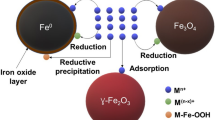
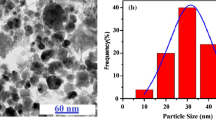
Abstract
After a brief historical classification of the main discoveries related to magnetism, magnetic materials have been rationally ordered in a simple (and hopefully clear) organization. A great effort was realized in the description of the different synthetic approaches for the preparation of magnet-sensitive materials (in particular, focusing on iron oxides). The principal useful techniques for evaluating the magnetic properties in materials (namely, MFM and magnetization hysteresis) have been presented, providing useful examples in order to understand both the potentiality and limits of these characterization methods. Finally, the application of magnet-sensitive materials in water remediation processes has been provided, highlighting both advantages and disadvantages of their use compared to conventional treatments. In this context, the action mechanism and the possible integration of this class of materials into processes involving wastewater treatments are widely discussed, keeping an eye toward the future perspectives.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
TED Conferences LLC. Richard Feynman: Physics is for to imagine. https://www.ted.com/talks/richard_feynman. Accessed 1 Dec 2016
A.-H. Lu, E.L. Salabas, F. Schüth, Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 1222–1244 (2007)
A.K. Gupta, M. Gupta, Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26, 3995–4021 (2005)
Y.-W. Jun, J.-H. Lee, J. Cheon, Chemical design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 5122–5135 (2008)
K.E. Peyer, L. Zhang, B.J. Nelson, Bio-inspired magnetic swimming microrobots for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 5, 1259–1272 (2013)
T. Hyeon, Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 9, 927–934 (2003)
D. Mehta, S. Mazumdar, S.K. Singh, Magnetic adsorbents for the treatment of water/wastewater—a review. J. Water Process Eng. 7, 244–265 (2015)
F. Franzoso, R. Nisticò, F. Cesano, I. Corazzari, F. Turci, D. Scarano, A. Bianco Prevot, G. Magnacca, L. Carlos, D.O. Mártire, Biowaste-derived substances as a tool for obtaining magnet-sensitive materials for environmental applications in wastewater treatments. Chem. Eng. J. 310, 307–316 (2017)
R. Nisticò, F. Franzoso, F. Cesano, D. Scarano, G. Magnacca, L. Carlos, M.E. Parolo, Chitosan-derived iron oxide systems for magnetically-guided and efficient water purification processes from polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 5, 793–801 (2017)
A.-H. Lu, W. Schmidt, N. Matoussevitch, H. Bonnermann, B. Spliethoff, B. Tesche, E. Bill, W. Kiefer, F. Schüth, Nanoengineering of a magnetically separable hydrogenation catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 4303–4306 (2004)
T. Shinjo, Nanomagnetism and Spintronics (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2009)
H.-W. Lee, K.-C. Kim, J. Lee, Review of Maglev train technologies. IEEE Trans. Magn. 42, 1917–1925 (2006)
B.W. Atkinson, F. Bux, H.C. Kasan, Considerations for applications of biosorption technology to remediate metal-contaminated industrial effluents. Water SA 24, 129–135 (1998)
B. Petrie, R. Barden, B. Kasprzyk-Hordern, A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water SA 72, 3–27 (2015)
P.R. Gogate, A.B. Pandit, A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv. Environ. Res. 8, 501–551 (2004)
P.R. Gogate, A.B. Pandit, A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment II: hybrid methods. Adv. Environ. Res. 8, 553–597 (2004)
Brilliant.org. Magnetic field lines. https://brilliant.org/wiki/magnetic-field-lines. Accessed 2 Dec 2016
R. Wiltschko, W. Wiltschko, Chapter 8—Magnetoreception, in Sensing in nature, ed. by C. López-Larrea (Springer, New York, 2012), pp. 126–141
R.A. Serway, J.W. Jewett Jr., Principles of Physics—a calculus-based text, 3rd edn. (Thomson, Stamford, 2002)
R.M. Bozorth, Magnetism. Rev. Mod. Phys. 19, 29–86 (1947)
