Abstract
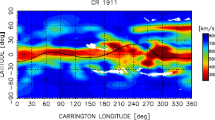
Thirteen synoptic maps of expansion rate of the coronal magnetic field (CMF; RBR) calculated by the so-called ‘potential model’ are constructed for 13 Carrington rotations from the maximum phase of solar activity cycle 22 through the maximum phase of cycle 23. Similar 13 synoptic maps of solar wind speed (SWS) estimated by interplanetary scintillation observations are constructed for the same 13 Carrington rotations as the ones for the RBR. The correlation diagrams between the RBR and the SWS are plotted with the data of these 13 synoptic maps. It is found that the correlation is negative and high in this time period. It is further found that the linear correlation is improved if the data are classified into two groups by the magnitude of radial component of photospheric magnetic field, |Bpho r |; group 1, 0.0 G ≦ |B r pho| < 17.8 G and group 2, 17.8 G ≦ |B r pho|. There exists a strong negative correlation between the RBR and the SWS for the group 1 in contrast with a weak negative correlation for the group 2. Group 1 has a double peak in the density distribution of data points in the correlation diagram; a sharp peak for high-speed solar wind and a low peak for low-speed solar wind. These two peaks are located just on the axis of maximum variance of data points in the correlation diagram. This result suggests that the solar wind consists of two major components and both the high-speed and the low-speed winds emanating from weak photospheric magnetic regions are accelerated by the same mechanism in the course of solar activity cycle. It is also pointed out that the SWS can be estimated by the RBR of group 1 with an empirical formula obtained in this paper during the entire solar activity cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschuler, M. D., Levine, R. H., Stix, M., and Harvey, J. W.: 1977, Solar Phys. 51, 345.
Altschuler, M. D. and Newkirk Jr., G.: 1969, Solar Phys. 9, 131.
Arge, C. N. and Pizzo, V. J.: 2000, J. Geophys. Res. 105, 10465.
Asai, K., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Yokobe, A., Jackson, B. V., and Manoharan, P. K.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 1991.
Hakamada, K.: 1995, Solar Phys. 159, 89.
Hakamada, K.: 1998, Solar Phys. 181, 73.
Hakamada, K. and Kojima, M.: 1994, Solar Phys. 153, 419.
Hakamada, K. and Kojima, M.: 1999, Solar Phys. 187, 115.
Hakamada, K., Kojima, M., and Kakinuma, T.: 1991, J. Geophys. Res. 96, 5397.
Hakamada, K., Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Ohmi, T., Yokobe, A., and Fujiki, K.: 2002, Solar Phys. 207, 173.
Hewish, A., Scott, P. F., and Wills, D.: 1964, Nature 203, 1214.
Hoeksema, J. T. and Scherrer, P. H.: 1986, {The Solar Magnetic Field – 1976 through 1985}, Report UAG-94, Boulder, Colorado: World Data Center A for Solar-Terrestial Physics, NOAA.
Jackson, B. V., Hick, P. L., Kojima, M., and A. Yokobe: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 12049.
Kojima, M., Fujiki, K., Ohmi, T., Tokumaru, M., Yokobe, A., and Hakamada, K.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 15677.
Kojima, M. and Kakinuma, T.: 1990, Space Sci. Rev. 53, 173.
Kojima, M., Tokumaru, M., Watanabe, H., Yokobe, A., Asai, K., Jackson, B. V., and Hick, P. L.: 1998, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 1981.
Levine, R. H.: 1978, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 4193.
Levine, R. H., Altschuler, M. D., and Harvey, J. W.: 1977, J. Geophys. Res. 82, 1061.
Ohmi, T., Kojima, M., Yokobe, A., Tokumaru, M., Fujiki, K., and Hakamada, K.: 2001, J. Geophys. Res. 106, 24923.
Riesebieter, W. and Neubauer, F. M.: 1979, Solar Phys. 63, 127.
Schatten, K. H., Wilcox, J. M., and Ness, N. F.: 1969, Solar Phys. 9, 442.
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley Jr., N. R.: 1990, Astrophys. J. 355, 726.
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley Jr., N. R.: 1992, Astrophys. J. 392, 310.
Wang, Y.-M. and Sheeley Jr., N. R.: 2003, Astrophys. J. 587, 818.
Wang, Y.-M., Sheeley Jr., N. R., Phillips, J. L., and Goldstein, B. E.: 1997, Astrophys. J. 488.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakamada, K., Kojima, M., Ohmi, T. et al. Correlation between Expansion Rate of the Coronal Magnetic Field and Solar Wind Speed in a Solar Activity Cycle. Sol Phys 227, 387–399 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-3304-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-005-3304-7