Abstract
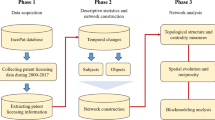
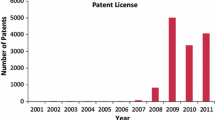
Recently, national governments have tried to improve technology ecology, by formulating research and development (R&D) policies and investing in R&D programs. For strategically designed national R&D plans, analytic approaches that identify and assess the impact of each technology from short-term and long-term perspectives are necessary. Further, in methodological perspective, the approaches should be able to synthetically consider the most recent technological information, the direct and hidden impacts among technologies, and the relative impacts of the focal technology in globally-linked technological relationship from the overall perspective. However, most previous studies based patent citation networks are insufficient for these requirements. As a remedy, we present a combined approach for constructing a technology impact network and identifying the impact and intermediating capability of technology areas from the perspective of a national technology system. To construct and analyze the technology impact network, our method integrates three network techniques: patent co-classification (PCA), decision making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL), and social network analysis (SNA). The advantages of the proposed method are threefold. First, it identifies the directed technological knowledge flows from the most recent patents, by employing PCA. Second, the proposed network contains both the direct and indirect impacts among different technology areas, by applying the DEMATEL method. Third, using SNA, the method can analyze the characteristics of the technologies in terms of the comprehensive impacts and the potential brokerage capabilities. The method is illustrated using all of the recent Korean patents (58,279) in the United States patent database from 2008 to 2012. We expect that our method can be used to provide input to decision makers for effective R&D planning.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breschi, S., Lissoni, F., & Malerba, F. (2003). Knowledge-relatedness in firm technological diversification. Research Policy, 32(1), 69–87.
Büyüközkan, G., & Çifçi, G. (2012). A novel hybrid MCDM approach based on fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy ANP and fuzzy TOPSIS to evaluate green suppliers. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(3), 3000–3011.
Cho, T.-S., & Shih, H.-Y. (2011). Patent citation network analysis of core and emerging technologies in Taiwan: 1997–2008. Scientometrics, 89(3), 795–811.
Choi, J. Y., Lee, J. H., & Sohn, S. Y. (2009). Impact analysis for national R&D funding in science and technology using quantification method II. Research Policy, 38(10), 1534–1544.
Érdi, P., Makovi, K., Somogyvári, Z., Strandburg, K., Tobochnik, J., Volf, P., et al. (2013). Prediction of emerging technologies based on analysis of the US patent citation network. Scientometrics, 95(1), 225–242.
Fan, Z.-P., Suo, W.-L., & Feng, B. (2012). Identifying risk factors of IT outsourcing using interdependent information: An extended DEMATEL method. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(3), 3832–3840.
Fontana, R., Nuvolari, A., & Verspagen, B. (2009). Mapping technological trajectories as patent citation networks. An application to data communication standards. Economics of Innovation and New Technology, 18(4), 311–336.
Fontela, E., & Gabus, A. (1976). The DEMATEL Observer, DEMATEL 1976 Report. Switzerland, Geneva: Battelle Geneva Research Center.
Foray, D., Mowery, D., & Nelson, R. (2012). Public R&D and social challenges: What lessons from mission R&D programs? Research Policy, 41(1), 1697–1702.
Franceschet, M. (2011). Collaboration in computer science: A network science approach. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 62(10), 1992–2012.
Garcia, A., & Mohnen, P. A. (2010). Impact of government support on R&D and innovation. UNU-MERIT, Maastricht Economic and Social Research and Training Centre on Innovation and Technology.
Hanneman, R. A., & Riddle, M. (2001). Social network analysis. Riverside: University of California.
Hsu, F.-M., Horng, D.-J., & Hsueh, C–. C. (2009). The effect of government-sponsored R&D programmes on additionality in recipient firms in Taiwan. Technovation, 29(3), 204–217.
Hsu, C.-W., Kuo, T.-C., Chen, S.-H., & Hu, A. H. (2011). Using DEMATEL to develop a carbon management model of supplier selection in green supply chain management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 56(1), 164–172.
Huang, C., Su, J., Zhao, X., Sui, J., Ru, P., Zhang, H., et al. (2011). Government funded renewable energy innovation in China. Energy Policy, 51, 121–127.
Hung, S.-W., & Wang, A.-P. (2010). Examining the small world phenomenon in the patent citation network: a case study of the radio frequency identification (RFID) network. Scientometrics, 82(1), 121–134.
Jiménez-Sáez, F., Zabala-Iturriagagoitia, J. M., Zofío, J. L., & Castro-Martínez, E. (2011). Evaluating research efficiency within National R&D Programmes. Research Policy, 40(2), 230–241.
Jin, J. H., Park, S. C., & Pyon, C. U. (2011). Finding research trend of convergence technology based on Korean R&D network. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(12), 15159–15171.
Kim, E., Cho, Y., & Kim, W. (2014). Dynamic patterns of technological convergence in printed electronics technologies: patent citation network. Scientometrics, 98(2), 975–998.
Kim, C., Lee, H., Seol, H., & Lee, C. (2011). Identifying core technologies based on technological cross-impacts: An association rule mining (ARM) and analytic network process (ANP) approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(10), 12559–12564.