M. Fowler, Historical Beginnings of Theories of Electricity and Magnetism (University of Virginia, Dept. Physics, 1997). http://galileoandeinstein.physics.virginia.edu/more_stuff/E&M_Hist.html
H.C. Oersted, Experiments on the effect of a current of electricity on the magnetic needles. Annal. Philos. 16, 273–277 (1820)
R. Singh, Unexpected magnetism in nanomaterials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 346, 58–73 (2013)
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism (Clarendon, Oxford (UK), 1873)
J.J. Thomson, Cathode rays. Phil. Mag. 44, 293 (1897)
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, 8th edn. (Wiley, New York, 2005)
I.S. Moosa, History and development of permanent magnets. Int. J. Res. Dev. Technol. 2, 18–26 (2014)
R.E. Rosensweig, Ferrofluids: Introduction, in Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd edn., ed. by K.H.J. Buschow, R.W. Cahn, M.C. Flemings, B. Ilschner, E.J. Kramer, S. Mahajan, P. Veyssière (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001), pp. 3093–3102
S. Genc, B. Derin, Synthesis and rheology of ferrofluids: a review. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 3, 118–124 (2014)
R. Sessoli, Chilling with magnetic molecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 43–45 (2012)
D. Gatteschi, R. Sessoli, Molecular nanomagnets: the first 10 years. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272–276, 1030–1036 (2004)
S.A. Chavan, J.V. Yakhmi, I.K. Gopalakrishnan, Molecular ferromagnets—a review. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 3, 175–179 (1995)
L. Solymar, D. Walsh, Electrical Properties of Materials, 8th edn. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2010)
J. Liu, Z. Wu, Q. Tian, W. Wu, X. Xiao, Shape-controlled iron oxide nanocrystals: synthesis, magnetic properties and energy conversion applications. CrystEngComm 18, 6303–6326 (2016)
M.D. Simons, A.K. Geim, Diamagnetic levitation: flying frogs and floating magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 6200–6204 (2000)
S. Chikazumi, C.D. Graham Jr., Physics of Ferromagnetism, 2nd edn. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2009)
R.M. Cornell, U. Schwertmann, The Iron Oxides, Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd edn. (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003)
Q.A. Pankhurst, J. Connolly, S.K. Jones, J. Dobson, Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D. 36, R167–R181 (2003)
M.S. Valera, S.L. Tomlinson, G.P. Heydon, A.N. Farley, S.R. Hoon, L. Zhou, S. McVitie, J.N. Chapman, Magnetic force microscopy of soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157(158), 555–556 (1996)
A. Schwarz, R. Wiesendanger, Magnetic sensitive force microscopy. NanoToday 3, 28–39 (2008)
H.D.A. Mohamed, S.M.D. Watson, B.R. Horrocks, A. Houlton, Magnetic and conductive magnetite nanowires by DNA-templating. Nanoscale 4, 5936–5945 (2012)
L. Abelmann, Magnetic Force Microscopy, In: J.C. Lindon, G.E. Tranter, D.W. Koppenaal (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, (3rd Ed.), Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017), pp. 675–684
F. Cesano, G. Fenoglio, L. Carlos, R. Nisticò, One-step synthesis of magnetic chitosan polymer composite films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 175–181 (2015)
O. Öztürk, M. Fidan, S. Mändl, MFM imaging of expanded austenite formed on 304 SS and CoCrMo alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 256, 15–22 (2014)
J. Jalli, Y.-K. Hong, G.S. Abo, S. Bae, J.-J. Lee, J.-H. Park, B.C. Choi, S.-G. Kim, MFM studies of magnetic domain patterns in bulk barium ferrite (BaFe12O19) single crystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2627–2631 (2011)
G. Bertotti, V. Basso, C. Beatrice, M. LoBue, A. Magni, P. Tiberto, Hysteresis in magnetic materials: the role of structural disorder, thermal relaxation, and dynamic effects. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226–230, 1206–1212 (2001)
H.W.F. Sung, C. Rudowicz, Physics behind the magnetic hysteresis loop—a survey of misconceptions in magnetism literature. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 260, 250–260 (2003)
