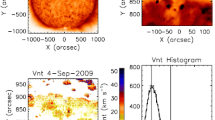
Unipolar streamers (also known as pseudo-streamers) are coronal structures that, at least in coronagraph images, and when viewed at the correct orientation, are often indistinguishable from dipolar (or “standard”) streamers. When interpreted with the aid of a coronal magnetic field model, however, they are shown to consist of a pair of loop arcades. Whereas dipolar streamers separate coronal holes of the opposite polarity and whose cusp is the origin of the heliospheric current sheet, unipolar streamers separate coronal holes of the same polarity and are therefore not associated with a current sheet. In this study, we investigate the interplanetary signatures of unipolar streamers. Using a global MHD model of the solar corona driven by the observed photospheric magnetic field for Carrington rotation 2060, we map the ACE trajectory back to the Sun. The results suggest that ACE fortuitously traversed through a large and well-defined unipolar streamer. We also compare heliospheric model results at 1 AU with ACE in-situ measurements for Carrington rotation 2060. The results strongly suggest that the solar wind associated with unipolar streamers is slow. We also compare predictions using the original Wang–Sheeley (WS) empirically determined inverse relationship between solar wind speed and expansion factor. Because of the very low expansion factors associated with unipolar streamers, the WS model predicts high speeds, in disagreement with the observations. We discuss the implications of these results in terms of theories for the origin of the slow solar wind. Specifically, premises relying on the expansion factor of coronal flux tubes to modulate the properties of the plasma (and speed, in particular) must address the issue that while the coronal expansion factors are significantly different at dipolar and unipolar streamers, the properties of the measured solar wind are, at least qualitatively, very similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antiochos, S.K., Mikić, Z., Titov, V.S., Lionello, R., Linker, J.A.: 2011, A model for the sources of the slow solar wind. Astrophys. J. 731, 112. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/731/2/112 .
Arge, C.N.: 2004, Working with the photospheric magnetic field observations from Mount Wilson, Wilcox, and Kitt Solar Observatories. AGU, Fall Meeting, SH52A-02.
Arge, C.N., Pizzo, V.J.: 2000, Improvement in the prediction of solar wind conditions using near-real time solar magnetic field updates. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10465. doi: 10.1029/1999JA900262 .
Arge, C.N., Odstrcil, D., Pizzo, V.J., Mayer, L.R.: 2003, Improved method for specifying solar wind speed near the Sun. In: Velli, M., Bruno, R., Malara, F., Bucci, B. (eds.) Solar Wind Ten, AIP Conf. Proc. 679, 190. doi: 10.1063/1.1618574 .
Cranmer, S.R.: 2010, An efficient approximation of the coronal heating rate for use in global Sun-heliosphere simulations. Astrophys. J. 710, 676. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/710/1/676 .
Cranmer, S.R., van Ballegooijen, A.A., Edgar, R.J.: 2007, Self-consistent coronal heating and solar wind acceleration from anisotropic magnetohydrodynamic turbulence. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 171, 520. doi: 10.1086/518001 .
Crooker, N.U., Huang, C., Lamassa, S.M., Larson, D.E., Kahler, S.W., Spence, H.E.: 2004a, Heliospheric plasma sheets. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 3107. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010170 .
Crooker, N.U., Kahler, S.W., Larson, D.E., Lin, R.P.: 2004b, Large-scale magnetic field inversions at sector boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 3108. doi: 10.1029/2003JA010278 .
Farrell, P.: 2011, New space weather forecasting model going operational with National Weather Service. www.bu.edu/cas/news/press-releases/cism/ .
Fisk, L.: 1996, Motion of the footpoints of heliospheric magnetic field lines at the Sun: Implications for recurrent energetic particle events at high heliographic latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 101, 15547. doi: 10.1029/96JA01005 .
Gosling, J.T., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C.: 1978, Solar wind stream interfaces. J. Geophys. Res. 83, 1401. doi: 10.1029/JA083iA04p01401 .
Gosling, J.T., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Feldman, W.C., Borrini, G., Hansen, R.T.: 1981, Coronal streamers in the solar wind at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5438. doi: 10.1029/JA086iA07p05438 .
Hakamada, K., Akasofu, S.: 1981, A cause of solar wind speed variations observed at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 1290. doi: 10.1029/JA086iA03p01290 .
Hundhausen, A.J.: 1972, Coronal Expansion and Solar Wind, Springer, New York, 7.
Laming, J.M.: 2004, On collisionless electron-ion temperature equilibration in the fast solar wind. Astrophys. J. 604, 874. doi: 10.1086/382066 .
Lionello, R., Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z.: 2005, The effects of differential rotation on the magnetic structure of the solar corona: magnetohydrodynamic simulations. Astrophys. J. 625, 463. doi: 10.1086/429268 .