Knoke, D., & Yang, S. (2008). Social network analysis (Vol. 154): Sage.
Ko, N., Yoon, J., & Seo, W. (2013). Analyzing interdisciplinarity of technology fusion using knowledge flows of patents. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(4), 1955–1963.
Lee, H., Kim, C., Cho, H., & Park, Y. (2009a). An ANP-based technology network for identification of core technologies: A case of telecommunication technologies. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(1), 894–908.
Lee, S., Kim, M.-S., & Park, Y. (2009b). ICT Co-evolution and Korean ICT strategy—An analysis based on patent data. Telecommunications Policy, 33(5), 253–271.
Lee, H., Park, Y., & Choi, H. (2009c). Comparative evaluation of performance of national R&D programs with heterogeneous objectives: A DEA approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 196(3), 847–855.
Li, X., Chen, H., Huang, Z., & Roco, M. C. (2007). Patent citation network in nanotechnology (1976–2004). Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 9(3), 337–352.
Lim, H., & Park, Y. (2010). Identification of technological knowledge intermediaries. Scientometrics, 84(3), 543–561.
Liu, C.-H., Tzeng, G.-H., Lee, M.-H., Tseng, H.-L., & Lee, P.-Y. (2012). Using a hybrid MCDM model combining fuzzy DEMATEL technique to examine the job stress of coach driver. Intelligent Decision Technologies (pp. 149–156). Berlin: Springer.
No, H. J., & Park, Y. (2010). Trajectory patterns of technology fusion: Trend analysis and taxonomical grouping in nanobiotechnology. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 77(1), 63–75.
Otte, E., & Rousseau, R. (2002). Social network analysis: a powerful strategy, also for the information sciences. Journal of information Science, 28(6), 441–453.
Park, H., & Yoon, J. (2014). Assessing coreness and intermediarity of technology sectors using patent co-classification analysis: the case of Korean national R&D. Scientometrics, 98(2), 853–890.
Shieh, J.-I., Wu, H–. H., & Huang, K–. K. (2010). A DEMATEL method in identifying key success factors of hospital service quality. Knowledge-Based Systems, 23(3), 277–282.
Shin, J., & Park, Y. (2007). Building the national ICT frontier: The case of Korea. Information Economics and Policy, 19(2), 249–277.
Sternitzke, C., Bartkowski, A., & Schramm, R. (2008). Visualizing patent statistics by means of social network analysis tools. World Patent Information, 30(2), 115–131.
Su, H.-N. (2012). Visualization of global science and technology policy research structure. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 63(2), 242–255.
Sung, K., Kim, T., & Kong, H.-K. (2010). Microscopic approach to evaluating technological convergence using patent citation analysis. U-and E-Service, Science and Technology (pp. 188–194). Berlin: Springer.
Tijssen, R. J., & Van Leeuwen, T. N. (2006). Measuring impacts of academic science on industrial research: A citation-based approach. Scientometrics, 66(1), 55–69.
Tsai, W.-H., & Chou, W.-C. (2010). Building an integrated multi-criteria decision-making model based on DEMATEL and ANP for selecting the risk management system of banking. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development, 8(4), 358–382.
Tsai, W.-H., & Hsu, W. (2010). A novel hybrid model based on DEMATEL and ANP for selecting cost of quality model development. Total Quality Management, 21(4), 439–456.
Tseng, M.-L. (2009). A causal and effect decision making model of service quality expectation using grey-fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(4), 7738–7748.
Verspagen, B. (1997). Measuring intersectoral technology spillovers: estimates from the European and US patent office databases. Economic Systems Research, 9(1), 47–65.
Verspagen, B. (2007). Mapping technological trajectories as patent citation networks: A study on the history of fuel cell research. Advances in Complex Systems, 10(01), 93–115.
Wu, W–. W. (2008). Choosing knowledge management strategies by using a combined ANP and DEMATEL approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 35(3), 828–835.
Yan, E., & Ding, Y. (2012). Scholarly network similarities: How bibliographic coupling networks, citation networks, cocitation networks, topical networks, coauthorship networks, and coword networks relate to each other. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 63(7), 1313–1326.
Yoon, J., & Kim, K. (2011). Identifying rapidly evolving technological trends for R&D planning using SAO-based semantic patent networks. Scientometrics, 88(1), 213–228.
Yoon, B., & Park, Y. (2004). A text-mining-based patent network: Analytical tool for high-technology trend. The Journal of High Technology Management Research, 15(1), 37–50.
Zha, X., & Chen, M. (2010). Study on early warning of competitive technical intelligence based on the patent map. Journal of Computers, 5(2), 274–281.
Zhou, Q., Huang, W., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Identifying critical success factors in emergency management using a fuzzy DEMATEL method. Safety Science, 49(2), 243–252.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (No. 2012R1A1A1039303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, SS., Ko, N., Kim, D. et al. Analyzing technology impact networks for R&D planning using patents: combined application of network approaches. Scientometrics 101, 917–936 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1343-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1343-2
Keywords
- Patent analysis
- Technology impact network
- Patent co-classification analysis
- DEMATEL
- Social network analysis
- R&D planning