IEEE Magnetics Society. Magnetic Units. http://www.ieeemagnetics.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=118&Itemid=107. Accessed 15 Dec 2016
B.D, Plouffe, S.K. Murthy, L.H. Lewis. Fundamentals and application of magnetic particles in cell isolation and enrichment: a review. Rep. Progress Phys. 78, 016601 (2015)
J.M.D. Coey, Magnetism in future. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226–230, 2107–2112 (2001)
R.D. James, Materials science: magnetic alloys break the rules. Nature 521, 298–299 (2015)
T. Wen, Y. Li, D. Zhang, Q. Zhan, Q. Wen, Y. Liao, Y. Xie, H. Zhang, C. Liu, L. Jin, Y. Liu, T. Zhou, Z. Zhong, Manipulate the magnetic anisotropy of nanoparticles assemblies in arrays. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 497, 14–22 (2017)
C.F. Hirjibehedin, C.-Y. Lin, A.F. Otte, M. Ternes, C.P. Lutz, B.A. Jones, A.J. Heinrich, Large magnetic anisotropy of a single atomic spin embedded in a surface molecular network. Science 317, 1199–1203 (2007)
W.H. Meiklejohn, C.P. Bean, New magnetic anisotropy. Phys. Rev. 105, 904–913 (1957)
S. Wang, K. Huang, C. Hou, L. Yuan, X. Wu, D. Lu, Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of RECrO3 (RE = La, Pr, Nd, Sm). Dalton Trans. 44, 17201–17208 (2015)
E.V. Ramana, F. Figueiras, A. Mahajan, D.M. Tobaldi, B.F.O. Costa, M.P.F. Graça, M.A. Valente, Effect of Fe-doping on the structure and magnetoelectric properties of (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1)O3 synthesized by a chemical route. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 1066–1079 (2016)
W. Wu, Q. He, C. Jiang, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 397–415 (2008)
W. Wu, Z. Wu, T. Yu, C. Jiang, W.-S. Kim, Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 16, 023501 (2015)
G. Magnacca, A. Allera, E. Montoneri, L. Celi, D.E. Benito, L.G. Gagliardi, M.C. Gonzalez, D.O. Mártire, L. Carlos, Novel magnetite nanoparticles coated with waste-sourced biobased substances as sustainable and renewable adsorbing materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1518–1524 (2014)
R. Dronskowski, The little maghemite story: a classical functional material. Adv. Func. Mater. 11, 27–29 (2001)
L. Demarchis, M. Minella, R. Nisticò, V. Maurino, C. Minero, D. Vione, Photo-Fenton reaction in the presence of morphologically controlled hematite as iron source. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 307, 99–107 (2015)
W. Jiang, K.-L. Lai, H. Hu, X.-B. Zeng, F. Lang, K.-X. Liu, Y. Wu, Z.-W. Gu, The effect of [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] molar ratio and iron salts concentration on the properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the water/ethanol/toluene system. J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 5135–5145 (2011)
S. Wu, A.Z. Sun, F.Q. Zhai, J. Wang, W.H. Xu, Q. Zhang, A.A. Volinsky, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater. Lett. 65, 1882–1884 (2011)
F. Yazdani, M. Seddigh, Magnetite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method: the effects of various iron anions on specifications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 184, 318–323 (2016)
R. Nisticò, G. Magnacca, M. Antonietti, N. Fechler, “Salted silica”: sol-gel chemistry of silica under hypersaline conditions. Z Anorgan Allgem Chem 640, 582–587 (2014)
R. Nisticò, G. Magnacca, N. Fechler, The hypersaline synthesis of titania: from powders to aerogels. RSC Adv. 5, 14333–14340 (2015). Correction on: 5, 18578 (2015)
R. Nisticò, G. Magnacca, M. Antonietti, N. Fechler, Highly porous silica glasses and aerogels made easy: the hypersaline route. Adv. Porous Mater. 2, 37–41 (2014)
R. Nisticò, S. Tabasso, G. Magnacca, T. Jordan, M. Shalom, N. Fechler, Reactive hypersaline route: one-pot synthesis of porous photoactive nanocomposites. Langmuir 33, 5213–5222 (2017)
R. Bhandari, P. Gupta, T. Dziubla, J.Z. Hilt, Single step synthesis, characterization and applications of curcumin functionalized iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 67, 59–64 (2016)