Liu, Y.C.M., Galvin, A.B., Popecki, M.A., Simunac, K.D.C., Kistler, L., Farrugia, C., Lee, M.A., Klecker, B., Bochsler, P., Luhmann, J.L., Jian, L.K., Moebius, E., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R., Wurz, P.: 2010, Proton enhancement and decreased O6+/H at the heliospheric current sheet: implications for the origin of slow solar wind. In: Twelfth International Solar Wind Conference, AIP Conf. Proc. 1216, 363. doi: 10.1063/1.3395875 .
Neugebauer, M., Snyder, C.W.: 1962, Solar plasma experiment. Science 138, 1095. doi: 10.1029/2004JA010456 .
Neugebauer, M., Liewer, P.C., Goldstein, B.E., Zhou, X., Steinberg, J.T.: 2004, Solar wind stream interaction regions without sector boundaries. J. Geophys. Res. 109, 10102.
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z.: 2001, An empirically-driven global MHD model of the corona and inner heliosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15889. doi: 10.1029/2000JA000121 .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Mikić, Z., Lionello, R., Ledvina, S.A., Luhmann, J.G.: 2006, A comparison between global solar magnetohydrodynamic and potential field source surface model results. Astrophys. J. 653, 1510. doi: 10.1086/508565 .
Riley, P., Lionello, R., Linker, J.A., Mikic, Z., Luhmann, J., Wijaya, J.: 2011, Global MHD modeling of the solar corona and inner heliosphere for the Whole Heliosphere Interval. Solar Phys. 145. doi: 10.1007/s11207-010-9698-x .
Sarabhai, V.: 1963, Some consequences of nonuniformity of solar wind velocity. J. Geophys. Res. 68, 1555. doi: 10.1029/JZ068i005p01555 .
Sheeley, N.R., Wang, Y.M., Hawley, S.H., Brueckner, G.E., Dere, K.P., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Korendyke, C.M., Michels, D.J., Paswaters, S.E., Socker, D.G., St. Cyr, O.C., Wang, D., Lamy, P.L., Llebaria, A., Schwenn, R., Simnett, G.M., Plunkett, S., Biesecker, D.A.: 1997, Measurements of flow speeds in the corona between 2 and 30 R Sun. Astrophys. J. 484, 472. doi: 10.1086/304338 .
Sonett, C.P., Colburn, D.S.: 1965, The SI+–SI− pair and interplanetary forward-reverse shock ensembles. Planet. Space Sci. 13, 675. doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(65)90046-2 .
Suess, S.T., Ko, Y.K., von Steiger, R., Moore, R.L.: 2009, Quiescent current sheets in the solar wind and origins of slow wind. J. Geophys. Res. 114, A04103. doi: 10.1029/2008JA013704 .
Uzzo, M., Ko, Y.K., Raymond, J.C., Wurz, P., Ipavich, F.M.: 2003, Elemental abundances for the 1996 streamer belt. Astrophys. J. 585, 1062. doi: 10.1086/346132 .
Wang, Y.M.: 1994, Two types of slow solar wind. Astrophys. J. Lett. 437, L67. doi: 10.1086/187684 .
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1990, Solar wind speed and coronal flux-tube expansion. Astrophys. J. 355, 726. doi: 10.1086/168805 .
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: 1997, The high-latitude solar wind near sunspot maximum. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 3141. doi: 10.1029/97GL53305 .
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R.: 2003, The solar wind and its magnetic sources at sunspot maximum. Astrophys. J. 587, 818. doi: 10.1086/368302 .
Wang, Y.M., Hawley, S.H., Sheeley, N.R.: 1996, The magnetic nature of coronal holes. Science 271, 464. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5248.464 .
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R., Rich, N.B.: 2007, Coronal pseudostreamers. Astrophys. J. 658, 1340. doi: 10.1086/511416 .
Wang, Y., Ko, Y., Grappin, R.: 2009, Slow solar wind from open regions with strong low-coronal heating. Astrophys. J. 691, 760. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/760 .
Wang, Y.M., Sheeley, N.R., Phillips, J.L., Goldstein, B.E.: 1997, Solar wind stream interactions and the wind speed–expansion factor relationship. Astrophys. J. Lett. 488, L51. doi: 10.1086/310918 .
Wang, Y.M., Robbrecht, E., Rouillard, A.P., Sheeley, N.R., Thernisien, A.F.R.: 2010, Formation and evolution of coronal holes following the emergence of active regions. Astrophys. J. 715, 39. doi: 10.1088/0004-637X/715/1/39 .
Winterhalter, D., Smith, E.J., Burton, M.E., Murphy, N., McComas, D.J.: 1994, The heliospheric plasma sheet. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 6667. doi: 10.1029/93JA03481 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riley, P., Luhmann, J.G. Interplanetary Signatures of Unipolar Streamers and the Origin of the Slow Solar Wind. Sol Phys 277, 355–373 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9909-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-011-9909-0