Abstract
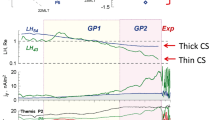
Transition-region explosive events (TREEs) have long been proposed as a consequence of magnetic reconnection. However, several critical issues have not been well addressed, such as the location of the reconnection site, their unusually short lifetime (about one minute), and the recently discovered repetitive behaviour with a period of three to five minutes. In this paper, we perform MHD numerical simulations of magnetic reconnection, where the effect of five-minute solar p-mode oscillations is examined. UV emission lines are synthesised on the basis of numerical results in order to compare with observations directly. It is found that several typical and puzzling features of the TREEs with impulsive bursty behaviour can only be explained if there exist p-mode oscillations and the reconnection site is located in the upper chromosphere at a height range of around 1900 km < h < 2150 km above the solar surface. Furthermore, the lack of proper motions of the high-velocity ejection may be due to a rapid change of temperature along the reconnection ejecta.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee, D., O’Shea, E., Doyle, J.G., and Goossens, M.: 2001 Astron. Astrophys. 371 1137.
Berghmans, D., Clette, F., and Moses, D.: 1998 Astron. Astrophys. 336 1039.
Brueckner, G.E. and Bartoe, J.-D.F.: 1983 Astrophys. J. 272 329.
Carlsson, M. and Stein, R.F.: 1998, in F. Deubner, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, and D. Kurtz (eds.), New Eyes to See Inside the Sun and the Stars, IAU Symposium, Kyoto, Japan, 185, p. 435.
Chae, J., Wang, H., Lee, C., Goode, P.R., and Schühle, U.: 1998 Astrophys. J. 497 L109.
Chen, P.F. et al.: 2006, in preparation.
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., and Ding, M.D.: 2001, Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 1, 179.
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., and Hu, Y.Q.: 2000, Chin. Sci. Bull. 45, 798.
Chen, P.F., Fang, C., Ding, M.D., and Tang, Y.H.: 1999 Astrophys. J. 520 853.
De Pontieu, B., Erdélyi, R., and James, S.P.: 2004, Nature 430, 536.
Dere, K.P.: 1994 Adv. Space Res. 14 13.
Dere, K.P., Bartoe, J.-D.F., and Brueckner, G.E.: 1989 Solar Phys. 123 41.
Dere, K.P., Bartoe, J.-D.F., Brueckner, G.E., Ewing, J., and Lund, P.: 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 9399.
Dere, K.P., Landi, E., Mason, H.E., Monsignori Fossi, B.C., and Young, P.R.: 1997, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 125, 149.
Doyle, J.G., Popescu, M.D., and Taroyan, Y.: 2006 Astron. Astrophys. 446 327.
Fan, Q.L., Feng, X.S., and Xiang, C.Q.: 2004, Comm. Theor. Phys. 41, 790.
Fan, Q.L., Feng, X.S., Xiang, C., and Zhong, D.K.: 2003, Phys. Plasma 10, 4575.
Harrison, R.A., Bryans, P., and Bingham, R.: 2001 Astron. Astrophys. 379 324.
Hu, Y.Q.: 1989, J. Comput. Phys. 84, 441.
Innes, D.E.: 2001 Astron. Astrophys. 378 1067.
Innes, D.E. and Tóth, G.: 1999 Solar Phys. 185 127.
Innes, D.E., Inhester, B., Axford, W.I., and Wilhelm, K.: 1997, Nature 386, 811.
Jin, S.-P., Hao, L., Shen, J.T.: 2000, Chin. Astron. Astrophys. 24, 224.
Jin, S.-P., Inhester, B., and Innes, D.E.: 1996 Solar Phys. 168 279.
Karpen, J.T., Antiochos, S.K., and DeVore, C.R.: 1995 Astrophys. J. 450 422.
Landi, E., Del Zanna, G., Young, P.R., Dere, K.P., Mason, H.E., and Landini, M.: 2006 Astrophys. J. Suppl. 162 261.
Magara, T., Mineshige, S., Yokoyama, T., and Shibata, K.: 1996 Astrophys. J. 466 1054.
Martin, S.F.: 1988 Solar Phys. 117 243.
Ning, Z., Innes, D.E., and Solanki, S.K.: 2004 Astron. Astrophys. 419 1141.
Parker, E.N.: 1988 Astrophys. J. 330 474.
Parnell, C.E.: 2002, Mon. Not. Roy Astron. Soc. 335, 389.
Parnell, C.E. and Priest, E.R.: 1995, Geophys. Astrophys. Fl. Dyn. 80, 255.
Pérez, M.E., Doyle, J.G., Erdélyi, R., and Sarro, L.M.: 1999 Astron. Astrophys. 342 279.
Pike, C.D. and Mason, H.E.: 1998 Solar Phys. 182 333.
Porter, J.G., Moore, R.L., Reichmann, E.J., Engvold, O., and Harvey, K.L.: 1987 Astrophys. J. 323 380.
Priest, E.R., Parnell, C.E., and Martin, S.F.: 1994 Astrophys. J. 427 459.
Rabin, D. and Dowdy, J.F., Jr.: 1992 Solar Phys. 398 665.
Roussev, I., Galsgaard, K., Erdélyi, R., and Doyle, J.G.: 2001a Astron. Astrophys. 370 298.
Roussev, I., Galsgaard, K., Erdélyi, R., and Doyle, J.G.: 2001b Astron. Astrophys. 375 228.
Roussev, I., Doyle, J.G., Galsgaard, K., and Erdélyi, R.: 2001c Astron. Astrophys. 380 719.
Sarro, L.M., Erdélyi, R., Doyle, J.G., and Perez, E.P.: 1999 Astron. Astrophys. 351 721.
Tajima, T. and Shibata, K.: 1997, Plasma Astrophysics, Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA.
Torrence, C. and Compo, G.P.: 1998, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79, 61.
Vernazza, J.E., Avrett, E.H., and Loeser, R.: 1981 Astrophys. J. Suppl. 45 635.
von Rekowski, B., Parnell, C.E., and Priest, E.R.: 2002, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 366, 125.
Whitelam, S., Ashbourn, J.M.A., Bingham, R., Shukla, P.K., and Spicer, D.S.: 2002 Solar Phys. 211 199.
Zhang, J., Lin, G., Wang, J., Wang, H., and Zirin, H.: 1998 Solar Phys. 338 322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P.F., Priest, E.R. Transition-Region Explosive Events: Reconnection Modulated by p-Mode Waves. Sol Phys 238, 313–327 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-006-0215-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-006-0215-1