H. Pardoe, W. Chua-anusorn, T.G. St. Pierre, J. Dobson, Structural and magnetic properties of nanoscale iron oxide particles synthesized in the presence of dextran or polyvinyl alcohol. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 225, 41–46 (2001)
L. Shen, Y. Qiao, Y. Guo, S. Meng, G. Yang, M. Wu, J. Zhao, Facile co-precipitation synthesis of shape-controlled magnetite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 40, 1519–1524 (2014)
A. Bianco Prevot, F. Baino, D. Fabbri, F. Franzoso, G. Magnacca, R. Nisticò, A. Arques, Urban biowaste-derived sensitizing materials for caffeine photodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24, 12599–12607 (2017)
K. Petcharoen, A. Sirivat, Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 177, 421–427 (2012)
D. Ramimoghadam, S. Bagheri, S.B.A. Hamid, In-situ precipitation of ultra-stable nano-magnetite slurry. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 74–79 (2015)
A. Shavel, L.M- Liz-Marzan, Shape control of iron oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 3762–3766 (2009)
Z. Jing, S. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse hematite nanoparticles modified by surfactants via hydrothermal approach. Mater. Lett. 58, 3637–3640 (2004)
W. Wu, X. Xiao, S. Zhang, J. Zhou, L. Fan, F. Ren, C. Jiang, Large-scale and controlled synthesis of iron oxide magnetic short nanotubes: shape evolution, growth mechanism, and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 16092–16103 (2010)
C. Solans, P. Izquierdo, J. Nolla, N. Azemar, M.J. Garcia-Celma, Nano-emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 10, 102–110 (2005)
R. Nisticò, D. Scalarone, G. Magnacca, Preparation and physico-chemical characterization of large-mesopore silica thin films templated by block copolymers for membrane technology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 190, 208–214 (2014)
R. Nisticò, P. Avetta, P. Calza, D. Fabbri, G. Magnacca, D. Scalarone, Selective porous gates made from colloidal silica nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 6, 2105–2112 (2015)
R. Nisticò, G. Magnacca, S.A. Jadhav, D. Scalarone, Polystyrene-block-poly(ethylene oxide) copolymers as templates for stacked, spherical large-mesopore silica coatings: dependence of silica pore size on the PS/PEO ratio. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 7, 1454–1460 (2016)
H. Maleki, L. Duraes, A. Portugal, An overview on silica aerogels synthesis and different mechanical reinforcing strategies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 385, 55–74 (2014)
R. Ciriminna, A. Fidalgo, V. Pandarus, F. Béland, L.M. Ilharco, M. Pagliaro, The sol-gel route to advanced silica-based materials and recent applications. Chem. Rev. 113, 6592–6620 (2013)
C.J. Brinker, G.W. Scherer, Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing (Academic, San Diego, 1990)
R. Nisticò, D. Scalarone, G. Magnacca, Sol-gel chemistry, templating and spin-coating deposition: a combined approach to control in a simple way the porosity of inorganic thin films/coatings. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 248, 18–29 (2017)
W.T. Dong, C. Zhu, Use of ethylene oxide in the sol-gel synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles from Fe(III) salts. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 1676–1683 (2002)
S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L.V. Elst, R.N. Muller, Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 108, 2064–2110 (2008)
H. Xu, B.W. Zeiger, K.S. Suslick, Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 2555–2567 (2013)
P. Lidström, J. Tierney, B. Wathey, J. Westm, Microwave assisted organic synthesis-a review. Tetrahedron 57, 9225–9283 (2001)
O. Pascu, E. Carenza, M. Gich, S. Estradé, F. Peiró, G. Herranz, A. Roig, Surface reactivity of iron oxide nanoparticles by microwave-assisted synthesis; comparison with the thermal decomposition route. J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 15108–15116 (2012)
L. Yan, S. Zhang, P. Chen, H. Liu, H. Yin, H. Li, Magnetotactic bacteria, magnetosomes and their application. Microbiol. Res. 167, 507–519 (2012)
