Abstract
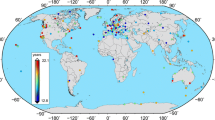
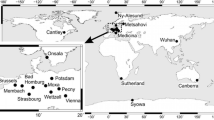
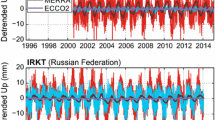
Each of the GPS time series that describes the changes of topocentric components consists of a deterministic and a stochastic part, whose character influences the errors of the deterministic parameters. As to the uncertainties of reliable velocities of permanent satellite station systems, surveys that estimate and take into account any dependencies that may affect subsequent operational efficiency are very important. For this analysis, we used 42 stations from the IGS (International GNSS Service) network from Europe, processed at the Military University of Technology EUREF Permanent Network Local Analysis Centre (MUT LAC). The deterministic part of the GPS time series was removed using the least squares method. The seasonal periods in topocentric components were determined assuming the existence of the residual Chandler oscillation (1.67 cpy), as well as the annual tropical (1 cpy) and draconitic (1.04 cpy) oscillations with their harmonics up to 4th. We assumed the character of the residue as a combination of white and powerlaw noise. The obtained results show, that in the case of the European sub-network of IGS stations we are dealing with the coloured noise between white and flicker noise with the amplitudes between 3 to 6 mm/year-k/4 for horizontal components and between 6 to 15 mm/year-κ/4 for the vertical ones, where κ is a spectral index. Finally, we showed that the amplitudes and spectral indices of noise are reduced after performing a spatio-temporal filtering. All the elicited results referred to the uncertainties of velocities by estimating them before and after filtration and the simulation of their values for different lengths of the time series.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew D.C., 1992. The time-domain behaviour of power-law noises. Geophys. Res. Lett., 19, 333–336.
Amiri-Simkooei A.R., 2013. On the nature of GPS draconitic year periodic pattern in multivariate position time series. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 2500–2511, DOI: 10.1002/jgrb.50199.
Amiri-Simkooei A.R., Tiberius C.C.J.M. and Teunissen P.J.G., 2007. Assessment of noise in GPS coordinate time series: Methodology and results. J. Geophys. Res., 112, B07413, DOI: 10.1029/2006JB004913.
Beavan J., 2005. Noise properties of continuous GPS data from concrete pillar geodetic monuments in New Zealand and comparison with data from U.S. deep drilled braced monuments. J. Geophys. Res., 110, B08410, DOI: 10.1029/2005JB003642.
Blewitt G. and Lavallee D., 2002. Effect of annual signals on geodetic velocity. J. Geophys. Res., 107, 2145, DOI: 10.1029/2001JB000570.
Bogusz J. and Figurski M., 2014. Annual signals observed in regional GPS networks. Acta Geodyn. Geomater., 11, 125–131, DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2014.0003.
Bogusz J., Gruszczynski M., Figurski M. and Klos A., 2015a. Spatio-temporal filtering for determination of common mode error in regional GNSS networks. Open Geosci., 7, 140–148, DOI: 0.1515/geo-2015-0021.
Bogusz J., Klos A., Figurski M. and Kujawa M., 2015b. Investigation of long-range dependencies in daily GPS solutions. Surv. Rev., DOI: 10.1179/1752270615Y.0000000022.
Bos M.S., Fernandes R.M.S., Williams S.D.P. and Bastos L., 2008. Fast error analysis of continuous GPS observations. J. Geodesy, 82, 157–166, DOI: 10.1007/s00190-007-0165-x.
Bruni S., Zerbini S., Raicich F., Errico M. and Santi E., 2014. Detecting discontinuities in GNSS coordinate time series with STARS: case study, the Bologna and Medicina GPS sites. J. Geodesy, 88, 1203–1214, DOI: 10.1007/s00190-014-0754-4.
Bruyninx C., Altamimi Z., Caporali A., Kenyeres A., Lidberg M., Stangl G. and Torres J.A., 2013. Guidelines for EUREF Densifications. ftp://epncb.oma.be/pub/general/. Downloaded on 23.12.2014.
Collilieux X., Altamimi Z., Coulot D., Ray J. and Sillard P., 2007. Comparison of very long baseline interferometry, GPS, and satellite laser ranging height residuals from ITRF2005 using spectral and correlation methods. J. Geophys. Res., 112, B12403, DOI: 10.1029/2007JB004933.
Dach R., Hugentobler U., Fridez P. and Meindl M., 2007. Bernese GPS Software Version 5.0. Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland.
Davis J.L., Wernicke B.P. and Tamisiea M.E., 2012. On seasonal signals in geodetic time series. J. Geophys. Res., 117, B01403, DOI: 10.1029/2011JB008690.
Dong D., Fang P., Bock Y., Webb F., Prawirodirdjo L., Kedar S. and Jamason P., 2006. Spatiotemporal filtering using principal component analysis and Karhunen-Loeve expansion approaches for regional GPS network analysis. J. Geophys. Res., 111, B03405, DOI: 10.1029/2005JB003806.
