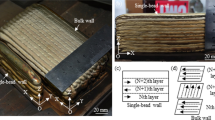
Microstructure and mechanical characteristics of aluminum bronze fabricated using electron beam additive manufacturing (EBAM) under adjusting the heat input as a function of the sample’s height are investigated. It is shown that this adjustment has an effect on the dendrite grain size, morphology and mechanical characteristics. Columnar high aspect ratio grains are formed during deposition at the maximum heat input values. The columnar grain width in the section parallel to the deposition direction is increasing in the EBAM conducted at a lower heat input. The tensile static tests show that the tensile strength values are improving from 435 to 483 MPa. A moderate degree of anisotropy is revealed between the samples oriented by their tensile axes parallel and perpendicular to the deposition direction. The samples with tensile axes parallel to the deposition direction show higher tensile strength and lower plasticity than those of the samples with perpendicular orientations of their tensile axes. Furthermore, the heat input adjustment has no effect on the mean width of the columnar grains measured in a section perpendicular to the deposition direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Meigh, Cast and Wrought Aluminium Bronzes: Properties, Processes and Structure, CRC Press (2018).
H. Harish and V. Manish, Tribology International, 42, Iss. 2, 378 (2009).
S. Zhu, J. Ma, H. Tan, et al., Tribology International, 131, 158 (2019).
R. Gheisari and A. A. Polycarpou, Tribology International, 148, Art. 106339 (2020).
R. A. Poggie, J. J. Wert, and L. A. Harris, J. Adhesion Sci. Technol., 8, Iss. 1, 11 (1994).
S. I. Shakil, C. Dharmendra, S. B. Amirkhiz, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 792, Art. 139773 (2020).
B. Li, C. Han, C. W. J. Lim, and K. Zhou, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 829, Art. 142101 (2020).
C. Dharmendra, A. Hadadzadeh, B. S. Amirkhiz, et al., Additive Manufacturing, 30, Art. 100872 (2019).
T. Wolf, Z. Fu, and C. Körner, Mater. Lett., 238, 241 (2019).
E. S. Khoroshko, A. V. Filippov, S.Yu. Tarasov, et al., Obrabotka metallov: tekhnologiya, oborudovanie, instrument (Metal Working and Material Science), 22, No. 2, 118 (2020).
E. G. Astafurova, S. V. Astafurov, K. A. Reunova, et al., Phys. Mesomech., 25(1), 1 (2022).
Y. D. Shchitsyn, E. A. Krivonosova, S. D. Neulybin, et al., Phys. Mesomech., 24, 716 (2021).
M. G. Krinitsyn, Yu. V. Donstov and V. A. Yurkina, Russ. Phys. J., 64, No. 6, 1086 (2021).
I. Richardson, Guide to Nickel Aluminium Bronze for Engineers, Copper Development Association (2016).
C. Dharmendra, K. P. Rice, B. S. Amirkhiz, and M. Mohammadi, Mater. Design, 202, Art. 109541 (2021).
S. Nair, R. Sellamuthu, and R. Saravanan, Mater. Today Proc., 5, No. 2, Part 2, 6617 (2018).
X. P. Tao, S. Zhang, C. H. Zhang, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol., 342, 76 (2018).
K. Oh-Ishi and T. R. McNelley, Metallurg. Mater. Trans. A, 35, 2951 (2004).
Rizi M. Saboktakin and Kokabi A. Hossein, J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 214, No. 8, 1524 (2014).
A. Jahanafrooz, F. Hasan, G. W. Lorimer, and N. Ridley, Mater. Trans. A, 14, No. 10, 1951 (1983).
K. N. Kalashnikov, A. V. Chumaevskii, T. A. Kalashnikova, et al., Russ. Phys. J., 63, No. 6, 962(2020).
S.Yu. Tarasov, A. V. Filippov, N. L. Savchenko, et al., Int. J. Adv. Manufactur. Technol., 99, 2353 (2018).
D. A. Gurianov, S. V. Fortuna, S. Yu. Nikonov, et al., Russ. Phys. J., 64, No. 8, 1415 (2021).
A. Filippov, N. Shamarin, E. Moskvichev, et al., Materials, 14(22), Art. 6948 (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 5, pp. 45–51, May, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zykova, A.P., Panfilov, A.O., Chumaevskii, A.V. et al. Formation of Microstructure and Mechanical Characteristics in Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing of Aluminum Bronze with an In-Situ Adjustment of the Heat Input. Russ Phys J 65, 811–817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02701-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02701-6