H. Vali, B. Weiss, Y.L. Li, S.K. Sears, S.S. Kim, J.L. Kirschvink, L. Zhang, Formation of tabular single-domain magnetite induced by Geobacter metallireducens GS-15. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 16121–16126 (2004)
A. Scheffel, M. Gruska, D. Faivre, A. Linaroudis, J.M. Plitzko, D. Schüler, An acidic protein aligns magnetosomes along a filamentous structure in magnetotactic bacteria. Nature 440, 110–114 (2006)
A.A. Bharde, R.Y. Parikh, M. Baidakova, S. Jouen, B. Hannoyer, T. Enoki, B.L. Prasad, Y.S. Shouche, S. Ogale, M. Sastry, Bacteria-mediated precursor dependent biosynthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide and iron sulfide nanoparticles. Langmuir 24, 5787–5794 (2008)
L. Cabrera, S. Gutierrez, N. Menendez, M.P. Morales, P. Herrasti, Magnetite nanoparticles: electrochemical synthesis and characterization. Electrochim. Acta 53, 3436–3441 (2008)
R.H. Kodama, Magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 359–372 (1999)
A. Ulman, Formation and structure of self-assembled monolayers. Chem. Rev. 96, 1533–1554 (1996)
D.-Y. Park, S.-T. Myung, Carbon-coated magnetite embedded on carbon nanotubes for rechargeable lithium and sodium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 11749–11757 (2014)
L.M. Rossi, N.J.S. Costa, F.P. Silva, R. Wojcieszak, Magnetic nanomaterials in catalysis: advanced catalysts for magnetic separation and beyond. Green Chem. 16, 2906–2933 (2014)
J.L. Lyon, D.A. Fleming, M.B. Stone, P. Schiffer, M.E. Williams, Synthesis of Fe oxide core/Au shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine seeding. Nano Lett. 4, 719–723 (2004)
S.K. Giri, T.K. Nath, Exchange bias effect in nanostructured magnetic oxides. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 1209–1230 (2014)
A.G. Trovó, T.F.S. Silva, O. Gomes Jr., A.E.H. Machado, W. Borges Neto, P.S. Muller Jr., D. Daniel, Degradation of caffeine by photo-Fenton process: optimization of treatment conditions using experimental design. Chemosphere 90, 170–175 (2013)
N. Klamerth, S. Malato, M.I. Maldonado, A. Aguera, A.R. Fernández-Alba, Application of photo-Fenton as a tertiary treatment of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 1792–1798 (2010)
N. Klamerth, L. Rizzo, S. Malato, M.I. Maldonado, A. Aguera, A.R. Fernández-Alba, Degradation of fifteen emerging contaminants at μg L−1 initial concentrations by mild solar photo-Fenton in MWTP effluents. Water Res. 44, 545–554 (2010)
C. Sirtori, A. Zapata, I. Oller, W. Gernjak, A. Agüera, S. Malato, Decontamination industrial pharmaceutical wastewater combining solar photo-Fenton and biological treatment. Water Res. 43, 661–668 (2009)
A. Zapata, I. Oller, L. Rizzo, S. Hilgert, M.I. Maldonado, J.A. Sánches-Pérez, S. Malato, Evaluation of operating parameters involved in solar photo-Fenton treatment of wastewater: interdependence of initial pollutant concentration, temperature and iron concentration. Appl. Catal. B 97, 292–298 (2010)
A. Bernabeu, S. Palacios, R. Vicente, R.F. Vercher, S. Malato, A. Arques, A.M. Amat, Solar photo-Fenton at mild conditions to treat a mixture of six emerging pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 198–199, 65–72 (2012)
M. Minella, G. Marchetti, E. De Laurentiis, M. Malandrino, V. Maurino, C. Minero, D. Vione, K. Hanna, Photo-Fenton oxidation of phenol with magnetite as iron source. Appl. Catal. B 154–155, 102–109 (2014)
L.M. Pastrana-Martinez, N. Pereira, R. Lima, J.L. Faria, H.T. Gomes, A.M.T. Silva, degradation of diphenhydramine by photo-fenton using magnetically recoverable iron oxide nanoparticles as catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 261, 45–52 (2015)
O.V. Kharissova, R. Dias, B.I. Kharisov, Magnetic adsorbents based on micro- and nano-structured materials. RSC Adv. 5, 6695–6719 (2014)
Y. Chu, Q. Pan, Three-dimensionally macroporous Fe/C nanocomposites as highly selective oil-absorption materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 4, 2420–2425 (2012)