Fukunaga K., 1990. Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition, Elsevier, New York.
Gazeaux J., Williams S., King M., Bos M., Dach R., Deo M., Moore A.W., Ostini L., Petrie E., Roggero M., Teferle F.N., Olivares G. and Webb F.H., 2013. Detecting offsets in GPS time series: first results from the detection of offsets in GPS experiment. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 2397–2407, DOI: 10.1002/jgrb.50152.
Gross R., Beutler G. and Plag H.-P., 2009. Integrated scientific and societal user requirements and functional specifications for the GGOS. In: Plag H.-P. and Pearlman M. (Eds), Global Geodetic Observing System. Springer-Verlag, Dordrecht, Heidelberg, London, New York, 209–224, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-02687-4.
Hammond W.C. and Plag H.P., 2005. Assessing land motion of Venice, Italy with GPS: Effects of regional filtering on vertical rate estimates. EOS Trans. AGU, 86, Fall Meeting Supplement, Abstract G41B-0359.
He X., Hua X., Yu K., Xuan W., Lu T., Zhang W. and Chen X., 2015. Accuracy enhancement of GPS time series using principal component analysis and block spatial filtering. Adv. Space Res., 55, 1316–1327, DOI: 10.1016/j.asr.2014.12.016.
Klos A., Bogusz J., Figurski M. and Kosek W., 2014a. Uncertainties of geodetic velocities from permanent GPS observations: The Sudeten case study. Acta Geodyn. Geomater., 11, 201–209, DOI: 10.13168/AGG.2014.0005.
Klos A., Bogusz J., Figurski M. and Kosek W., 2014b. Irregular variations in the GPS time series by the probability and noise analysis. Surv. Rev., 47, 163–173, DOI: 10.1179/1752270614Y.0000000133.
Klos A., Bogusz J., Figurski M., Kosek W., 2015. On the handling of outliers in the GNSS time series by means of the noise and probability analysis. In: Rizos C. and Willis P. (Eds), IAG 150 Years. International Association of Geodesy Symposia, 143. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany, DOI: 10.1007/1345_2015_78 (in print).
Langbein J. and Johnson H., 1997. Correlated errors in geodetic time series: Implications for timedependent deformation. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 591–603.
Nikolaidis R., 2002. Observation of Geodetic and Seismic Deformation with the Global Positioning System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA.
Prawirodirdjo L., Ben-Zion Y. and Bock Y., 2006. Observation and modeling of thermoelasticstrain in Southern California Integrated GPS Network daily position time series. J. Geophys. Res., 111, DOI: 10.1029/2005JB003716.
Rundle J.B., Klein W., Tiampo K. and Gross S., 2000. Linear pattern dynamics in nonlinear threshold systems. Phys. Rev. E, 61, 2418–2431.
Teferle F.N., 2003. Strategies for Long-Term Monitoring of Tide Gauges with GPS. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Nottingham, Nottingham, U.K.
Teferle F.N., Bingley R.M., Orliac E.J., Williams S.D.P., Woodworth P., McLaughlin D., Baker T.F., Shennan I., Milne G.A., Bradley S.A. and Hansen D., 2009. Crustal motions in Great Britain: Evidence from continuous GPS, absolute gravity and Holocene sea-level data. Geophys. J. Int., 178, 23–46, DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-1246X.2009.04185.x.
Wang W., Zhao B., Wang Q. and Yang S., 2012. Noise analysis of continuous GPS coordinate time series for CMONOC. Adv. Space Res., 49, 943–956, DOI: 10.1016/j.asr.2011.11.032.
Wdowinski S., Bock Y., Zhang J., Fang P. and Genrich J., 1997. Southern California permanent GPS geodetic array: Spatial filtering of daily positions for estimating coseismic and postseismic displacements induced by the 1992 Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 18057–18070, DOI: 10.1029/97JB01378.
Wessel P., Smith W.H.F., Scharroo R., Luis J.F. and Wobbe F., 2013. Generic mapping tools: improved version released. EOS Trans. AGU, 94, 409–410.
Williams S.D.P., 2008. CATS: GPS coordinate time series analysis software. GPS Solut., 12, 147–153, DOI: 10.1007/s10291-007-0086-4.
Williams S.D.P., Bock Y., Fang P., Jamason P., Nikolaidis R.M., Prawirodirdjo L., Miller M. and Johnson D., 2004. Error analysis of continuous GPS position time series. J. Geophys. Res., 109, B03412, DOI: 10.1029/2003JB002741, 2004.
Zhang J., Bock Y., Johnson H., Fang P., Williams S., Genrich J., Wdowinski S. and Behr J., 1997. Southern California permanent GPS geodetic array: Error analysis of daily position estimates and site velocities. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 18035–18055.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klos, A., Bogusz, J., Figurski, M. et al. Error analysis for European IGS stations. Stud Geophys Geod 60, 17–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-015-0828-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-015-0828-7