A.Z.M. Badruddoza, Z.B.Z. Shawon, T.W.J. Daniel, K. Hidajat, M.S. Uddin, Fe3O4/cyclodextrin polymer nanocomposites for selective heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater. Carbohyd. Polym. 91, 322–332 (2013)
J.P. Rao, P. Gruenberg, K.E. Geckeler, Magnetic zero-valent metal polymer nanoparticles: current trends, scope, and perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 40, 138–147 (2015)
M. Respaud, J.M. Broto, H. Rakoto, A.R. Fert, L. Thomas, B. Barbara, M. Verelst, E. Snoeck, P. Lecante, A. Mosset, J. Osuna, T.O. Ely, C. Amiens, B. Chau-dret, Surface effects on the magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt particles. Phys. Rev. B 57, 2925–2935 (1998)
X. Zhao, W. Liu, Z. Cai, B. Han, T. Qian, D. Zhao, An overview of preparation and applications of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for soil and groundwater remediation. Water Res. 100, 245–266 (2016)
S. Liu, W. Yan, W.X. Zhang, Solvent-free production of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with precision milling. Green Chem. 11, 1618–1626 (2009)
F. Fu, D.D. Dionysiou, H. Liuc, The use of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 267, 194–205 (2014)
P.G. Tratnyek, R.L. Johnson, Nanotechnologies for environmental cleanup. Nano Today 1, 44–48 (2006)
R.A. Crane, T.B. Scott, Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 211–212, 112–125 (2012)
D.H.K. Reddy, Y.-S. Yun, Spinel ferrite magnetic adsorbents: alternative future materials for water purification? Coord. Chem. Rev. 315, 90–111 (2016)
D.S. Mathew, R.-S. Juang, An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 129, 51–65 (2007)
K.E. Sickafus, J.M. Wills, N.W. Grimes, Structure of spinel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 3279–3292 (1999)
C.M.B. Henderson, J.M. Charnock, D.A. Plant, Cation occupancies in Mg Co, Ni, Zn, Al ferrite spinels: a multi-element EXAFS study. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19, 076214 (2007)
Y. Xiao, H. Liang, W. Chen, Z. Wang, Synthesis and adsorption behavior of chitosan-coated MnFe2O4 nanoparticles for trace heavy metal ions removal. Appl. Surface Sci. 285 B, 498–504 (2013)
Y. Meng, D. Chen, Y. Sun, D. Jiao, D. Zeng, Z. Liu, Adsorption of Cu2+ ions using chitosan-modified magnetic Mn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 324, 745–750 (2015)
J. Wei, X. Zhang, Q. Liu, Z. Li, L. Liu, J. Wang, Magnetic separation of uranium by CoFe2O4 hollow spheres. Chem. Eng. J. 241, 228–234 (2014)
Z. Jia, Q. Qin, J. Liu, H. Shi, X. Zhang, R. Hu, S. Li, R. Zhu, The synthesis of hierarchical ZnFe2O4 architecture and their application for Cr(VI) adsorption removal from aqueous solution. Superlattices Microstruct. 82, 174–187 (2015)
A. Kraus, K. Jainae, F. Unob, N. Sukpirom, Synthesis of MPTS-modified cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and their adsorption properties in relation to Au(III). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 338, 359–365 (2009)
L. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Liu, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, T. Zhang, L. Zhang, The investigation of synergistic and competitive interaction between dye Congo red and methyl blue on magnetic MnFe2O4. Chem. Eng. J. 246, 88–96 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was realized with the financial support for academic interchange by the Marie Sklodowska-Curie Research and Innovation Staff Exchange project funded by the European Commission H2020-MSCA-RISE-2014 within the framework of the research project Mat4treaT (Project Number: 645551). Compagnia di San Paolo and University of Torino are gratefully acknowledged for funding Project Torino_call2014_L2_126 through “Bando per il finanziamento di progetti di ricerca di Ateneo – anno 2014” (Project acronym: Microbusters).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisticò, R. Magnetic materials and water treatments for a sustainable future. Res Chem Intermed 43, 6911–6949 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-3029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-3029-x